Abstract
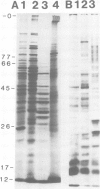
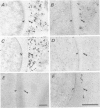
Three rat hybridoma lines that produced monoclonal antibodies reacting with the peribacteroid membrane from Pisum sativum were isolated, and these all appeared to recognise the same antigenic structure. Using one of these monoclonal antibodies, AFRC MAC 64, electron microscopy of immunogold-stained thin sections of nodule tissue revealed that the antigen, present in the peribacteroid membrane, was also found in the plant plasma membranes and in the Golgi bodies, but not in the endoplasmic reticulum. When peribacteroid membrane proteins were separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred to nitrocellulose by electro-blotting, it was found that MAC 64 bound to a series of protease-sensitive bands that migrated in the mol. wt. range 50-85 K. The epitope was sensitive to periodate oxidation and its structure may therefore involve the carbohydrate component of a membrane glycoprotein. We suggest that this structure originates in the Golgi apparatus and is subsequently transferred to the peribacteriod membranes and plasma membranes. The monoclonal antibody also reacted with peribacteroid membranes from nodules of Vicia and lupin, and with plasma membranes and Golgi membranes from uninfected plant cells, including root tip cells from onion (Allium cepa), indicating that the antigen is highly conserved in the plasma membranes of plant cells.
Keywords: Rhizobium, peribacteroid membrane, plasma membrane, monoclonal antibody, pea
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. A., Sandrin M. S., Clarke A. E. A high proportion of hybridomas raised to a plant extract secrete antibody to arabinose or galactose. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1013–1016. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisseling T., Been C., Klugkist J., Kammen A., Nadler K. Nodule-specific host proteins in effective and ineffective root nodules of Pisum sativum. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):961–966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M., Kupferer P., Morris C. F. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins and nucleic acids from slab gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or nitrocellulose sheets. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzandu J. K., Deh M. E., Barratt D. L., Wise G. E. Detection of erythrocyte membrane proteins, sialoglycoproteins, and lipids in the same polyacrylamide gel using a double-staining technique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1733–1737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C., Wright B. Rat x rat hybrid myelomas and a monoclonal anti-Fd portion of mouse IgG. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):131–133. doi: 10.1038/277131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. E., Kornfeld S. Evidence for extensive subcellular organization of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing and lysosomal enzyme phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3159–3165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi H., Cleve H. Solubilization of human erythrocyte membrane glycoproteins and separation of the MN glycoprotein from a glycoprotein with I, S, and A activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 29;278(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legocki R. P., Verma D. P. Identification of "nodule-specific" host proteins (nodoulins) involved in the development of rhizobium-legume symbiosis. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. G., Lyttleton P., Bullivant S., Grayston G. F. Membranes in lupin root nodules. I. The role of Golgi bodies in the biogenesis of infection threads and peribacteroid membranes. J Cell Sci. 1978 Apr;30:129–149. doi: 10.1242/jcs.30.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. G., Lyttleton P. Division of peribacteroid membranes in root nodules of white clover. J Cell Sci. 1984 Jul;69:147–157. doi: 10.1242/jcs.69.1.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. G., Warburton M. P., Lyttleton P., Fordyce A. M., Bullivant S. Membranes in lupin root nodules. II. Preparation and properties of peribacteroid membranes and bacteroid envelope inner membranes from developing lupin nodules. J Cell Sci. 1978 Apr;30:151–174. doi: 10.1242/jcs.30.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E., Roberts K., Butcher G. W., Galfre G. Monoclonal antibody screening: two methods using antigens immobilized on nitrocellulose. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90778-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma D. P., Kazazian V., Zogbi V., Bal A. K. Isolation and characterization of the membrane envelope enclosing the bacteroids in soybean root nodules. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):919–936. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]