Abstract
Neural crest cells migrate extensively during embryonic development and differentiate into a wide variety of cell types. Our working hypothesis is that during migration, embryonic cells secrete proteases which modify local microenvironments, thereby facilitating directed cellular movements. In this communication, we report studies on the migration of cephalic neural crest cells in the avian embryo. We demonstrate that these cells produce high levels of the serine protease, plasminogen activator (PA), at the time of their initial migration from the neural tube and during their migration to and colonization of the developing head and neck.
Full text
PDF
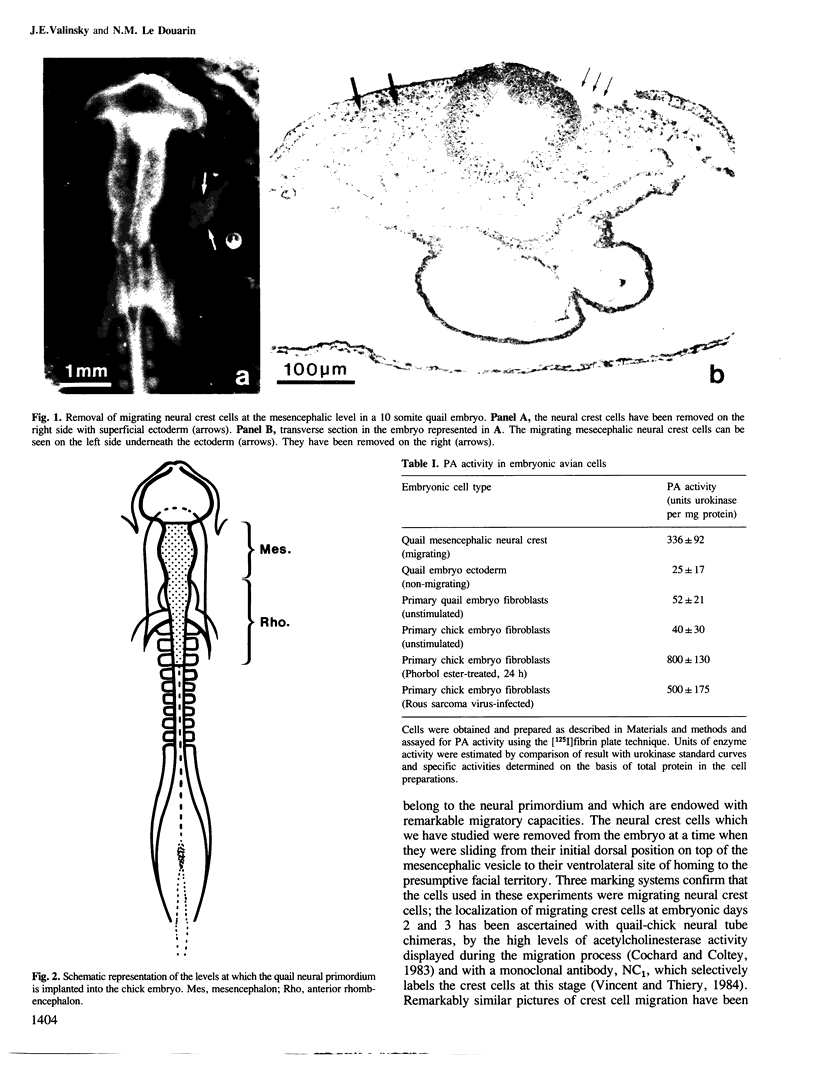


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong P. B., Quigley J. P., Sidebottom E. Transepithelial invasion and intramesenchymal infiltration of the chick embryo chorioallantois by tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1982 May;42(5):1826–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode V. C., Dziadek M. A. Plasminogen activator secretion during mouse embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1979 Dec;73(2):272–289. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucaut J. C., Darribère T., Boulekbache H., Thiery J. P. Prevention of gastrulation but not neurulation by antibodies to fibronectin in amphibian embryos. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):364–367. doi: 10.1038/307364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucaut J. C., Darribère T., Poole T. J., Aoyama H., Yamada K. M., Thiery J. P. Biologically active synthetic peptides as probes of embryonic development: a competitive peptide inhibitor of fibronectin function inhibits gastrulation in amphibian embryos and neural crest cell migration in avian embryos. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1822–1830. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochard P., Coltey P. Cholinergic traits in the neural crest: acetylcholinesterase in crest cells of the chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):221–238. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90351-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duband J. L., Thiery J. P. Distribution of fibronectin in the early phase of avian cephalic neural crest cell migration. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):308–323. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson C. A., Tosney K. W., Weston J. A. Analysis of migratory behavior of neural crest and fibroblastic cells in embryonic tissues. Dev Biol. 1980 Jun 1;77(1):142–156. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. A study of proteases and protease-inhibitor complexes in biological fluids. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):223–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., DeClerck Y. A. Destruction of extracellular matrices containing glycoproteins, elastin, and collagen by metastatic human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Sep;40(9):3222–3227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Klebe R. J., Martin G. R. Role of collagenous matrices in the adhesion and growth of cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):473–485. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. H., Nicolson G. L. Interactions of tumor cells with vascular endothelial cell monolayers: a model for metastatic invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5704–5708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. A biological cell labeling technique and its use in expermental embryology. Dev Biol. 1973 Jan;30(1):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. Particularites du noyau interphasique chez la caille Japonaise (Coturnix coturnix japonica) Bull Biol Fr Belg. 1969;103(3):435–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Lièvre C. S., Le Douarin N. M. Mesenchymal derivatives of the neural crest: analysis of chimaeric quail and chick embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1975 Aug;34(1):125–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lievre C. L. Rôle des cellules mésectodermiques issues des crêtes neurales céphaliques dans la formation des arcs branchiaux et du squelette viscéral. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1974 Apr;31(2):453–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Abe S., Robey P. G., Martin G. R. Preferential digestion of basement membrane collagen by an enzyme derived from a metastatic murine tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2268–2272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Goldfarb R. H., Brundage R., Siegal G. P., Terranova V., Garbisa S. Effect of plasminogen activator (urokinase), plasmin, and thrombin on glycoprotein and collagenous components of basement membrane. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4629–4636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Tryggvason K., Garbisa S., Hart I., Foltz C. M., Shafie S. Metastatic potential correlates with enzymatic degradation of basement membrane collagen. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):67–68. doi: 10.1038/284067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotti K. R., Belin D., Strickland S. The production of distinct forms of plasminogen activator by mouse embryonic cells. Dev Biol. 1982 Mar;90(1):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgreen D., Thiery J. P. Fibronectin in early avian embryos: synthesis and distribution along the migration pathways of neural crest cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1980;211(2):269–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00236449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Reich E. Antibodies to plasminogen activator inhibit human tumor metastasis. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):611–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley J. P. Association of a protease (plasminogen activator) with a specific membrane fraction isolated from transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):472–486. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J., Fauquet M., Ziller C., Le Douarin N. M. Acetylcholine synthesis by mesencephalic neural crest cells in the process of migration in vivo. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):853–855. doi: 10.1038/282853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. K., Strickland S. Structural components and characteristics of Reichert's membrane, an extra-embryonic basement membrane. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4654–4661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Beers W. H. Studies on the role of plasminogen activator in ovulation. In vitro response of granulosa cells to gonadotropins, cyclic nucleotides, and prostaglandins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5694–5702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan A. P., Heasman J., Wylie C. C. The invasion of cultured cell layers and intact epithelia. Scan Electron Microsc. 1981;4:99–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Duband J. L., Delouvée A. Pathways and mechanisms of avian trunk neural crest cell migration and localization. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):324–343. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valinsky J. E., Reich E., Le Douarin N. M. Plasminogen activator in the bursa of Fabricius: correlations with morphogenetic remodeling and cell migrations. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):471–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valinsky J. E., Reich E. Plasminogen in the chick embryo. Transport and biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12470–12475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M., Thiery J. P. A cell surface marker for neural crest and placodal cells: further evolution in peripheral and central nervous system. Dev Biol. 1984 Jun;103(2):468–481. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. L., Reich E. Plasminogen activator in chick fibroblasts: induction of synthesis by retinoic acid; synergism with viral transformation and phorbol ester. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





