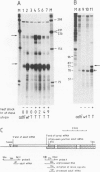
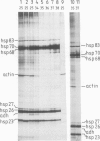
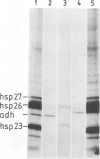
Abstract
One of the effects of a temperature increase above 35 degrees C on Drosophila melanogaster is a rapid switch in selectivity of the translational apparatus. Protein synthesis from normal, but not from heat shock, mRNA is much reduced. Efficient translation at high temperature might be a result of the primary sequence of heat shock genes. Alternatively a mRNA modification mechanism, altered as a consequence of heat shock, might allow for efficient high temperature translation of any mRNA synthesized during a heat shock. The gene for alcohol dehydrogenase (Adh) was fused to the controlling elements of a heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) gene. Authentic Adh mRNA, synthesized from this fusion gene at elevated temperatures was not translated during heat shock. A second Adh fusion gene in which the mRNA synthesized contained the first 95 nucleotides of the Hsp70 non-translated leader sequence gave rise, at high temperature, to mRNA which was translated during the heat shock. Thus, the signal(s) in the mRNAs controlling translation efficiency at heat shock temperatures is encoded within the heat shock genes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballinger D. G., Pardue M. L. The control of protein synthesis during heat shock in Drosophila cells involves altered polypeptide elongation rates. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Gurdon J. B. The heat-shock response in Xenopus oocytes is controlled at the translational level. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):811–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. J., Parks C., Parker-Thornburg J., Mortin M. A., Pelham H. R. The use of promoter fusions in Drosophila genetics: isolation of mutations affecting the heat shock response. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):979–991. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90432-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Dawid I. B. Transient expression of genes introduced into cultured cells of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7095–7098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudler R., Travers A. A. Upstream elements necessary for optimal function of the hsp 70 promoter in transformed flies. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90494-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. R., Ben-Ze'av A., Benecke B. J., Penman S. Altered translatability of messenger RNA from suspended anchorage-dependent fibroblasts: reversal upon cell attachment to a surface. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V. Heat shock induces rapid dephosphorylation of a ribosomal protein in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grell E. H., Jacobson K. B., Murphy J. B. Alterations of genetics material for analysis of alcohol dehydrogenase isozymes of Drosophila melanogaster. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Jun 14;151(1):441–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb11907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juan E., González-Duarte R. Purification and enzyme stability of alcohol dehydrogenase from Drosophila simulans, Drosophila virilis and Drosophila melanogaster adhS. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 1;189(1):105–110. doi: 10.1042/bj1890105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch F., Török I., Tissières A. Extensive regions of homology in front of the two hsp70 heat shock variant genes in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman M. Nucleotide polymorphism at the alcohol dehydrogenase locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):412–417. doi: 10.1038/304412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger C., Benecke B. J. In vitro translation of Drosophila heat-shock and non--heat-shock mRNAs in heterologous and homologous cell-free systems. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):595–603. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. Regulation of protein synthesis during heat shock. Nature. 1981 Sep 24;293(5830):311–314. doi: 10.1038/293311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Shenk T. Adenovirus tripartite leader sequence enhances translation of mRNAs late after infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3655–3659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. L., Henikoff S., Meselson M. Localization of RNA from heat-induced polysomes at puff sites in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1117–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirault M. E., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Moran L., Arrigo A. P., Tissières A. The effect of heat shock on gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):819–827. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirault M. E., Southgate R., Delwart E. Regulation of heat-shock genes: a DNA sequence upstream of Drosophila hsp70 genes is essential for their induction in monkey cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1279–1285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palatnik C. M., Wilkins C., Jacobson A. Translational control during early Dictyostelium development: possible involvement of poly(A) sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. S., Mitchell H. K. Recovery of protein synthesis after heat shock: prior heat treatment affects the ability of cells to translate mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1708–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Hogness D. S. Effect of heat shock on the synthesis of low molecular weight RNAs in drosophilia: accumulation of a novel form of 5S RNA. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl P., Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Steward R., Gehring W. J., Mirault M. E., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Moran L., Tissières A. Two hybrid plasmids with D. melanogaster DNA sequences complementary to mRNA coding for the major heat shock protein. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):921–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Pardue M. L. Translational control in lysates of Drosophila melanogaster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3353–3357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate R., Ayme A., Voellmy R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the Drosophila small heat shock gene cluster at locus 67B. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 25;165(1):35–57. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A., Pardue M. L., Penman S. Messenger RNA in heat-shocked Drosophila cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 5;109(4):559–587. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. Regulated expression of genes injected into early Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):165–173. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01778.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storti R. V., Scott M. P., Rich A., Pardue M. L. Translational control of protein synthesis in response to heat shock in D. melanogaster cells. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90559-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanguay R. M. Genetic regulation during heat shock and function of heat-shock proteins: a review. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;61(6):387–394. doi: 10.1139/o83-053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher D. R., Sawyer L. Secondary-structure prediction from the sequence of Drosophila melanogaster (fruitfly) alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):884–886. doi: 10.1042/bj1870884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C., Tjian R., Hu S. L., Grodzicker T. Translational control of SV40 T antigen expressed from the adenovirus late promoter. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):455–464. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90427-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Török I., Karch F. Nucleotide sequences of heat shock activated genes in Drosophila melanogaster. I. Sequences in the regions of the 5' and 3' ends of the hsp 70 gene in the hybrid plasmid 56H8. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 25;8(14):3105–3123. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.14.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worsfold V., Marshall M. J., Ellis E. B. Enzyme detection using phenazine methosulphate and tetrazolium salts: interference by oxygen. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):152–156. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90389-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]