Abstract
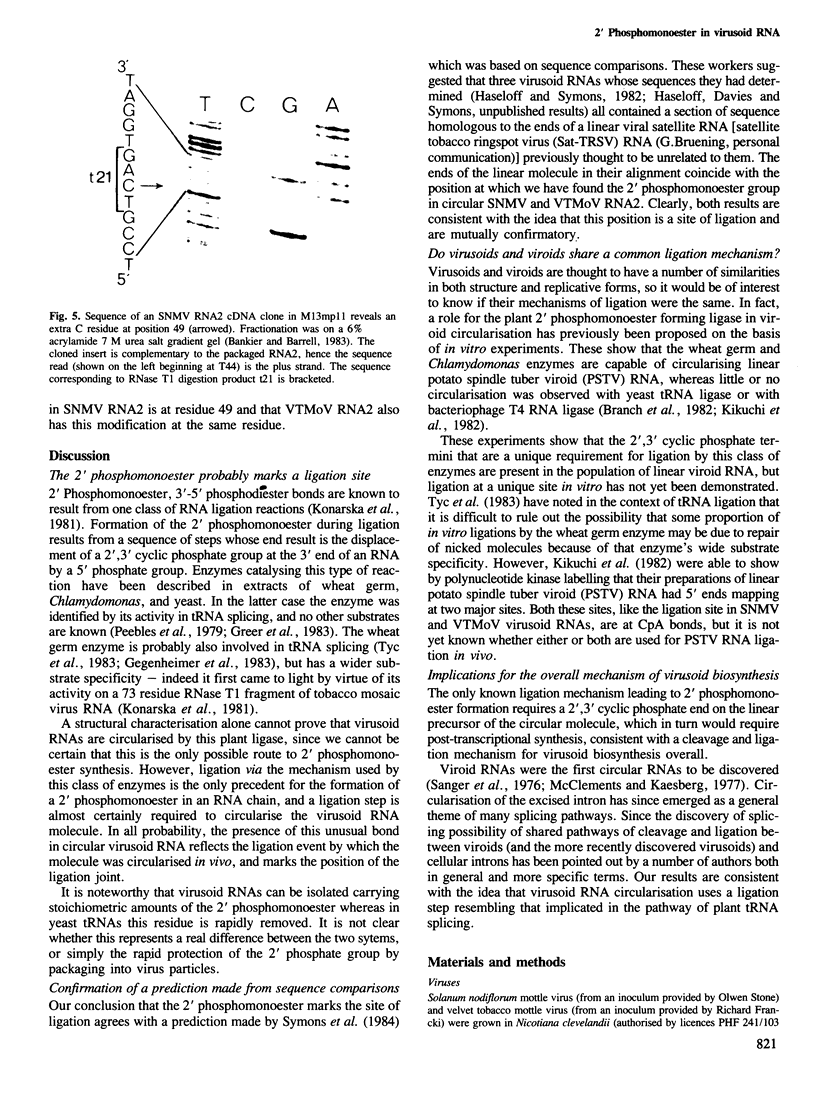
Solanum nodiflorum mottle virus (SNMV) RNA2 is a single-stranded, covalently closed circular molecule. RNase T2 or nuclease P1 digests of this RNA contain a minor nucleotide of unusual chromatographic and electrophoretic mobility. This nucleotide is resistant to further digestion by T2 or P1 ribonucleases, or by alkali, but is sensitive to venom phosphodiesterase digestion. Alkaline phosphatase digestion yields a product which is RNase T2 and P1 sensitive. The products of these various digests show that the minor nucleotide is a ribonuclease-resistant dinucleotide carrying a 2' phosphomonoester group with the core structure C2'p3'p5'A. This dinucleotide is found in a unique RNase T1 product of SNMV RNA2, thus establishing a unique location in the sequence for the 2' phosphomonoester group at residue 49. Identical results have been obtained with a second related virus. The phosphomonoester group probably results from the RNA ligation event by which the molecules were circularised.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branch A. D., Robertson H. D., Dickson E. Longer-than-unit-length viroid minus strands are present in RNA from infected plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6381–6385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch A. D., Robertson H. D., Greer C., Gegenheimer P., Peebles C., Abelson J. Cell-free circularization of viroid progeny RNA by an RNA ligase from wheat germ. Science. 1982 Sep 17;217(4565):1147–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.217.4565.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. RNA splicing: three themes with variations. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90527-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Tanner N. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Weir B. R., Zuker M., Perlman P. S. Secondary structure of the Tetrahymena ribosomal RNA intervening sequence: structural homology with fungal mitochondrial intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener T. O. Potato spindle tuber "virus". IV. A replicating, low molecular weight RNA. Virology. 1971 Aug;45(2):411–428. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90342-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegenheimer P., Gabius H. J., Peebles C. L., Abelson J. An RNA ligase from wheat germ which participates in transfer RNA splicing in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8365–8373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer C. L., Peebles C. L., Gegenheimer P., Abelson J. Mechanism of action of a yeast RNA ligase in tRNA splicing. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90473-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseloff J., Symons R. H. Comparative sequence and structure of viroid-like RNAs of two plant viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3681–3691. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa M., Meshi T., Ohno T., Okada Y., Sano T., Ueda I., Shikata E. A revised replication cycle for viroids: the role of longer than unit length RNA in viroid replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):421–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00436189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiberstis P. A., Zimmern D. Translational strategy of Solanum nodiflorum mottle virus RNA: synthesis of a coat protein precursor in vitro and in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):933–943. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Tyc K., Filipowicz W., Sänger H. L., Gross H. J. Circularization of linear viroid RNA via 2'-phosphomonoester, 3', 5'-phosphodiester bonds by a novel type of RNA ligase from wheat germ and Chlamydomonas. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7521–7529. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B., Gingrich J. C., Stiegler G. L., Farley M. A., Delius H., Hallick R. B. Nine introns with conserved boundary sequences in the Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):545–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90247-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M., Filipowicz W., Domdey H., Gross H. J. Formation of a 2'-phosphomonoester, 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage by a novel RNA ligase in wheat germ. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):112–116. doi: 10.1038/293112a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClements W. L., Kaesberg P. Size and secondary structure of potato spindle tuber viroid. Virology. 1977 Feb;76(2):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. A., Diener T. O. RNA intermediates in potato spindle tuber viroid replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):113–117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Lariat RNA's as intermediates and products in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):898–903. doi: 10.1126/science.6206566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Ogden R. C., Knapp G., Abelson J. Splicing of yeast tRNA precursors: a two-stage reaction. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger H. L., Klotz G., Riesner D., Gross H. J., Kleinschmidt A. K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3852–3856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signer E. R., Manly K. F., Brunstetter M. A. Deletion mapping of the c-3-N region of bacteriophage. Virology. 1969 Sep;39(1):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90356-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyc K., Kikuchi Y., Konarska M., Filipowicz W., Gross H. J. Ligation of endogenous tRNA 3' half molecules to their corresponding 5' halves via 2'-phosphomonoester,3',5'-phosphodiester bonds in extracts of Chlamydomonas. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):605–610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Voorde A., Rogiers R., Van Herreweghe J., Van Heuverswyn H., Volckaert G., Fiers W. Deoxynucleotide substitution: a new technique for sequence analysis of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Aug;1(8):1059–1067. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.8.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace J. C., Edmonds M. Polyadenylylated nuclear RNA contains branches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):950–954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Scazzocchio C., Brown T. A., Davies R. W. Close relationship between certain nuclear and mitochondrial introns. Implications for the mechanism of RNA splicing. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):595–605. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]