Abstract
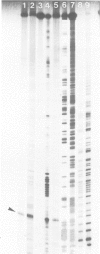
AT-rich DNA, which constitutes a distinct fraction of the cellular DNA of the archaebacterium Methanococcus voltae, was shown to consist of non-repetitive sequences dispersed on the chromosome and to lack continuous open reading frames in five out of six randomly analyzed cases. Upon subsequent analysis of intergenic regions, AT-rich sequences were again detected. Transcription start points were mapped in front of three open reading frames. The 5' ends of the transcripts were found in variable positions relative to the AT-rich sequences in the different cases. Shine-Dalgarno type sequences complementary to the 3' end of 16S rRNA were discovered at suitable distances from the 5' ends of the genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betlach M., Pfeifer F., Friedman J., Boyer H. W. Bacterio-opsin mutants of Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1416–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassarma S., Rajbhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. Bacterio-opsin mRNA in wild-type and bacterio-opsin-deficient Halobacterium halobium strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):125–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn R., McCoy J., Simsek M., Majumdar A., Chang S. H., Rajbhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. The bacteriorhodopsin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6744–6748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S., Woese C. R. Classification of methanogenic bacteria by 16S ribosomal RNA characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4537–4541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarsch M., Böck A. DNA sequence of the 16S rRNA/23S rRNA intercistronic spacer of two rDNA operons of the archaebacterium Methanococcus vannielii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7537–7544. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein A., Schnorr M. Genome complexity of methanogenic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):628–631. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.628-631.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Brammar W. J. A bacteriophage lambda vector for cloning large DNA fragments made with several restriction enzymes. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIYAZAWA Y., THOMAS C. A., Jr NUCLEOTIDE COMPOSITION OF SHORT SEGMENTS OF DNA MOLECULES. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:223–237. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meile L., Kiener A., Leisinger T. A plasmid in the archaebacterium Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(3):480–484. doi: 10.1007/BF00425766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. M., Loeblich L. A., Klotz L. C., Loeblich A. R., 3rd DNA organization of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1082–1084. doi: 10.1126/science.377486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. L., McCarthy B. J. Base sequence homology and renaturation studies of the deoxyribonucleic acid of extremely halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):255–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.255-262.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. L., McCarthy B. J. Characterization of the deoxyribonucleic acid of various strains of halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.248-254.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Friedman J., Boyer H. W., Betlach M. Characterization of insertions affecting the expression of the bacterio-opsin gene in Halobacterium halobium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2489–2497. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Backman K., Humayun M. Z., Jeffrey A., Maurer R., Meyer B., Sauer R. T. Autoregulation and function of a repressor in bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):156–161. doi: 10.1126/science.959843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern C. P. Satellite DNA of Anopheles stephensi Liston (Diptera: Culicidae). Chromosomal location and under-replication in polytene nuclei. Chromosoma. 1981;82(4):561–581. doi: 10.1007/BF00295013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., Doolittle W. F. Unusual physical organization of the Halobacterium genome. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):384–389. doi: 10.1038/295384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., Rose M. R., Doolittle W. F. High-frequency genomic rearrangements involving archaebacterial repeat sequence elements. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):182–185. doi: 10.1038/299182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel R., Thomm M., Gerardy-Schahn R., Zillig W., Stetter K. O., Huet J. Structural homology between different archaebacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerases analyzed by immunological comparison of their components. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):751–755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01495.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. E., Rhodes C., Rigby P. W., Berg P. Biochemical method for mapping mutational alterations in DNA with S1 nuclease: the location of deletions and temperature-sensitive mutations in simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):989–993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U. Nucleotide sequence of the three major early promoters of bacteriophage T7. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(5):1895–1907. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.5.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Methanogenic bacteria. Nature. 1978 May 4;273(5657):10–10. doi: 10.1038/273010a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomm M., Altenbuchner J., Stetter K. O. Evidence for a plasmid in a methanogenic bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1060–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1060-1062.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wich G., Jarsch M., Böck A. Apparent operon for a 5S ribosomal RNA gene and for tRNA genes in the archaebacterium Methanococcus vannielii. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(1):146–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00334107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Fox G. E. Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01734485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. G., Redborg A. H., Cue D. R., Whitman W. B., Konisky J. Complementation of argG and hisA mutations of Escherichia coli by DNA cloned from the archaebacterium Methanococcus voltae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):19–29. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.19-29.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]