Abstract
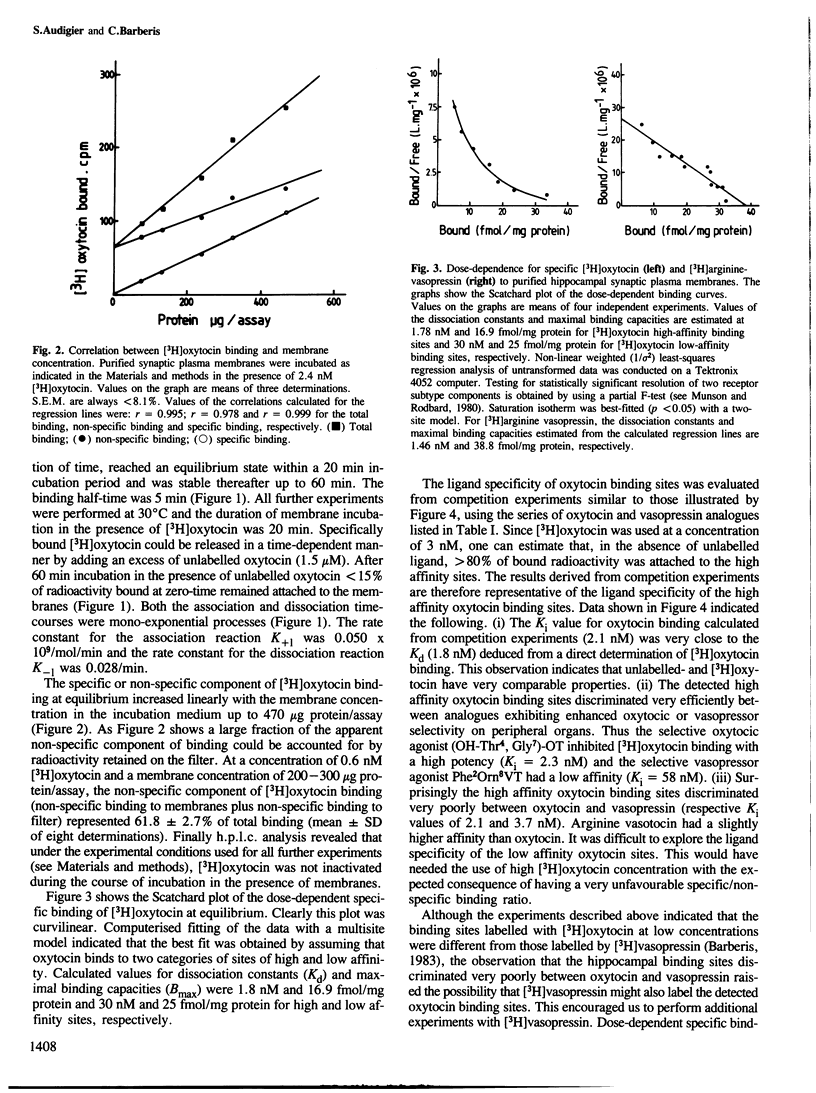
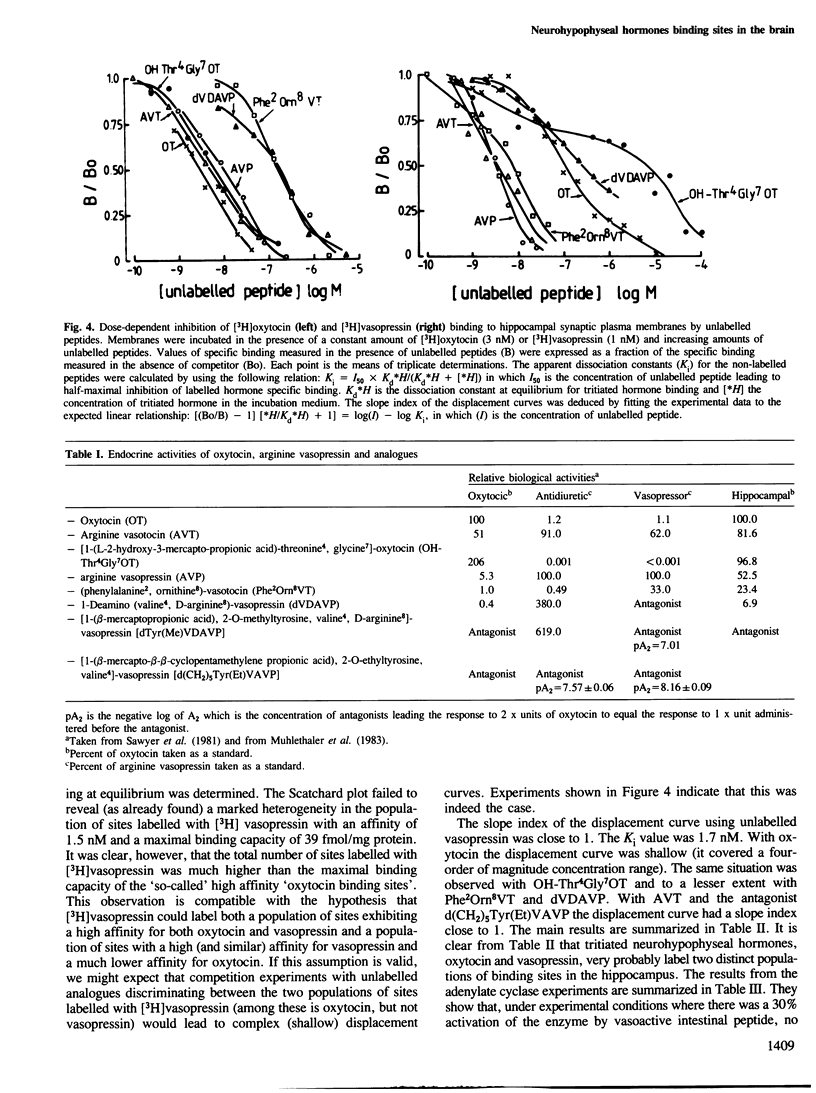
Synaptic plasma membranes containing binding sites for tritiated oxytocin and arginine vasopressin were isolated from rat hippocampus. The binding parameters for oxytocin and vasopressin sites were determined and statistically analysed. The fitted curve for oxytocin binding was compatible with a model where the ligand interacts with two classes of receptors with different capacities and affinities. The sites with low binding capacity had an apparent dissociation constant at equilibrium of 1.8 nM and a maximal binding capacity of 17 fmol/mg protein. By contrast, the Scatchard plot failed to reveal a marked heterogeneity in the population of sites labelled with [3H]vasopressin with an affinity of 1.5 nM and a maximal binding capacity of 39 fmol/mg protein. The specificity of these binding sites, tested in competition experiments, revealed that these neurohypophyseal hormones labelled two distinct populations of sites. One population with a high affinity for vasopressin, oxytocin and vasotocin, the other population with a high affinity for vasopressin and vasotocin and a low affinity for oxytocin. Adenylate cyclase activity was not affected by arginine-vasopressin or oxytocin. These receptors are compared with previously characterized peripheral receptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N., EMERY R. C., STREET B. W. A tissue homogenizer. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77:326–327. doi: 10.1042/bj0770326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis C. [3H]vasopressin binding to rat hippocampal synaptic plasma membrane. Kinetic and pharmacological characterization. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 17;162(2):400–405. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80795-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskin D. G., Petracca F., Dorsa D. M. Autoradiographic localization of specific binding sites for [3H][Arg8]vasopressin in the septum of the rat brain with tritium-sensitive film. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 May 20;90(1):155–157. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biegon A., Terlou M., Voorhuis T. D., de Kloet E. R. Arginine-vasopressin binding sites in rat brain: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Feb 24;44(3):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockaert J., Roy C., Jard S. Oxytocin-sensitive adenylate cyclase in frog bladder epithelial cells. Role of calcium, nucleotides, and other factors in hormonal stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7073–7081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonne D., Cohen P. Characterization of oxytocin receptors on isolated rat fat cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):295–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton R. E., Wamsley J. K., Gee K. W., Wan Y. P., Yamamura H. I. [3H]oxytocin binding sites in the rat brain demonstrated by quantitative light microscopic autoradiography. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul 13;102(2):365–367. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90270-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buijs R. M. Vasopressin and oxytocin--their role in neurotransmission. Pharmacol Ther. 1983;22(1):127–141. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(83)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camier M., Alazard R., Cohen P. Hormonal interactions at the molecular level. A study of oxytocin and vasopressin binding to bovine neurophysins. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 15;32(2):207–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Kloet E. R., Rotteveel F., Voorhuis T. A., Terlou M. Topography of binding sites for neurohypophyseal hormones in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Mar 26;110(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsa D. M., Majumdar L. A., Petracca F. M., Baskin D. G., Cornett L. E. Characterization and localization of 3H-arginine8-vasopressin binding to rat kidney and brain tissue. Peptides. 1983 Sep-Oct;4(5):699–706. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(83)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund-Mercier M. J., Richard P. Excitatory effects of intraventricular injections of oxytocin on the milk ejection reflex in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1981 May 6;23(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbon S., Clauser H. Cyclic adenosine 3',5' monophosphate levels in rat myometrium under the influence of epinephrine, prostaglandins and oxytocin, correlations with uterus motility. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Sep 17;44(6):1496–1503. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Matus A. I. Isolation of synaptic plasma membrane from brain by combined flotation-sedimentation density gradient centrifugation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 9;356(3):276–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joëls M., Urban I. J. The effect of microiontophoretically applied vasopressin and oxytocin on single neurones in the septum and dorsal hippocampus of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Nov 16;33(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski G. P., Nilaver G., Zimmerman E. A. Distribution of neurohypophysial hormones in the brain. Pharmacol Ther. 1983;21(3):325–349. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(83)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas M., Bockaert J. Use of (-)-[3H]dihydroalprenolol to study beta adrenergic receptor-adenylate cyclase coupling in C6 glioma cells: role of 5'-guanylylimidodiphosphate. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;13(2):314–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R., Salt T. E., Sofroniew M. V., Hill R. G. Actions of microiontophoretically applied oxytocin, and immunohistochemical localization of oxytocin, vasopressin and neurophysin in the rat caudal medulla. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Jun;18(2):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlethaler M., Sawyer W. H., Manning M. M., Dreifuss J. J. Characterization of a uterine-type oxytocin receptor in the rat hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6713–6717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlmutter A. F., Costantini M. G., Loeser B. Characterization of 3H-AVP binding sites in particulate preparations of rat brain. Peptides. 1983 May-Jun;4(3):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(83)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer W. H., Grzonka Z., Manning M. Neurohypophysial peptides. Design of tissue-specific agonists and antagonists. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 May;22(2):117–134. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloff M. S., Schroeder B. T., Chakraborty J., Pearlmutter A. F. Characterization of oxytocin receptors in the uterus and mammary gland. Fed Proc. 1977 May;36(6):1861–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leeuwen F. W., Wolters P. Light microscopic autoradiographic localization of [3H]arginine-vasopressin binding sites in the rat brain and kidney. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Oct 31;41(1-2):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Gee K. W., Brinton R. E., Davis T. P., Hadley M., Wamsley J. K. Light microscopic autoradiographic visualization of [3H]-arginine vasopressin binding sites in rat brain. Life Sci. 1983 Apr 18;32(16):1919–1924. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wied D. Behavioural actions of neurohypophysial peptides. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Oct 29;210(1178):183–195. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



