Abstract
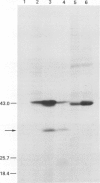
A plasmid designated pNF101 was isolated by transforming rad10 mutants with a yeast genomic library and screening transformed cells for enhanced resistance to killing by u.v. radiation. Plasmid pNF101 fully complements the u.v. sensitivity of rad10 mutant strains and was shown to contain the RAD10 gene by genetic analysis of integrant strains. The nucleotide sequence of the RAD10 gene was determined. The coding region consists of 195 codons and could encode a polypeptide of calculated mol. wt. 22 616 daltons. RAD10 protein expressed in Escherichia coli maxicells has a mol. wt of approximately 30 kd measured by gel electrophoresis. The RAD10 gene was localized to chromosome XIII of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by hybridization of the cloned gene to yeast chromosomes resolved by electrophoresis, and by genetic analysis.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderon I. L., Contopoulou C. R., Mortimer R. K. Isolation of a DNA fragment that is expressed as an amber suppressor when present in high copy number in yeast. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90167-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Stiegler P., Mackie G. A., Zimmermann R. A., Ebel J. P., Fellner P. Primary sequence of the 16S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Feb;2(2):265–278. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. R., Prakash L., Reynolds P., Prakash S. Isolation and characterization of the RAD2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. R., Prakash S., Reynolds P., Polakowska R., Weber S., Prakash L. Isolation and characterization of the RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and inviability of rad3 deletion mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5680–5684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. R., Prakash S., Reynolds P., Prakash L. Molecular cloning and characterization of the RAD1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. A., Fink G. R. Meiotic recombination between duplicated genetic elements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1985 Feb;109(2):303–332. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H. L., Petes T. D. Intrachromosomal gene conversion in yeast. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):144–148. doi: 10.1038/289144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Klinz F. J., Donath C., Gallwitz D. Point mutations identify the conserved, intron-contained TACTAAC box as an essential splicing signal sequence in yeast. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Hawthorne D. C. Genetic mapping in yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;11:221–233. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Chu G., Berg P., Friedberg E. C. RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence of wild-type and mutant alleles, transcript mapping, and aspects of gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):17–26. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. A DNA repair gene required for the incision of damaged DNA is essential for viability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4818–4821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. Molecular cloning of eucaryotic genes required for excision repair of UV-irradiated DNA: isolation and partial characterization of the RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):323–331. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.323-331.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD2 gene: isolation, subcloning, and partial characterization. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):290–295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry J. M., Parry E. M. The effects of UV-light post-treatments on the survival characteristics of 21 UV-sensitive mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mutat Res. 1969 Nov-Dec;8(3):545–557. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(69)90072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash L. Defective thymine dimer excision in radiation-sensitive mutants rad10 and rad16 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Apr 29;152(3):125–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00268808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Korn L. J. A comprehensive sequence analysis program for the IBM personal computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):581–599. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R. J., Friedberg E. C. Molecular mechanisms of pyrimidine dimer excision in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: incision of ultraviolet-irradiated deoxyribonucleic acid in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):692–704. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.692-704.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow R. Mutants of yeast sensitive to ultraviolet light. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):571–575. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.571-575.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox D. R., Prakash L. Incision and postincision steps of pyrimidine dimer removal in excision-defective mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):618–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.618-623.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang E., Friedberg E. C. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2161–2169. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]