Abstract
[3H]2-Nitroimipramine ([3H]2-NI), a compound with high affinity for the serotonin uptake system, is shown to be an effective photoaffinity probe which incorporates covalently into membrane homogenates prepared from human platelets, as well as rat brain and liver. In all cases, [3H]2-NI preferentially incorporated into a minor membrane component of 30 kd protein, as determined by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and subsequent fluorography. A number of selective and general serotonin uptake inhibitors quantitatively chased labeling of the 30-kd band at nanomolar concentrations. Pharmacological characterizing agents unrelated to the serotonin uptake system generally had little effect on labeling. In platelet membranes, a broad band of approximately 35-kd protein was also labeled by [3H]2-NI, but this labeling was not inhibited by any of the selective serotonin uptake blockers. Interestingly, serotonin itself increased incorporation into the 30-kd band and selectively decreased labeling of the 35-kd band. Photolytic incorporation into the 30-kd band was of high affinity, saturable, and Scatchard analyses of irreversible labeling were linear. In contrast, Scatchard transformations of [3H]2-NI equilibrium binding saturation isotherms were markedly curvilinear. Cross-linking unlabeled 2-NI to intact platelets, followed by extensive dialysis, decreased the maximal velocity (Vmax) of platelet serotonin uptake, but did not alter the affinity (Km) of serotonin for its transport site. These results are noteworthy since current theories implicate prejunctional allosteric interactions between serotonin and imipramine at serotonergic synapses.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel I., Paul S. M. Inhibition of synaptosomal 5-[3H]hydroxytryptamine uptake by endogenous factor(s) in human blood. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jun 11;171(2):280–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80504-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arora R. C., Meltzer H. Y. Imipramine binding in subpopulations of normal human blood platelets. Biol Psychiatry. 1984 Feb;19(2):257–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas D., Friedman Z., Litvin Y., Steer M. L. Synthesis of new haloperidol analogues and characterization of their interactions with alpha-adrenoceptors in rat parotid slices and human platelet membranes. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):213–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08775.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V., BRICKNELL J. The uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine by blood platelets in the cold. J Physiol. 1959 Jun 23;147(1):153–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbaccia M. L., Brunello N., Chuang D. M., Costa E. On the mode of action of imipramine: relationship between serotonergic axon terminal function and down-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Mar;22(3 Spec No):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90186-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbaccia M. L., Gandolfi O., Chuang D. M., Costa E. Modulation of neuronal serotonin uptake by a putative endogenous ligand of imipramine recognition sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5134–5138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P. A., Maître L. Blockade of presynaptic alpha-receptors and of amine uptake in the rat brain by the antidepressant mianserine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;300(1):31–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00505077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biegon A., Rainbow T. C. Distribution of imipramine binding sites in the rat brain studied by quantitative autoradiography. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Jun 30;37(3):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90432-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondeau J. P., Robel P. Determination of protein-ligand binding constants at equilibrium in biological samples. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 1;55(2):375–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briley M. S., Raisman R., Langer S. Z. Human platelets possess high-affinity binding sites for 3H-imipramine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct 1;58(3):347–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90489-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Chuang D. M., Barbaccia M. L., Gandolfi O. Molecular mechanisms in the action of imipramine. Experientia. 1983 Aug 15;39(8):855–858. doi: 10.1007/BF01990403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A., Morris J., Tang S. W. Solubilization and assay of [3H]imipramine binding sites from human platelets. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond A. H., Gordon J. L. Uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine by rat blood platelets and its inhibition by adenosine 5'-diphosphate. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;56(4):417–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07452.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
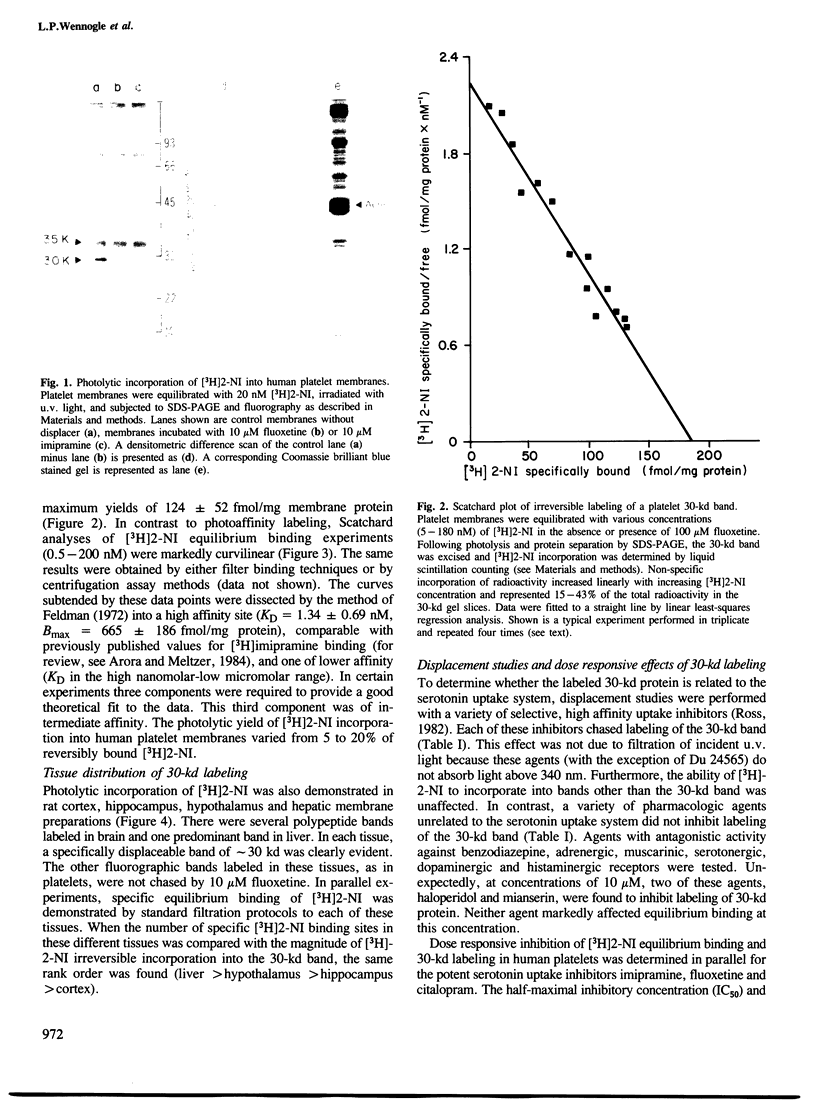
- Feldman H. A. Mathematical theory of complex ligand-binding systems of equilibrium: some methods for parameter fitting. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):317–338. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Göthert M., Ender H. P., Schümann H. J. 3H-Imipramine binding sites in the rat brain. Selective localization on serotoninergic neurones. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1981;317(4):310–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00501311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFSTEE B. H. J. On the evaluation of the constants Vm and KM in enzyme reactions. Science. 1952 Sep 26;116(3013):329–331. doi: 10.1126/science.116.3013.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyttel J. Citalopram--pharmacological profile of a specific serotonin uptake inhibitor with antidepressant activity. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1982;6(3):277–295. doi: 10.1016/s0278-5846(82)80179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ieni J. R., Zukin S. R., Van Praag H. M. Human platelets possess multiple [3H]imipramine binding sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Nov 27;106(3):669–672. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z., Zarifian E., Briley M., Raisman R., Sechter D. High-affinity 3H-imipramine binding: a new biological marker in depression. Pharmacopsychiatria. 1982 Jan;15(1):4–10. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1019502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Fur G., Uzan A. Effects of 4-(3-indolyl-alkyl)piperidine derivatives on uptake and release of noradrenaline, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in rat brain synaptosomes, rat heart and human blood platelets. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Mar 15;26(6):497–503. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90324-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingjaerde O. Inhibitory effect of clomipramine and related drugs on serotonin uptake in platelets: more complicated than previously thought. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1979 Mar 28;61(3):245–249. doi: 10.1007/BF00432266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald R. E., Changeux J. P. Selective labeling of the delta subunit of the acetylcholine receptor by a covalent local anesthetic. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 8;20(25):7166–7174. doi: 10.1021/bi00528a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxenkrug G. F. The effect of neuroleptic derivatives of butyrophenone on the uptake of 5-HT by human blood platelets. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;30(11):740–740. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1978.tb13383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxenkrug G. H., Prakhje I., Mikhalenko I. N. Disturbed circadian rhythm of 5HT uptake by blood platelets in depressive psychosis. Act Nerv Super (Praha) 1978 Feb;20(1):66–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits M., Raisman R., Briley M., Langer S. Z. Regional distribution of [3H]imipramine binding in rat brain. Brain Res. 1981 Apr 6;210(1-2):493–498. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90933-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S. M., Rehavi M., Rice K. C., Ittah Y., Skolnick P. Does high affinity [3H] imipramine binding label serotonin reuptake sites in brain and platelet? Life Sci. 1981 Jun 15;28(24):2753–2760. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90177-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S. M., Rehavi M., Skolnick P., Goodwin F. K. Demonstration of specific "high affinity" binding sites for [3H] imipramine on human platelets. Life Sci. 1980 Mar 24;26(12):953–959. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips O. M., Wood K. M., Williams D. C. Binding of [3H]imipramine to human platelet membranes with compensation for saturable binding to filters and its implication for binding studies with brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1984 Aug;43(2):479–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb00924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainbow T. C., Biegon A. Quantitative autoradiography of [3H]nitroimipramine binding sites in rat brain. Brain Res. 1983 Mar 7;262(2):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisman R., Briley M., Langer S. Z. High-affinity 3H-imipramine binding in rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 1;54(3):307–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
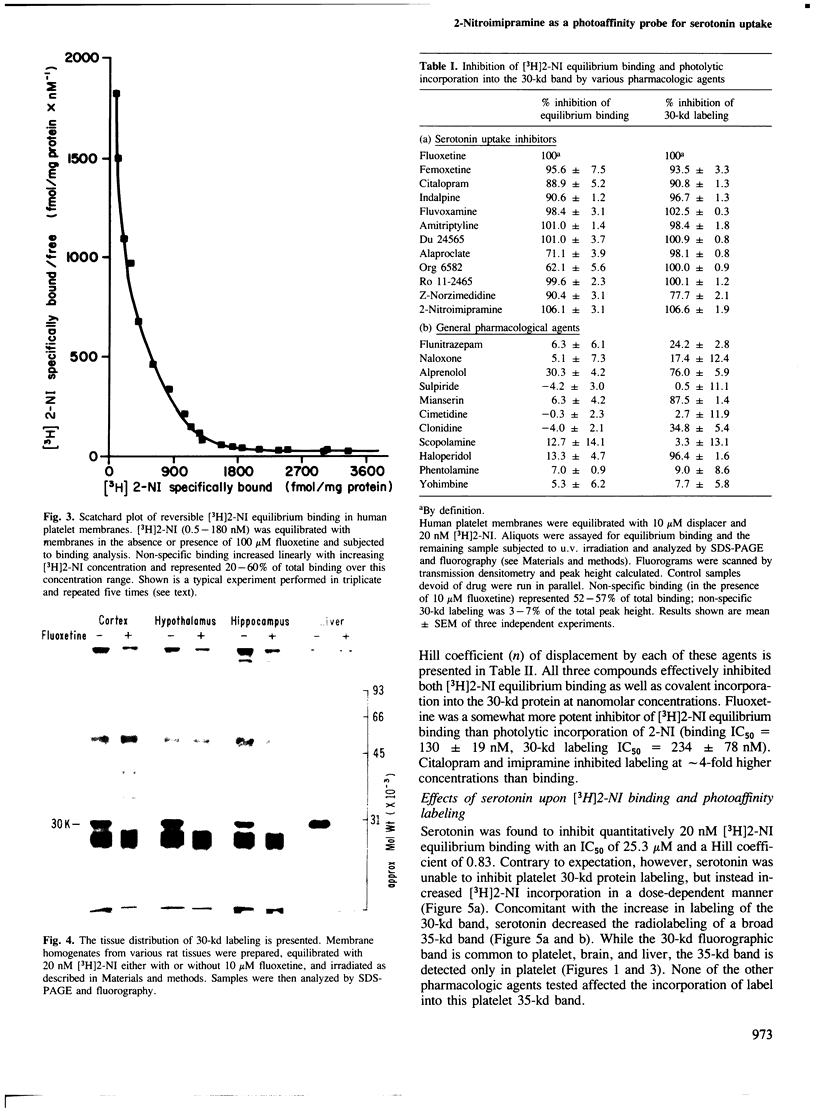
- Rehavi M., Ittah Y., Rice K. C., Skolnick P., Goodwin F. K., Paul S. M. 2-nitroimipramine: a selective irreversible inhibitor of [3H] serotonin uptake and [3H] imipramine binding in platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 15;99(3):954–959. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91255-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehavi M., Skolnick P., Paul S. M. Solubilization and partial purification of the high affinity [3H] imipramine binding site from human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):514–518. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80802-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehavi M., Tracer H., Rice K., Skolnick P., Paul S. M. [3H]2-Nitroimipramine: a selective "slowly-dissociating" probe of the imipramine binding site ("serotonin transporter") in platelets and brain. Life Sci. 1983 Feb 7;32(6):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90210-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith M. E., Sershen H., Allen D., Lajtha A. High- and low-affinity binding of [3H]imipramine in mouse cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1983 Feb;40(2):389–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb11294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotman A. Blood platelets in psychopharmacological research. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1983;7(2-3):135–151. doi: 10.1016/0278-5846(83)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotman A., Pribluda V. Photoaffinity labelling of the serotonin carrier protein in platelets and brain synaptosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 12;714(1):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick G., Talvenheimo J., Fishkes H., Nelson P. J. Sodium ion requirements for serotonin transport and imipramine binding. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1983;19(3):545–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarai K., Kayano M. The level and diurnal rhythm of serum serotonin in manic-depressive patients. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn. 1968;22(3):271–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.1968.tb01425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette M., Briley M. S., Langer S. Z. Complex inhibition of [3H]imipramine binding by serotonin and nontricyclic serotonin uptake blockers. J Neurochem. 1983 Mar;40(3):622–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talvenheimo J., Rudnick G. Solubilization of the platelet plasma membrane serotonin transporter in an active form. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8606–8611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomisto J. A new modification for studying 5-HT uptake by blood platelets: a re-evaluation of tricyclic antidepressants as uptake inhibitors. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;26(2):92–100. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1974.tb09231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B., Coignet J. L., de Vos C. J., Grijsen H., Bonta I. L. Mianserin hydrochloride: peripheral and central effects in relation to antagonism against 5-hydroxytryptamine and tryptamine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971 Nov-Dec;16(3):336–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennogle L. P., Beer B., Meyerson L. R. Human platelet imipramine recognition sites: biochemical and pharmacological characterization. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1981 Dec;15(6):975–982. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(81)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennogle L. P., Meyerson L. R. Serotonin modulates the dissociation of [3H]imipramine from human platelet recognition sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 24;86(2):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90333-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennogle L. P., Meyerson L. R. Serotonin uptake inhibitors differentially modulate high affinity imipramine dissociation in human platelet membranes. Life Sci. 1985 Apr 22;36(16):1541–1550. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90378-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wielosz M., Salmona M., de Gaetano G., Garattini S. Uptake of 14C-5-hydroxytryptamine by human and rat platelets and its pharmacological inhibition. A comparative kinetic analysis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;296(1):59–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00498840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirz-Justice A., Kräuchi K., Morimasa T., Willener R., Feer H. Circadian rhythm of [3H]imipramine binding in the rat suprachiasmatic nuclei. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Feb 18;87(2-3):331–333. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90348-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirz-Justice A. Possible circadian and seasonal rhythmicity in an in vitro model: monoamine uptake in rat brain slices. Experientia. 1974 Nov 15;30(11):1240–1241. doi: 10.1007/BF01945159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. T., Bymaster F. P., Reid L. R., Threlkeld P. G. Fluoxetine and two other serotonin uptake inhibitors without affinity for neuronal receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Apr 1;32(7):1287–1293. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]