Abstract
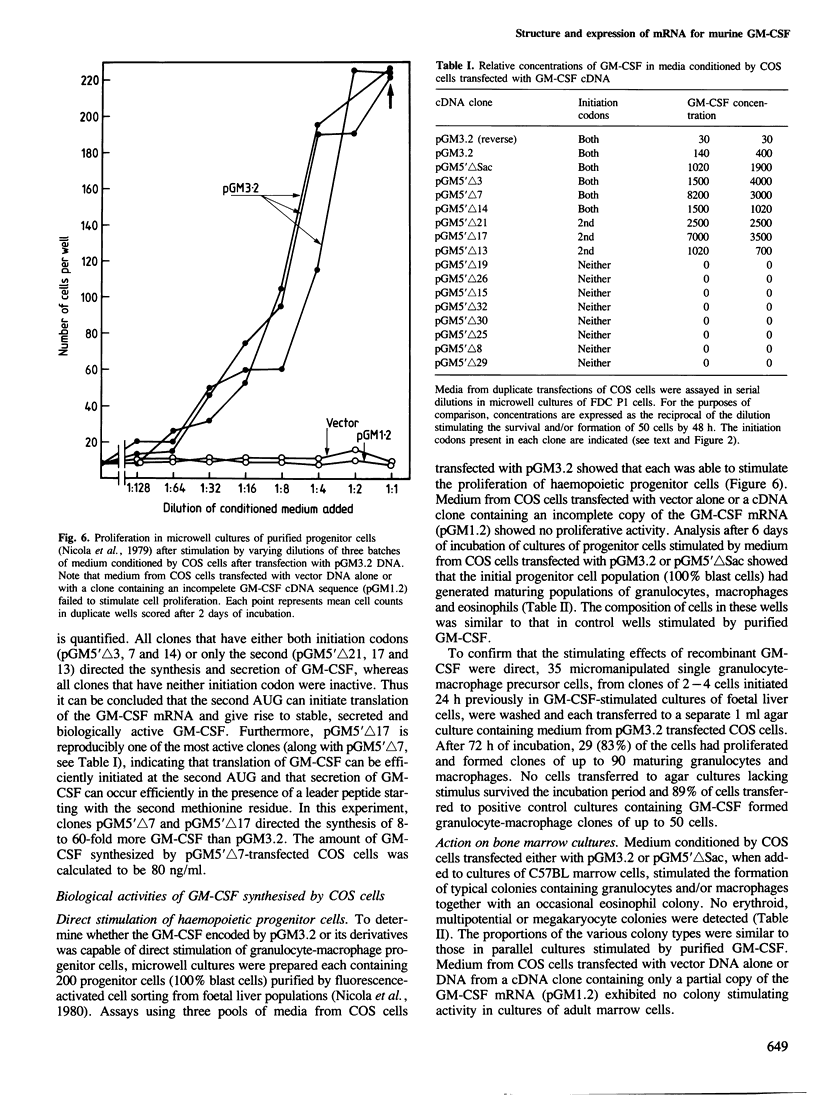
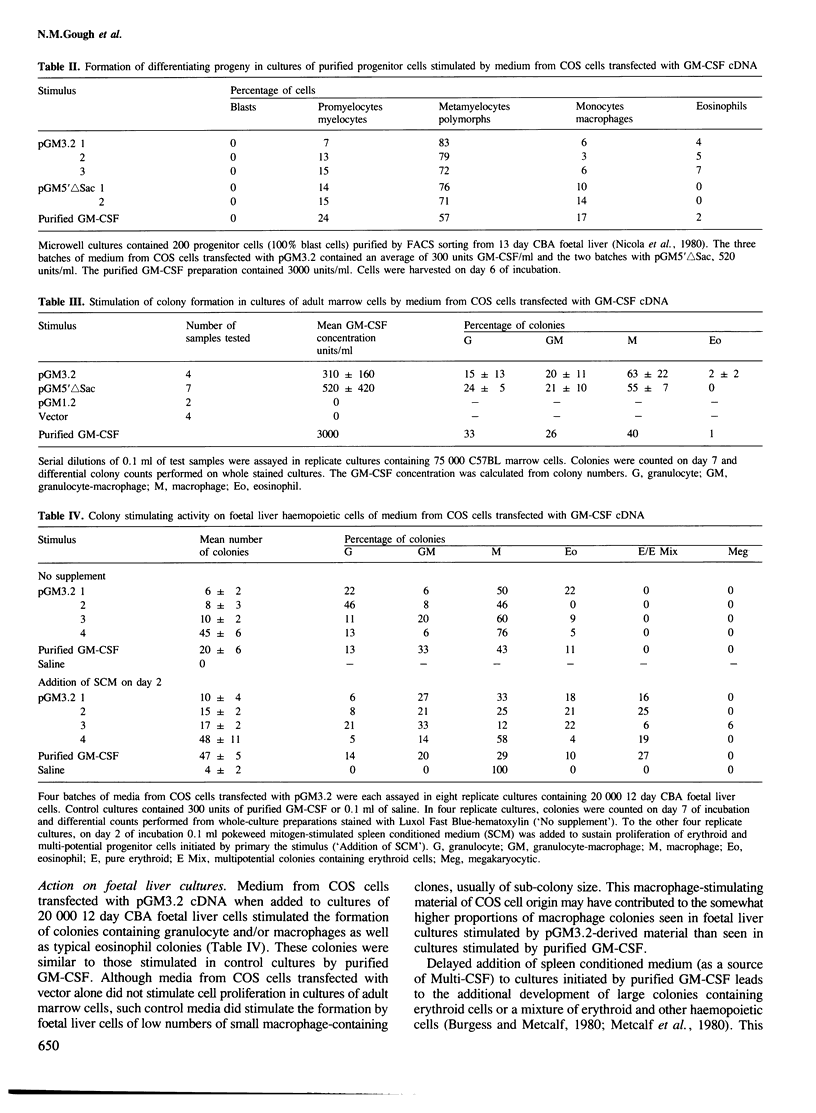
A cDNA containing a virtually complete copy of the mRNA for the haemopoietic growth regulator, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF), has been isolated from a murine T lymphocyte cDNA library. When a eukaryotic expression vector with this cDNA coupled to the SV40 late promoter was introduced into simian COS cells, significant quantities of GM-CSF were secreted. Since all of the biological activities previously ascribed to highly purified GM-CSF were exhibited in the COS cell-derived GM-CSF, all of these activities are intrinsic to the product of a single gene. There are two potential translational initiation codons in the GM-CSF mRNA; the first is buried in the stem and the second located in the loop of a very stable hairpin structure. Expression studies using deletion derivatives of the cDNA indicated that the second AUG is able to initiate the translation and secretion of GM-CSF. The amino acid sequence of the leader peptide is rather atypical for a secreted protein and we speculate that molecules which initiate at the first AUG might exist as integral membrane proteins whereas those initiating at the second are secreted.
Full text
PDF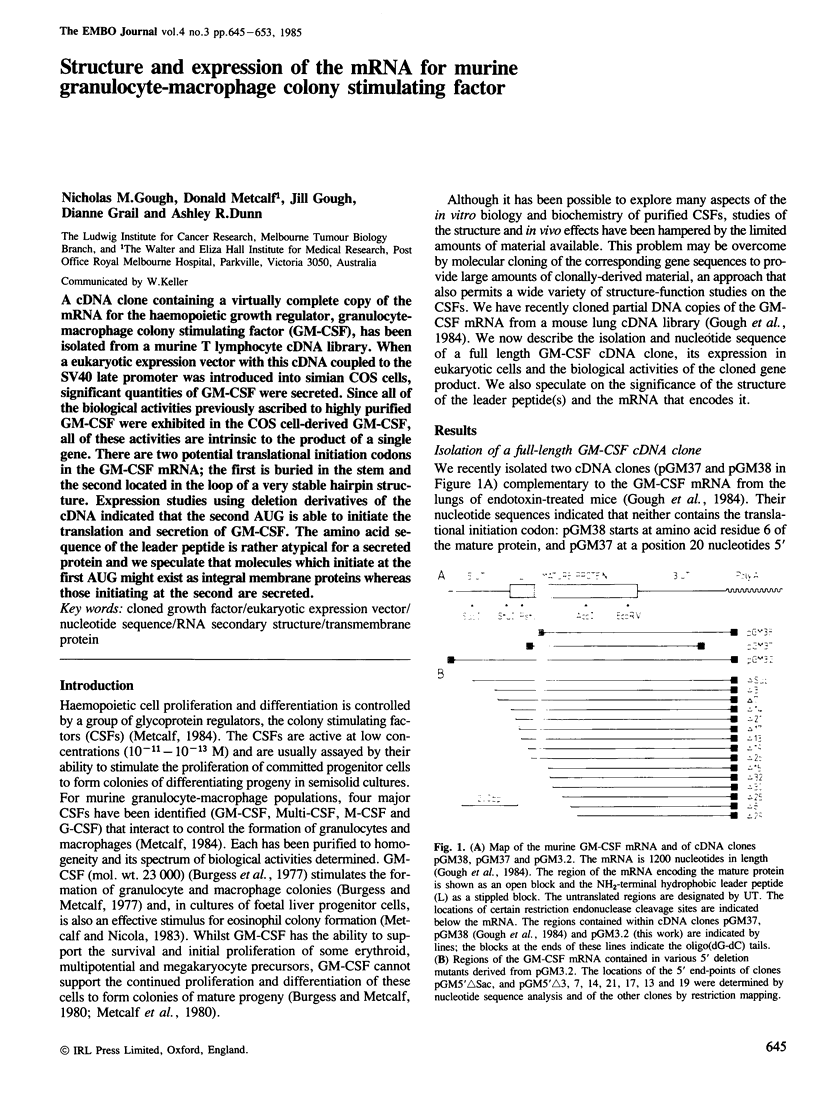




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen T. D., Dexter T. M. Cellular interrelationships during in vitro granulopoiesis. Differentiation. 1976 Oct 7;6(3):191–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1976.tb01486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen T. D. Haemopoietic microenvironments in vitro: ultrastructural aspects. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;84:38–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley S. A. Close range cell:cell interaction required for stem cell maintenance in continuous bone marrow culture. Exp Hematol. 1981 Mar;9(3):308–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn D. E., Hobbs A. A., Rosen J. M. Rat beta casein cDNA: sequence analysis and evolutionary comparisons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2295–2307. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Camakaris J., Metcalf D. Purification and properties of colony-stimulating factor from mouse lung-conditioned medium. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1998–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Metcalf D. The nature and action of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factors. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):947–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet M., Gannon F., Hen R., Maroteaux L., Perrin F., Chambon P. Organization and sequence studies of the 17-piece chicken conalbumin gene. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):567–574. doi: 10.1038/282567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danna K. J., Sompayrac L. M. Efficient infection of monkey cells with SV40 DNA. II. Use of low-molecular-weight DEAE-dextran for large-scale experiments. J Virol Methods. 1982 Dec;5(5-6):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Garland J., Scott D., Scolnick E., Metcalf D. Growth of factor-dependent hemopoietic precursor cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):1036–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K. Complete amino acid sequence of a membrane receptor for glycoproteins. Sequence of the chicken hepatic lectin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5827–5839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K., Mamon J. F., Binns G., Leung J. O. Primary structure of the rat liver asialoglycoprotein receptor. Structural evidence for multiple polypeptide species. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):770–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maniatis T. The primary structure of rabbit beta-globin mRNA as determined from cloned DNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):571–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Ansorge W. Improvements of DNA sequencing gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Choudary P. V., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. The 5'-terminal leader sequence of late 16 S mRNA from cells infected with simian virus 40. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3643–3647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M. Core and E antigen synthesis in rodent cells transformed with hepatitis B virus DNA is associated with greater than genome length viral messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 25;165(4):683–699. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
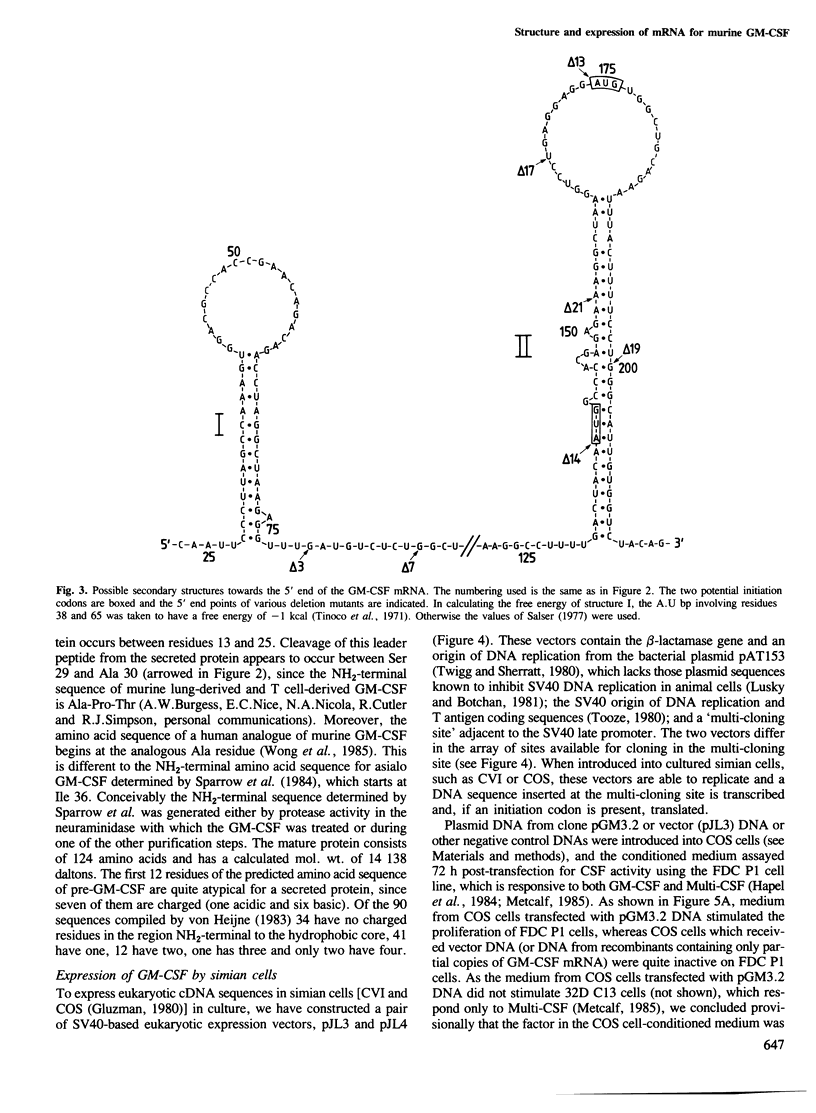
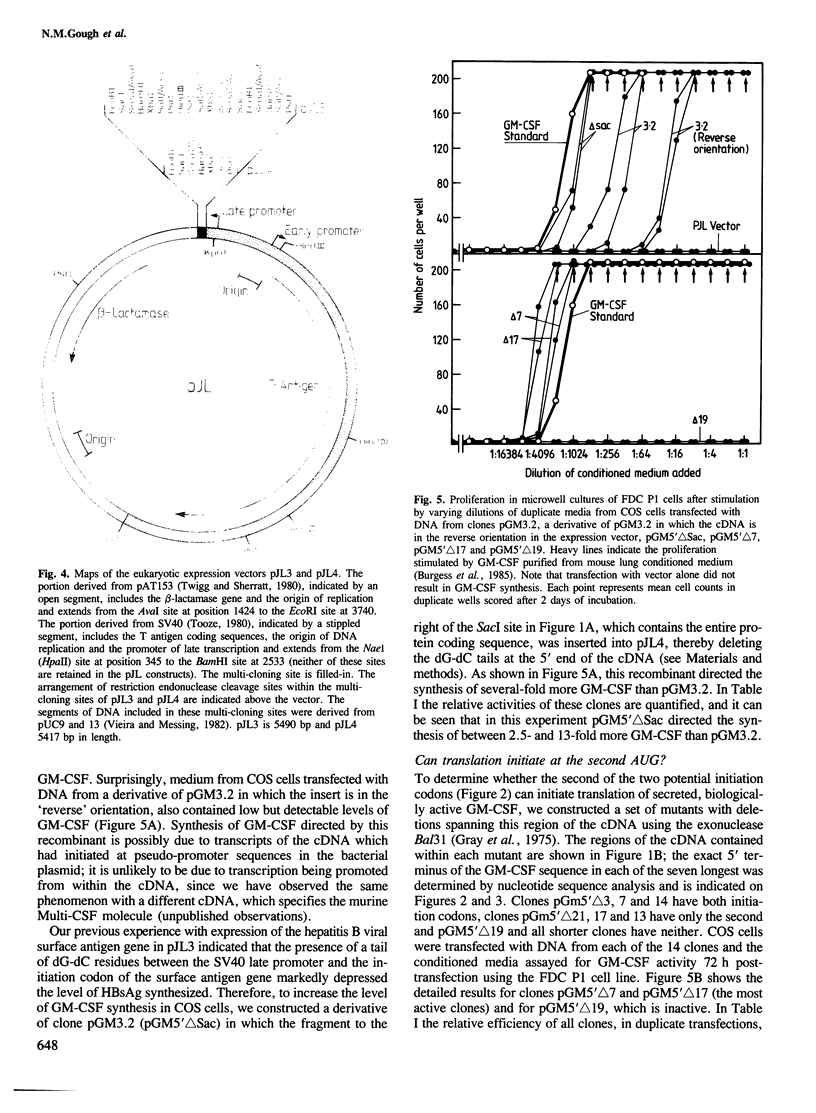
- Gough N. M., Gough J., Metcalf D., Kelso A., Grail D., Nicola N. A., Burgess A. W., Dunn A. R. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a murine haematopoietic growth regulator, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):763–767. doi: 10.1038/309763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray H. B., Jr, Ostrander D. A., Hodnett J. L., Legerski R. J., Robberson D. L. Extracellular nucleases of Pseudomonas BAL 31. I. Characterization of single strand-specific deoxyriboendonuclease and double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Sep;2(9):1459–1492. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.9.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapel A. J., Warren H. S., Hume D. A. Different colony-stimulating factors are detected by the "interleukin-3"-dependent cell lines FDC-Pl and 32D cl-23. Blood. 1984 Oct;64(4):786–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland E. C., Leung J. O., Drickamer K. Rat liver asialoglycoprotein receptor lacks a cleavable NH2-terminal signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7338–7342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery W. R., Brawerman G. Characterization of the steady-state population of messenger RNA and its poly(adenylic acid) segment in mammalian cells. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 22;13(22):4633–4637. doi: 10.1021/bi00719a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelso A., MacDonald H. R., Smith K. A., Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Interleukin 2 enhancement of lymphokine secretion by T lymphocytes: analysis of established clones and primary limiting dilution microcultures. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2932–2938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. How do eucaryotic ribosomes select initiation regions in messenger RNA? Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1109–1123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influence of mRNA secondary structure on binding and migration of 40S ribosomal subunits. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L., O'Malley B. W., Nisbet A. D., Fothergill J. E., Givol D., Fields S., Robertson M., Brownlee G. G. Sequence of chicken ovalbumin mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):723–728. doi: 10.1038/273723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Johnson G. R., Burgess A. W. Direct stimulation by purified GM-CSF of the proliferation of multipotential and erythroid precursor cells. Blood. 1980 Jan;55(1):138–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Nicola N. A. Proliferative effects of purified granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) on normal mouse hemopoietic cells. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Aug;116(2):198–206. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041160211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A., Burgess A. W., Staber F. G., Johnson G. R., Metcalf D., Battye F. L. Differential expression of lectin receptors during hemopoietic differentiation: enrichment for granulocyte-macrophage progenitor cells. J Cell Physiol. 1980 May;103(2):217–237. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasek M., Goto T., Gilbert W., Zink B., Schaller H., MacKay P., Leadbetter G., Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):575–579. doi: 10.1038/282575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Lockard R. E., Vamvakopoulos N., Rieser L., RajBhandary U. L., Vournakis J. N. Secondary structure of mouse and rabbit alpha- and beta-globin mRNAs: differential accessibility of alpha and beta initiator AUG codons towards nucleases. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90391-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price G. B., McCulloch E. A., Till J. E. Cell membranes as sources of granulocyte colony stimulating activities. Exp Hematol. 1975 Aug;3(4):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Basu S. K., Osborne T. F., Chin D. J., Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Luskey K. L. HMG CoA reductase: a negatively regulated gene with unusual promoter and 5' untranslated regions. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W. Globin mRNA sequences: analysis of base pairing and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):985–1002. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Owen M. J., Banville D., Williams J. G. Primary structure of human transferrin receptor deduced from the mRNA sequence. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):675–678. doi: 10.1038/311675b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow L. G., Metcalf D., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Burgess A. W. Purification and partial amino acid sequence of asialo murine granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):292–296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubin M., Mach B., Long E. O. The complete sequence of the mRNA for the HLA-DR-associated invariant chain reveals a polypeptide with an unusual transmembrane polarity. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):869–872. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Uhlenbeck O. C., Levine M. D. Estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nature. 1971 Apr 9;230(5293):362–367. doi: 10.1038/230362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N., Burgess A. W. The effect of mouse lung granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and other colony-stimulating activities on the proliferation and differentiation of murine bone marrow cells in long-term cultures. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Mar;102(3):287–295. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041020303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipori D. Cell interactions in the bone marrow microenvironment: role of endogenous colony-stimulating activity. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;17(4):347–357. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.380170406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]