Abstract
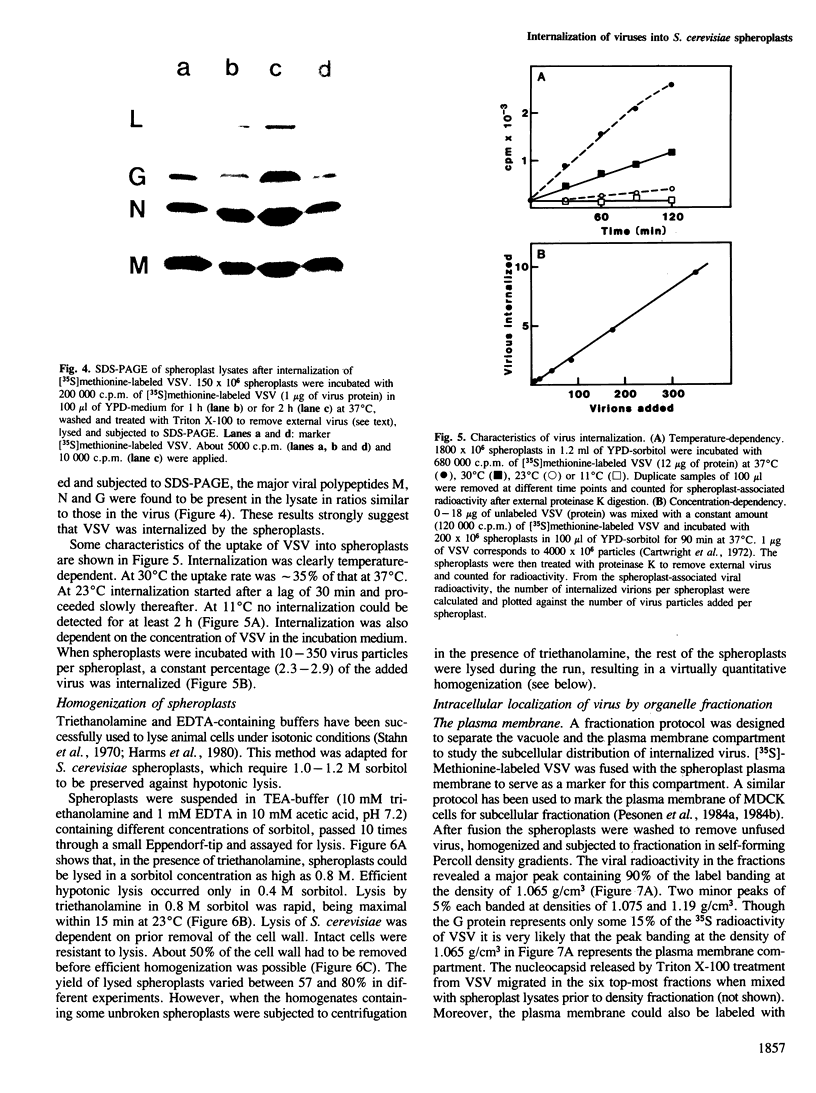
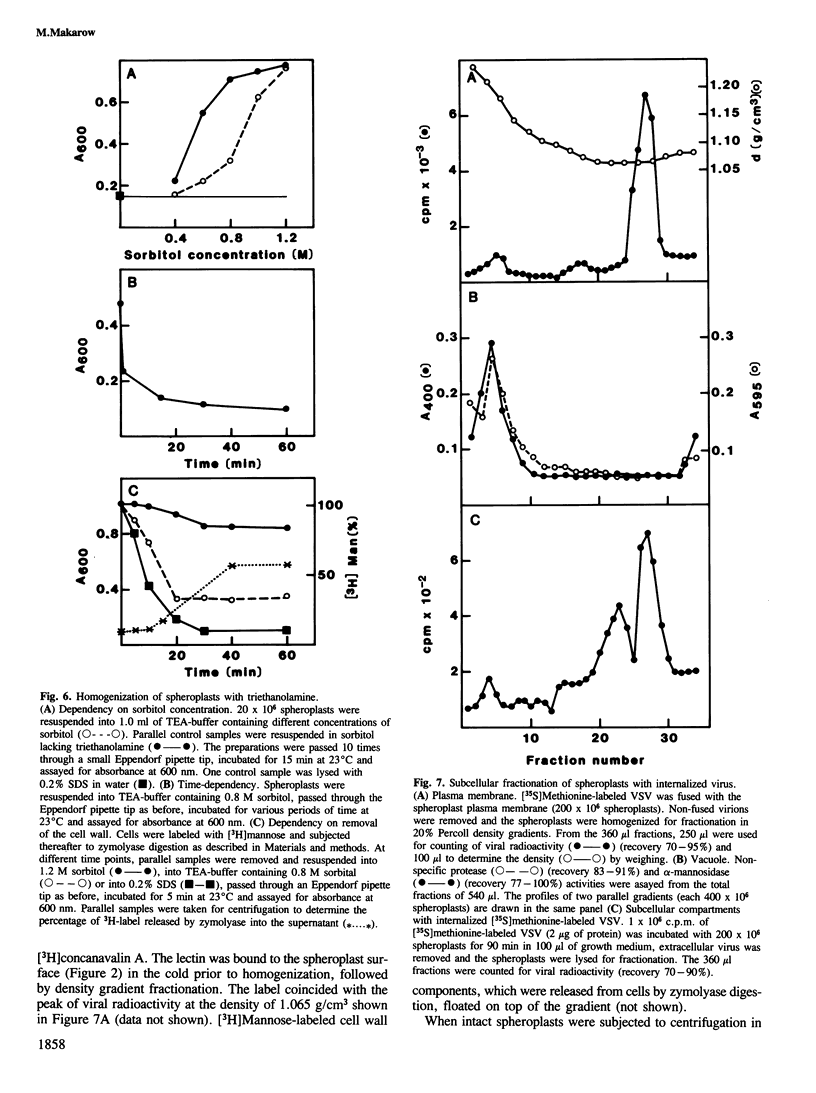
When vesicular stomatitis virus was incubated with Saccharomyces cerevisiae spheroplasts at 37 degrees C, part of the virus was internalized by the spheroplasts as shown by the following criteria. (i) The spheroplast-associated virus was protected from proteinase K digestion, which releases surface-bound virus by degrading the envelope glycoproteins. (ii) The spheroplast-associated virus was resistant to mild Triton X-100 treatment, which readily solubilizes the virus. The same results were obtained with Semliki Forest virus. Internalization of the two viruses followed linear kinetics up to 90 min at 37 degrees C. Internalization was concentration- and temperature-dependent. At 11 degrees C no uptake could be detected for at least 2 h. Homogenization and organelle fractionation protocols were designed for the S. cerevisiae spheroplasts to study the compartments into which the virions were internalized. Three compartments containing both marker viruses could be separated in density gradients. One coincided with vacuole markers, one banded at a slightly higher and one at a similar density to the plasma membrane markers. Thus, S. cerevisiae spheroplasts appear to have the capability of endocytosing particulate markers like viruses. The companion paper describes internalization of two soluble macromolecules, alpha-amylase and fluorescent dextran, into intact cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballou C. Structure and biosynthesis of the mannan component of the yeast cell envelope. Adv Microb Physiol. 1976;14(11):93–158. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Duerr A., Solomon F., Penman S. The outer boundary of the cytoskeleton: a lamina derived from plasma membrane proteins. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):859–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll A. R., Wagner R. R. Role of the membrane (M) protein in endogenous inhibition of in vitro transcription by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.134-142.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright B., Smale C. J., Brown F., Hull R. Model for vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):256–260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.256-260.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn W. A., Hubbard A. L., Aronson N. N., Jr Low temperature selectively inhibits fusion between pinocytic vesicles and lysosomes during heterophagy of 125I-asialofetuin by the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5971–5978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway C. J., Dean G. E., Marsh M., Rudnick G., Mellman I. Acidification of macrophage and fibroblast endocytic vesicles in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3334–3338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms E., Kern H., Schneider J. A. Human lysosomes can be purified from diploid skin fibroblasts by free-flow electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6139–6143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Kartenbeck J., Simons K., Fries E. On the entry of Semliki forest virus into BHK-21 cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):404–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Marsh M. Endocytosis of enveloped animal viruses. Ciba Found Symp. 1982;(92):59–76. doi: 10.1002/9780470720745.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Söderlund H. Properties of Semliki Forest virus nucleocapsid. 1. Sensitivity to pancreatic ribonuclease. Virology. 1971 Jan;43(1):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Bolzau E., Helenius A. Penetration of Semliki Forest virus from acidic prelysosomal vacuoles. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):931–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Adsorptive endocytosis of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):439–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K., Bainton D. F., Pesonen M., Louvard D., Genty N., Simons K. Transepithelial transport of a viral membrane glycoprotein implanted into the apical plasma membrane of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. I. Morphological evidence. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):627–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oker-Blom C., Kalkkinen N., Käriäinen L., Pettersson R. F. Rubella virus contains one capsid protein and three envelope glycoproteins, E1, E2a, and E2b. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):964–973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.964-973.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi P. The uptake of bovine serum albumin by a strain of Saccharomyces and its physiopathological consequences. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1967;36(6):95–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen M., Ansorge W., Simons K. Transcytosis of the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus after implantation into the apical plasma membrane of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. I. Involvement of endosomes and lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):796–782. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen M., Bravo R., Simons K. Transcytosis of the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus after implantation into the apical membrane of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. II. Involvement of the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):803–809. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen M., Simons K. Transepithelial transport of a viral membrane glycoprotein implanted into the apical plasma membrane of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. II. Immunological quantitation. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):638–643. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Geokas M. C., Silverman P., Haverback B. J. A new ultrasensitive method for the determination of proteolytic activity. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Aug;21(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLENK F., DAINKO J. L. ACTION OF RIBONUCLEASE PREPARATIONS ON VIABLE YEAST CELLS AND SPHEROPLASTS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:428–436. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.428-436.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahn R., Maier K. P., Hannig K. A new method for the preparation of rat liver lysosomes. Separation of cell organelles of rat liver by carrier-free continuous electrophoresis. J Cell Biol. 1970 Sep;46(3):576–591. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.3.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Mellman I. S., Muller W. A., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis and the recycling of plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):1–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svihla G., Dainko J. L., Schlenk F. Ultraviolet micrography of penetration of exogenous cytochrome c into the yeast cell. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):498–504. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.498-504.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tycko B., Maxfield F. R. Rapid acidification of endocytic vesicles containing alpha 2-macroglobulin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):643–651. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kartenbeck J., Helenius A. Fusion of Semliki forest virus with the plasma membrane can be induced by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):264–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yphantis D. A., Dainko J. L., Schlenk F. Effect of some proteins on the yeast cell membrane. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1509–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1509-1515.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]