Abstract
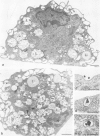
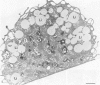
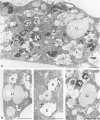
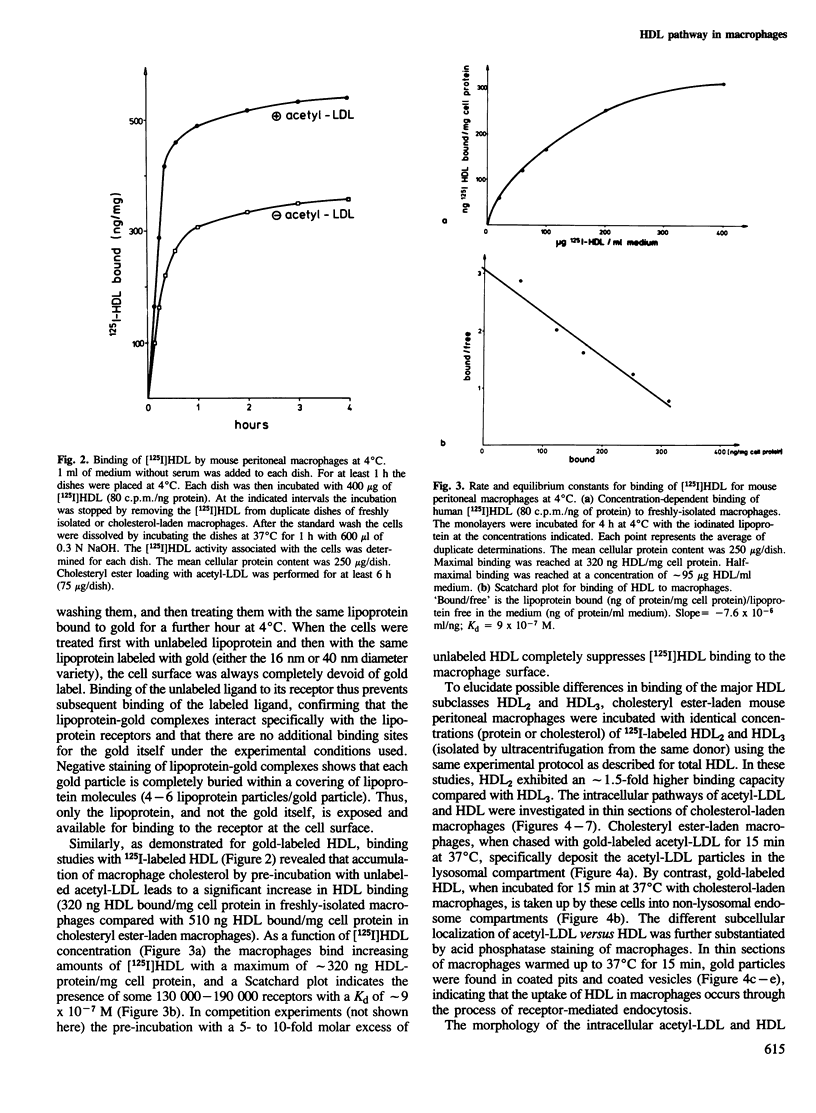
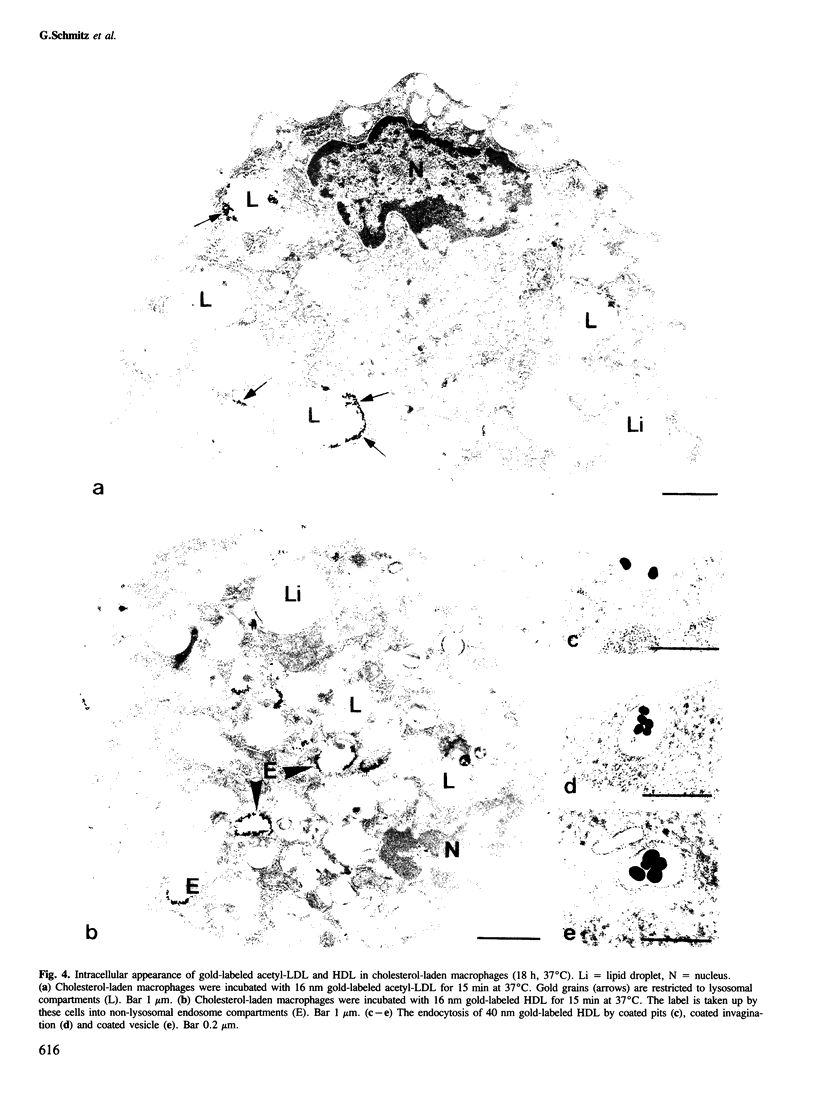
Morphological and biochemical experiments were carried out to investigate the interaction of human serum high density lipoproteins (HDL) with mouse peritoneal macrophages. It is demonstrated that resident mouse peritoneal macrophages express HDL receptors. Subsequent to receptor-mediated binding, HDL are internalized and intracellularly transported into endosomes. These endosomes do not fuse with the lysosomal compartment but interact with the margin of intracellular plasma lipid droplets. Macrophages do not degrade, but rather resecrete internalized HDL particles as described for the transferrin-receptor pathway. HDL binding to freshly isolated macrophages is saturable at a concentration of approximately 320 ng HDL-protein/mg cell protein and a Scatchard plot indicates the presence of some 130 000-190 000 receptors/cell with a Kd of approximately 9 X 10(-7) M. Binding of HDL on the macrophage surface is significantly enhanced in cholesterol-laden macrophages, whereas the increase in the rate of uptake and secretion is less pronounced. Within the HDL fraction the HDL2 subclass showed higher binding, uptake and secretion activity as compared with HDL3. From these experimental data we postulate that cholesterol uptake from macrophages is mediated by HDL particles which interact with these cells via a receptor-mediated retroendocytosis pathway.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu S. K., Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Havel R. J., Goldstein J. L. Mouse macrophages synthesize and secrete a protein resembling apolipoprotein E. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7545–7549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Independent pathways for secretion of cholesterol and apolipoprotein E by macrophages. Science. 1983 Feb 18;219(4586):871–873. doi: 10.1126/science.6823554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Ho Y. K., Brown M. S., Bilheimer D. W., Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L. Biochemical and genetic studies of the apoprotein E secreted by mouse macrophages and human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9788–9795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Krieger M., Ho Y. K., Anderson R. G. Reversible accumulation of cholesteryl esters in macrophages incubated with acetylated lipoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):597–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein metabolism in the macrophage: implications for cholesterol deposition in atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:223–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. The cholesteryl ester cycle in macrophage foam cells. Continual hydrolysis and re-esterification of cytoplasmic cholesteryl esters. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9344–9352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. The low-density lipoprotein pathway in human fibroblasts: relation between cell surface receptor binding and endocytosis of low-density lipoprotein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;275:244–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb43358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith R. M., Werner P., Arnaud P., Galbraith G. M. Transferrin binding to peripheral blood lymphocytes activated by phytohemagglutinin involves a specific receptor. Ligand interaction. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1135–1143. doi: 10.1172/JCI109943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Ho Y. K., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Binding site on macrophages that mediates uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley D. A., Arbeeny C. M., Eder H. A., Chien S. Hepatic binding and internalization of low density lipoprotein-gold conjugates in rats treated with 17 alpha-ethinylestradiol. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):778–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C., Heuser J., Stahl P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):329–339. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. K., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Hydrolysis and excretion of cytoplasmic cholesteryl esters by macrophages: stimulation by high density lipoprotein and other agents. J Lipid Res. 1980 May;21(4):391–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Lipoprotein binding to canine hepatic membranes. Metabolically distinct apo-E and apo-B,E receptors. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5646–5655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Cellular and molecular biology of lipoprotein metabolism in atherosclerosis. Diabetes. 1981;30(Suppl 2):60–65. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.2.s60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L. Lipoprotein receptors and cholesterol homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):197–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robenek H., Rassat J., Hesz A., Grünwald J. A correlative study on the topographical distribution of the receptors for low density lipoprotein (LDL) conjugated to colloid gold in cultured human skin fibroblasts employing thin section, freeze-fracture, deep-etching, and surface replication techniques. Eur J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;27(2):242–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robenek H., Schmitz G., Assmann G. Topography and dynamics of receptors for acetylated and malondialdehyde-modified low-density lipoprotein in the plasma membrane of mouse peritoneal macrophages as visualized by colloidal gold in conjunction with surface replicas. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Oct;32(10):1017–1027. doi: 10.1177/32.10.6481148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. Atherosclerosis and the arterial smooth muscle cell: Proliferation of smooth muscle is a key event in the genesis of the lesions of atherosclerosis. Science. 1973 Jun 29;180(4093):1332–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4093.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
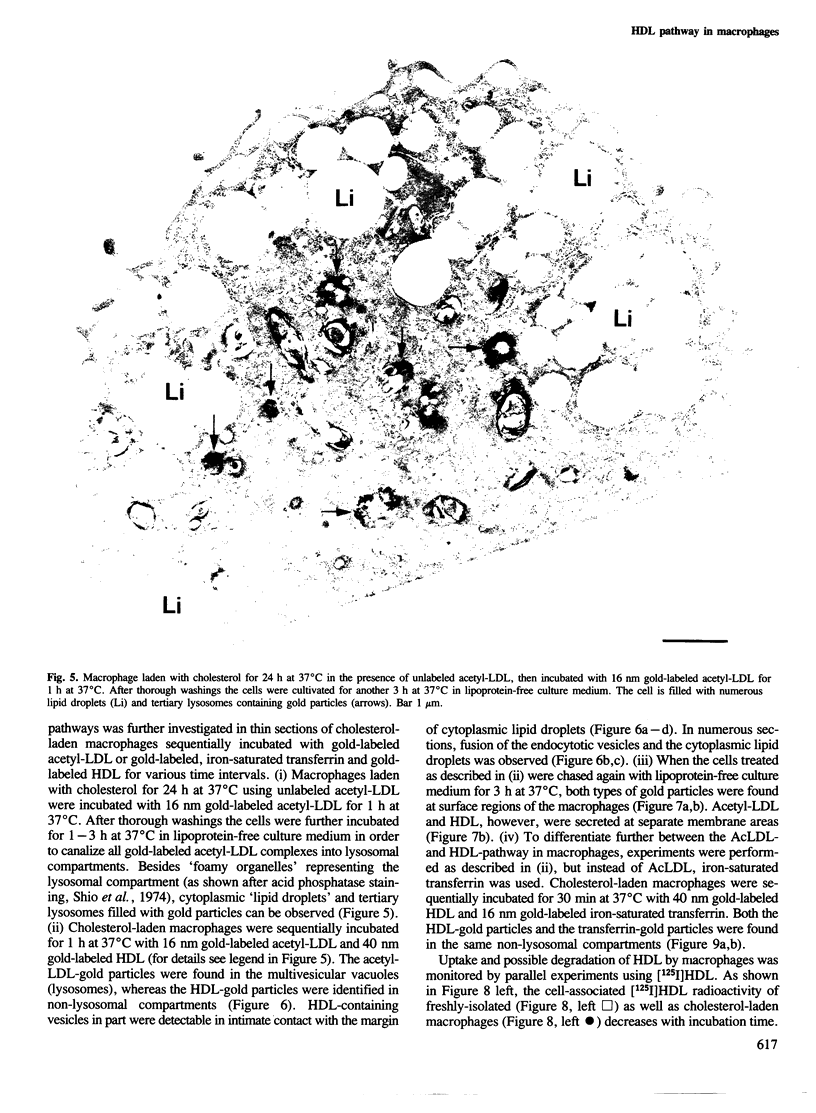
- Shio H., Farquhar M. G., de Duve C. Lysosomes of the arterial wall. IV. Cytochemical localization of acid phosphatase and catalase in smooth muscle cells and foam cells from rabbit atheromatous aorta. Am J Pathol. 1974 Jul;76(1):1–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., Mathur S. N., Kaduce T. L. Role of acylcoenzyme A: cholesterol o-acyltransferase in cholesterol metabolism. Prog Lipid Res. 1979;18(1):31–53. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(79)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein Y., Glangeaud M. C., Fainaru M., Stein O. The removal of cholesterol from aortic smooth muscle cells in culture and Landschutz ascites cells by fractions of human high-density apolipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 24;380(1):106–118. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]