Abstract
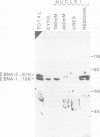
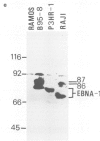
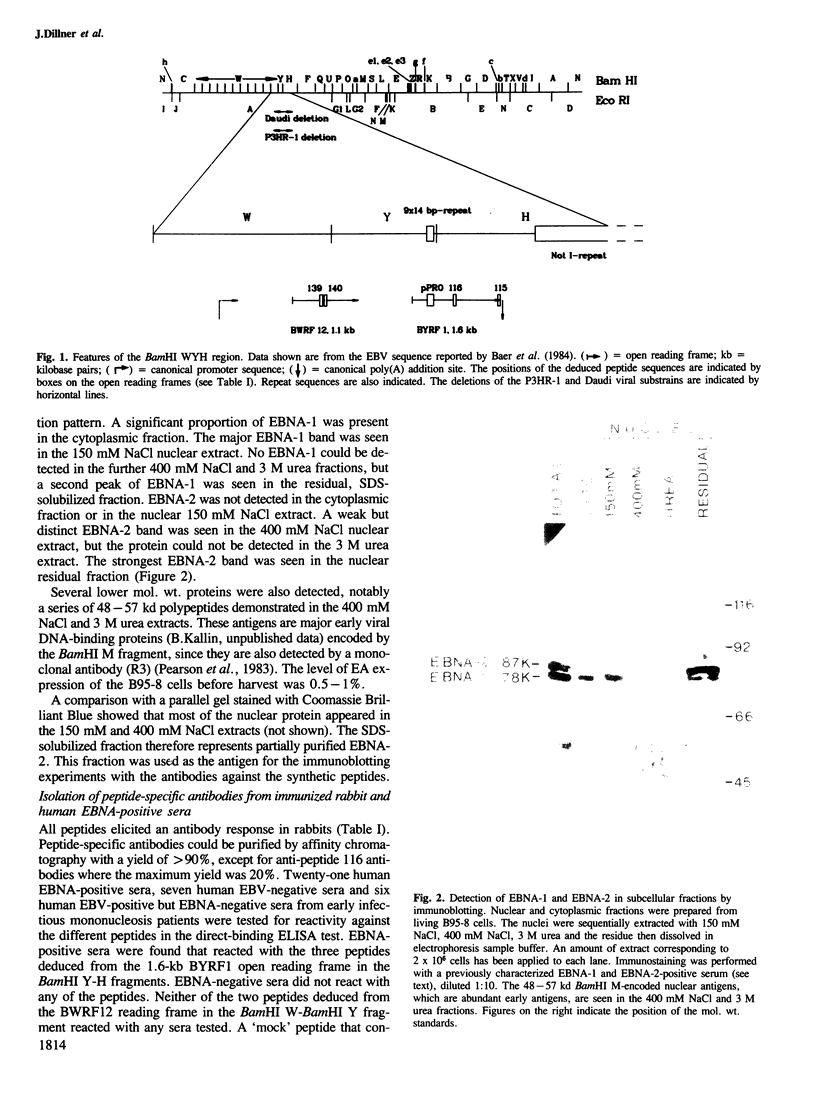
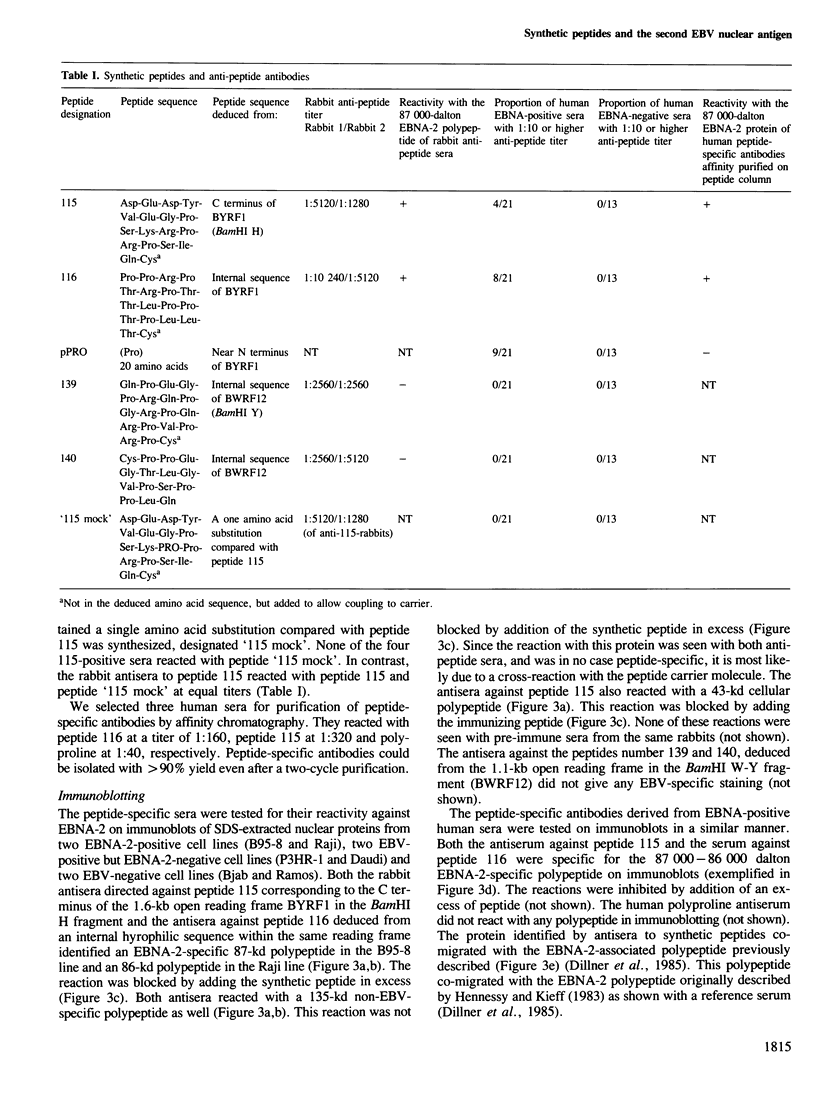
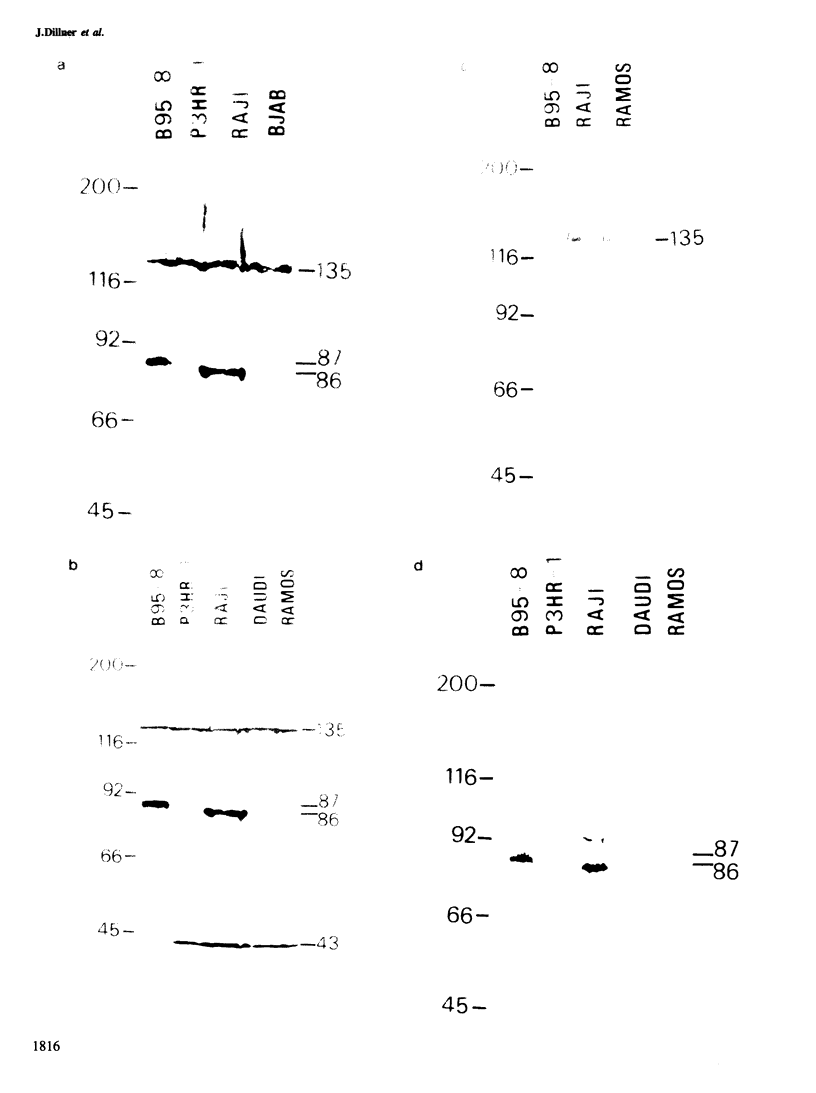
Five peptides were synthesized on the basis of amino acid sequences predicted from the transformation-associated BamHI WYH region of the genome of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Antisera to two peptides deduced from a 1.6-kb open reading frame in the BamHI H fragment identified an 87 000-dalton nuclear polypeptide that was present in EBV-carrying cell lines that expressed the second EBV-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA-2). This polypeptide was not detected in cell lines that carried EBV variants with a deleted BamHI WYH region or in EBV-negative cell lines. Three peptides deduced from the 1.6-kb open reading frame reacted with human EBNA-positive sera, but not with EBNA-negative sera. Following affinity purification with the peptides, two of the corresponding human antibodies also reacted with the 87 000-dalton polypeptide.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Chambraud B., Farrell P., Perricaudet M. Spliced RNA from the IR1-U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus: presence of an open reading frame for a repetitive polypeptide. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1913–1917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Hennessy K., Chamnankit L., Kieff E. U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus DNA may encode Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7632–7636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Bornkamm G. W. Heterogeneity of Epstein-Barr virus. III. Comparison of a transforming and a nontransforming virus by partial denaturation mapping of their DNAs. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):81–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.81-89.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Timar L., Klein G. Characterization of a second Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen associated with the BamHI WYH region of EBV DNA. Int J Cancer. 1985 Mar 15;35(3):359–366. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Sternås L., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Jörnvall H., Klein G., Lerner R. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide identify the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4652–4656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresen K. O., Cho M. S., zur Hausen H. Recovery of transforming EBV from non-producer cells after superinfection with non-transforming P3HR-1 EBV. Int J Cancer. 1978 Oct 15;22(4):378–383. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Diehl V., Kohn G., Zur Hausen H., Henle G. Herpes-type virus and chromosome marker in normal leukocytes after growth with irradiated Burkitt cells. Science. 1967 Sep 1;157(3792):1064–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3792.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. A second nuclear protein is encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent infection. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.2983420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. One of two Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens contains a glycine-alanine copolymer domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel M., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA. VIII. Viral RNA in permissively infected B95-8 cells. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):262–272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.262-272.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel M., Kieff E. Mapping of polypeptides encoded by the Epstein-Barr virus genome in productive infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5698–5702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. D., Foster L., Sheedy T., Griffin B. E. The EB virus genome in Daudi Burkitt's lymphoma cells has a deletion similar to that observed in a non-transforming strain (P3HR-1) of the virus. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):813–821. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01890.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieff E., Dambaugh T., Heller M., King W., Cheung A., van Santen V., Hummel M., Beisel C., Fennewald S., Hennessy K. The biology and chemistry of Epstein-Barr virus. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):506–517. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B. C., Lindahl T., Fialkow P. J., Singh S., Stehlin J. S. Direct evidence for the presence of Epstein-Barr virus DNA and nuclear antigen in malignant epithelial cells from patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of the nasopharynx. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4737–4741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L., Lipman M. Differences between laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr virus based on immortalization, abortive infection, and interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Vroman B., Chase B., Sculley T., Hummel M., Kieff E. Identification of polypeptide components of the Epstein-Barr virus early antigen complex with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.193-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculley T. B., Walker P. J., Moss D. J., Pope J. H. Identification of multiple Epstein-Barr virus-induced nuclear antigens with sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):88–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.88-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelsberg T. C., Sculley T. B., Pikler G. M., Gilbert J. A., Pearson G. R. Evidence for two classes of chromatin-associated Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):555–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.555-565.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad B. C., Schuster T. C., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. Identification of an Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen by fluoroimmunoelectrophoresis and radioimmunoelectrophoresis. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.996-1004.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Grogan E. A., Shedd D., Robert M., Liu C. R., Miller G. Stable expression in mouse cells of nuclear neoantigen after transfer of a 3.4-megadalton cloned fragment of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Shinnick T. M., Green N., Liu F. T., Niman H. L., Lerner R. A. Chemical synthesis of a polypeptide predicted from nucleotide sequence allows detection of a new retroviral gene product. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):801–805. doi: 10.1038/287801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Bauer H., Birr C., Pipkorn R. Antibodies against synthetic peptides as a tool for functional analysis of the transforming protein pp60src. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):587–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima Y., Marczynska B., Nonoyama M. Transforming activity of Epstein-Barr virus obtained by superinfection of Raji cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2008–2010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V., Cheung A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA VII: size and direction of transcription of virus-specified cytoplasmic RNAs in a transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1930–1934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]