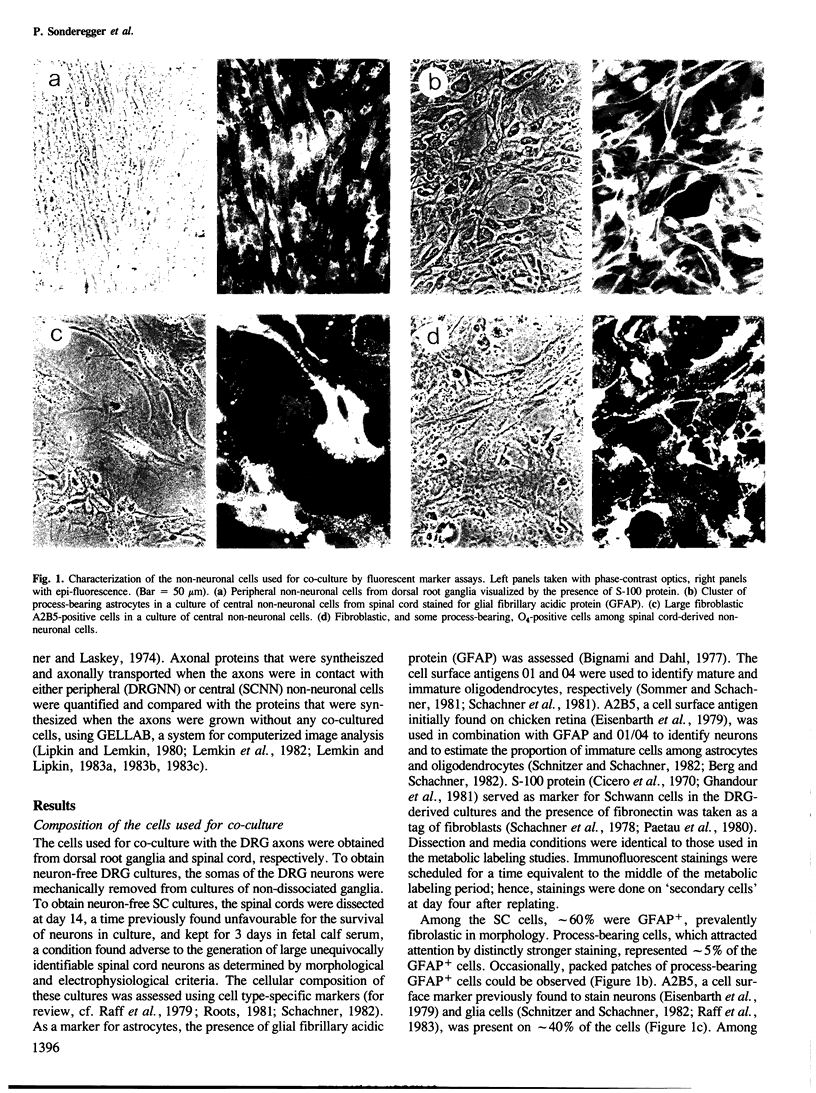
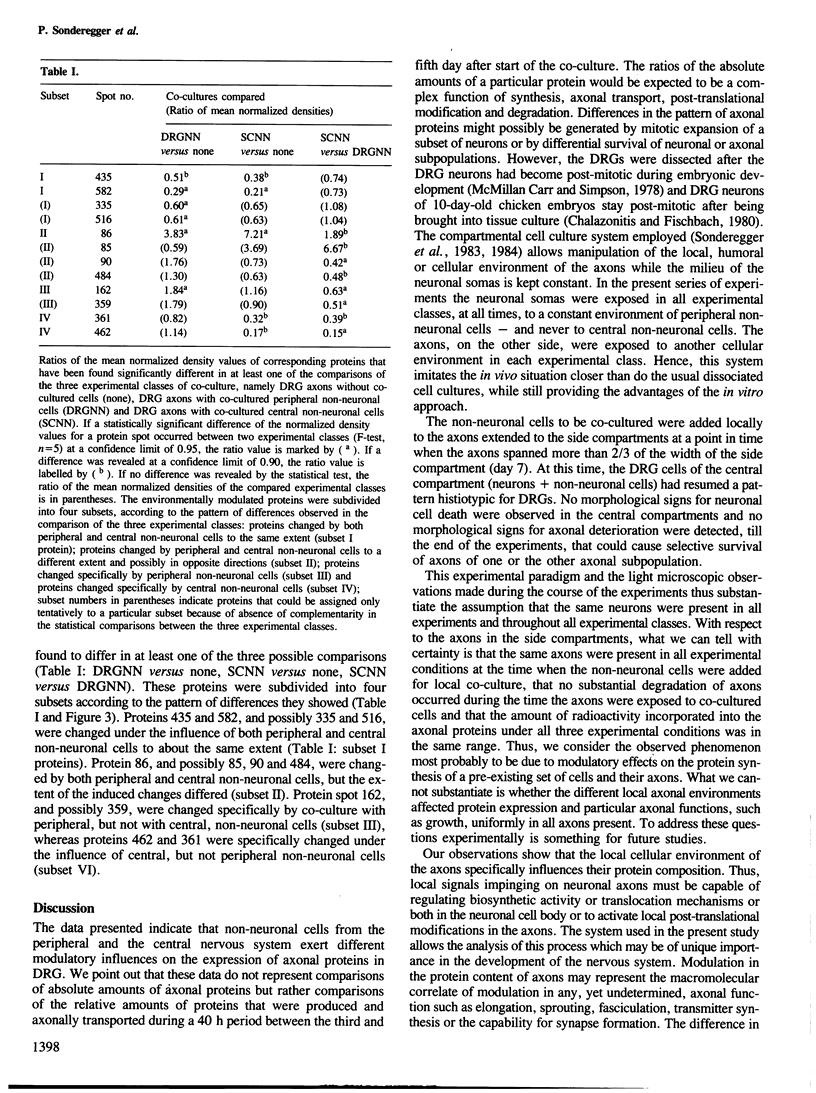
Abstract
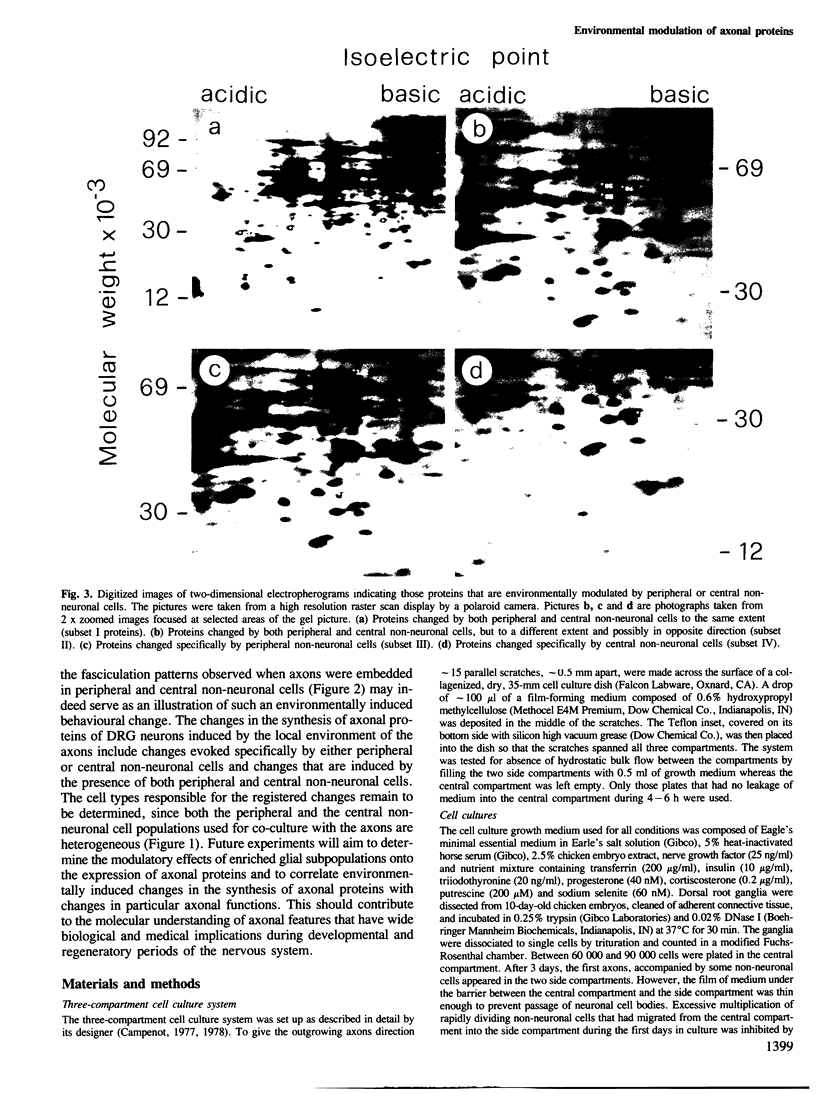
Axonal behavior during the formation of the neuronal network of the nervous system has been shown to be under environmental control. Hence, as a first step in a project aiming to elucidate the molecular basis of axonal functions, we have identified axonal proteins whose synthesis is subject to environmentally induced changes. Neurons from chicken embryonic dorsal root ganglia (DRG) were grown in a compartmental cell culture system that allows selective examination of axonal proteins. Non-neuronal cells of the peripheral or central nervous system were co-cultured with the DRG axons. The axonal proteins expressed under these different environmental conditions were examined by metabolic labeling and two-dimensional SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Computerized quantification revealed that 12 out of 400 axonal proteins responded to changes in the local axonal environment by a change in their relative abundance. Some proteins changed in response to both types of co-cultures whereas some changed specifically under the influence of either peripheral or central non-neuronal cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron-Van Evercooren A., Kleinman H. K., Ohno S., Marangos P., Schwartz J. P., Dubois-Dalcq M. E. Nerve growth factor, laminin, and fibronectin promote neurite growth in human fetal sensory ganglia cultures. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):179–193. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey M., Aguayo A. J. Extensive elongation of axons from rat brain into peripheral nerve grafts. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):150–152. doi: 10.1038/296150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg G. J., Schachner M. Electron-microscopic localization of A2B5 cell surface antigen in monolayer cultures of murine cerebellum and retina. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;224(3):637–645. doi: 10.1007/BF00213758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami A., Dahl D. Specificity of the glial fibrillary acidic protein for astroglia. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jun;25(6):466–469. doi: 10.1177/25.6.69656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campenot R. B. Independent control of the local environment of somas and neurites. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:302–307. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campenot R. B. Local control of neurite development by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4516–4519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr V. M., Simpson S. B., Jr Proliferative and degenerative events in the early development of chick dorsal root ganglia. I. Normal development. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Dec 15;182(4):727–739. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalazonitis A., Fischbach G. D. Elevated potassium induces morphological differentiation of dorsal root ganglionic neurons in dissociated cell culture. Dev Biol. 1980 Jul;78(1):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90327-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicero T. J., Cowan W. M., Moore B. W., Suntzeff V. The cellular localization of the two brain specific proteins, S-100 and 14-3-2. Brain Res. 1970 Feb 17;18(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90454-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Walsh F. S., Nirenberg M. Monoclonal antibody to a plasma membrane antigen of neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghandour M. S., Langley O. K., Labourdette G., Vincendon G., Gombos G. Specific and artefactual cellular localizations of S 100 protein: an astrocyte marker in rat cerebellum. Dev Neurosci. 1981;4(1):66–78. doi: 10.1159/000112742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen R. W., Barrett J. N. Neuronal chemotaxis: chick dorsal-root axons turn toward high concentrations of nerve growth factor. Science. 1979 Nov 30;206(4422):1079–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.493992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R., MEYER H., HAMBURGER V. In vitro experiments on the effects of mouse sarcomas 180 and 37 on the spinal and sympathetic ganglia of the chick embryo. Cancer Res. 1954 Jan;14(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemkin P. F., Lipkin L. E., Lester E. P. Some extensions to the GELLAB two-dimensional electrophoretic gel analysis system. Clin Chem. 1982 Apr;28(4 Pt 2):840–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneau P. C. Cell-to-substratum adhesion and guidance of axonal elongation. Dev Biol. 1975 May;44(1):92–101. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin L. E., Lemkin P. F. Data-base techniques for multiple two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analyses. Clin Chem. 1980 Sep;26(10):1403–1412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudge A. W. Effect of chemical environment on levels of substance P and somatostatin in cultured sensory neurones. Nature. 1981 Aug 20;292(5825):764–767. doi: 10.1038/292764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudge A. W. Schwann cells induce morphological transformation of sensory neurones in vitro. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):367–369. doi: 10.1038/309367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paetau A., Mellström K., Westermark B., Dahl D., Haltia M., Vaheri A. Mutually exclusive expression of fibronectin and glial fibrillary acidic protein in cultured brain cells. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Oct;129(2):337–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90501-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson P. H. Environmental determination of autonomic neurotransmitter functions. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:1–17. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Abney E. R., Cohen J., Lindsay R., Noble M. Two types of astrocytes in cultures of developing rat white matter: differences in morphology, surface gangliosides, and growth characteristics. J Neurosci. 1983 Jun;3(6):1289–1300. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-06-01289.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Fields K. L., Hakomori S. I., Mirsky R., Pruss R. M., Winter J. Cell-type-specific markers for distinguishing and studying neurons and the major classes of glial cells in culture. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 5;174(2):283–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90851-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. M., Ebendal T. Nerve growth activities in rat peripheral nerve. Brain Res. 1982 Aug 19;246(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. M., McGuinness U. M., Aguayo A. J. Axons from CNS neurons regenerate into PNS grafts. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):264–265. doi: 10.1038/284264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roots B. I. Comparative studies on glial markers. J Exp Biol. 1981 Dec;95:167–180. doi: 10.1242/jeb.95.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Gall W. E., Edelman G. M. Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. IV. Role of the cell surface molecule CAM in the formation of neurite bundles in cultures of spinal ganglia. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):382–393. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPERRY R. W. CHEMOAFFINITY IN THE ORDERLY GROWTH OF NERVE FIBER PATTERNS AND CONNECTIONS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:703–710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachner M. Cell type-specific surface antigens in the mammalian nervous system. J Neurochem. 1982 Jul;39(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb04694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachner M., Kim S. K., Zehnle R. Developmental expression in central and peripheral nervous system of oligodendrocyte cell surface antigens (O antigens) recognized by monoclonal antibodies. Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 30;83(2):328–338. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90478-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J., Schachner M. Cell type specificity of a neural cell surface antigen recognized by the monoclonal antibody A2B5. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;224(3):625–636. doi: 10.1007/BF00213757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer I., Schachner M. Monoclonal antibodies (O1 to O4) to oligodendrocyte cell surfaces: an immunocytological study in the central nervous system. Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 30;83(2):311–327. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90477-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonderegger P., Fishman M. C., Bokoum M., Bauer H. C., Neale E. A., Nelson P. G. A few axonal proteins distinguish ventral spinal cord neurons from dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):364–368. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonderegger P., Fishman M. C., Bokoum M., Bauer H. C., Nelson P. G. Axonal proteins of presynaptic neurons during synaptogenesis. Science. 1983 Sep 23;221(4617):1294–1297. doi: 10.1126/science.6612344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. M. Separation of functional Schwann cells and neurons from normal peripheral nerve tissue. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 22;115(3):361–375. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90355-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]