Abstract
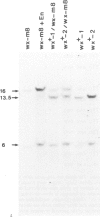
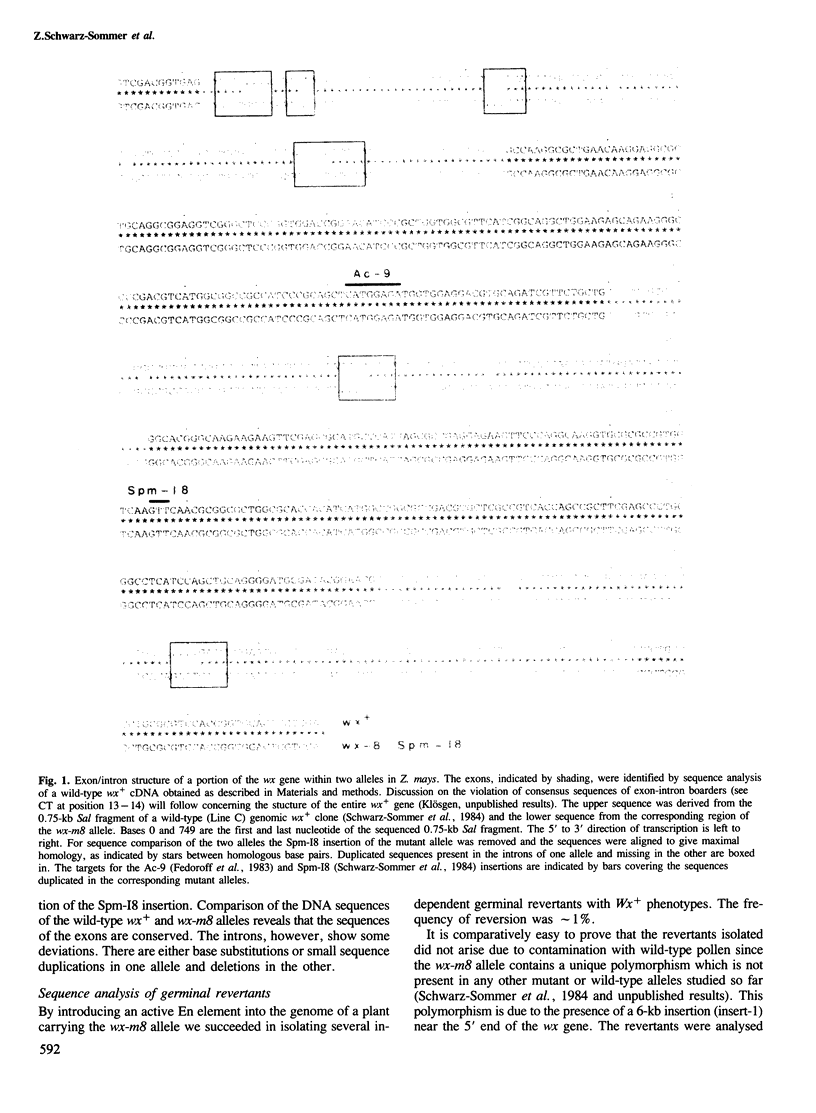
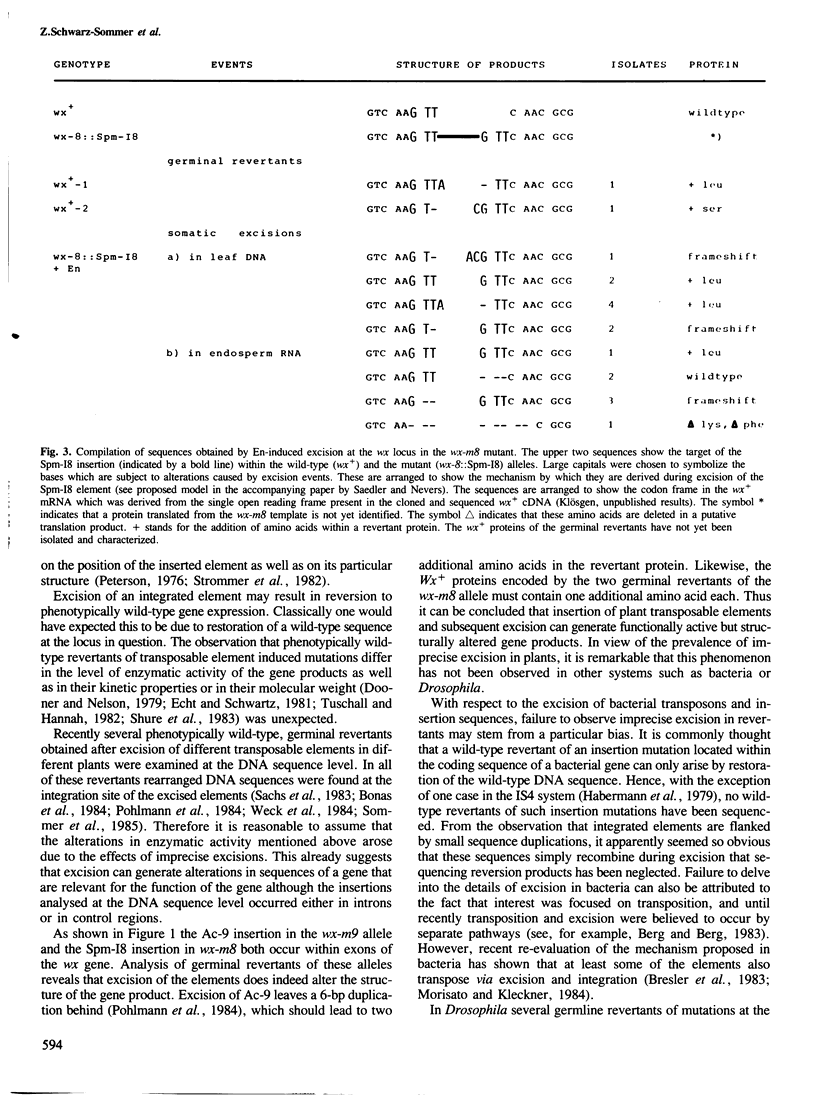
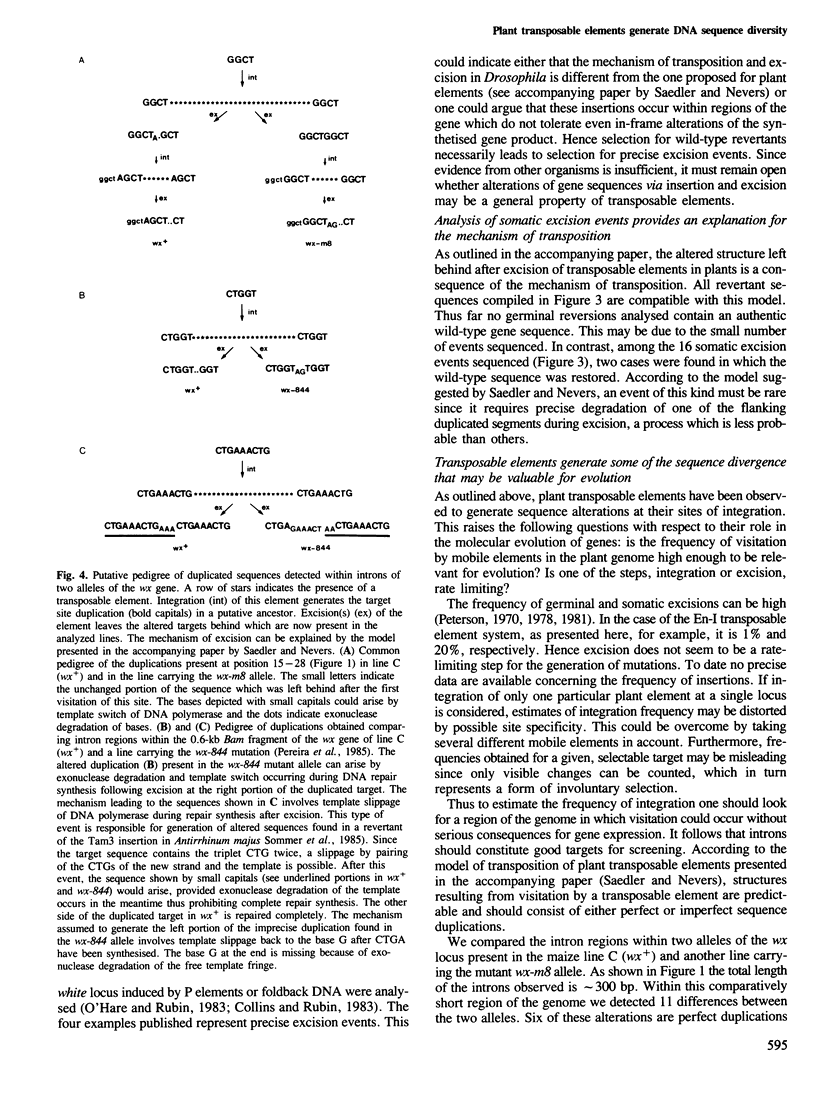
Two germinal and 16 somatic reversion events induced by the Enhancer (En) transposable element system at the wx-8::Spm-I8 allele of Zea mays were cloned and studied by sequence analysis. Excision of the Spm-I8 receptor element from the wx gene results in various mutant DNA sequences. This leads to altered gene products, some of which are still capable of restoring the wild-type phenotype. Possible `footprint' sequences that may have arisen by the excision of transposable elements were observed when intron sequences of the wild-type (wx+) and the mutant (wx-m8) alleles of the wx gene were compared. The sequence divergence generated by visitation of a locus by plant transposable elements is discussed with respect to the molecular evolution of new gene functions.
Keywords: Enhancer (En), wx-m8, Zea mays, reversion, DNA sequence
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonas U., Sommer H., Saedler H. The 17-kb Tam1 element of Antirrhinum majus induces a 3-bp duplication upon integration into the chalcone synthase gene. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1015–1019. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresler S. E., Tamm S. E., Goryshin IYu, Lanzov V. A. Postexcision transposition of the transposon Tn10 in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(1):139–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00330336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M., Rubin G. M. High-frequency precise excision of the Drosophila foldback transposable element. Nature. 1983 May 19;303(5914):259–260. doi: 10.1038/303259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courage-Tebbe U., Döring H. P., Fedoroff N., Starlinger P. The controlling element Ds at the Shrunken locus in Zea mays: structure of the unstable sh-m5933 allele and several revertants. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooner H. K., Nelson O. E. Controlling element-induced alterations in UDPglucose:flavonoid glucosyltransferase, the enzyme specified by the bronze locus in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5623–5627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooner H. K., Nelson O. E. Heterogeneous flavonoid glucosyltransferases in purple derivatives from a controlling element-suppressed bronze mutant in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2369–2371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring H. P., Starlinger P. Barbara McClintock's controlling elements: now at the DNA level. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echt C. S., Schwartz D. Evidence for the Inclusion of Controlling Elements within the Structural Gene at the Waxy Locus in Maize. Genetics. 1981 Oct;99(2):275–284. doi: 10.1093/genetics/99.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Wessler S., Shure M. Isolation of the transposable maize controlling elements Ac and Ds. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fincham J. R., Sastry G. R. Controlling elements in maize. Annu Rev Genet. 1974;8:15–50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.08.120174.000311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierl A., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Saedler H. Molecular interactions between the components of the En-I transposable element system of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):579–583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann P., Klaer R., Kühn S., Starlinger P. IS4 is found between eleven or twelve base pair duplications. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 1;175(3):369–373. doi: 10.1007/BF00397237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCLINTOCK B. Chromosome organization and genic expression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:13–47. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The significance of responses of the genome to challenge. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):792–801. doi: 10.1126/science.15739260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisato D., Kleckner N. Transposase promotes double strand breaks and single strand joints at Tn10 termini in vivo. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevers P., Saedler H. Transposable genetic elements as agents of gene instability and chromosomal rearrangements. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):109–115. doi: 10.1038/268109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Structures of P transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira A., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Gierl A., Bertram I., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Genetic and molecular analysis of the Enhancer (En) transposable element system of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):17–23. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02311.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P A. The Pale Green Mutable System in Maize. Genetics. 1960 Jan;45(1):115–133. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A. Instability among the components of a regulatory element transposon in maize. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):447–455. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman R. F., Fedoroff N. V., Messing J. The nucleotide sequence of the maize controlling element Activator. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G., Telford J., Baldari C., Pirrotta V. Isolation of cloned genes differentially expressed at early and late stages of Drosophila embryonic development. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):438–447. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Gierl A., Klösgen R. B., Wienand U., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. The Spm (En) transposable element controls the excision of a 2-kb DNA insert at the wx allele of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1021–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuschall D. M., Hannah L. C. Altered Maize Endosperm Adp-Glucose Pyrophosphorylases from Revertants of a SHRUNKEN-2-DISSOCIATION ALLELE. Genetics. 1982 Jan;100(1):105–111. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck E., Courage U., Döring H. P., Fedoroff N., Starlinger P. Analysis of sh-m6233, a mutation induced by the transposable element Ds in the sucrose synthase gene of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1713–1716. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]