Abstract
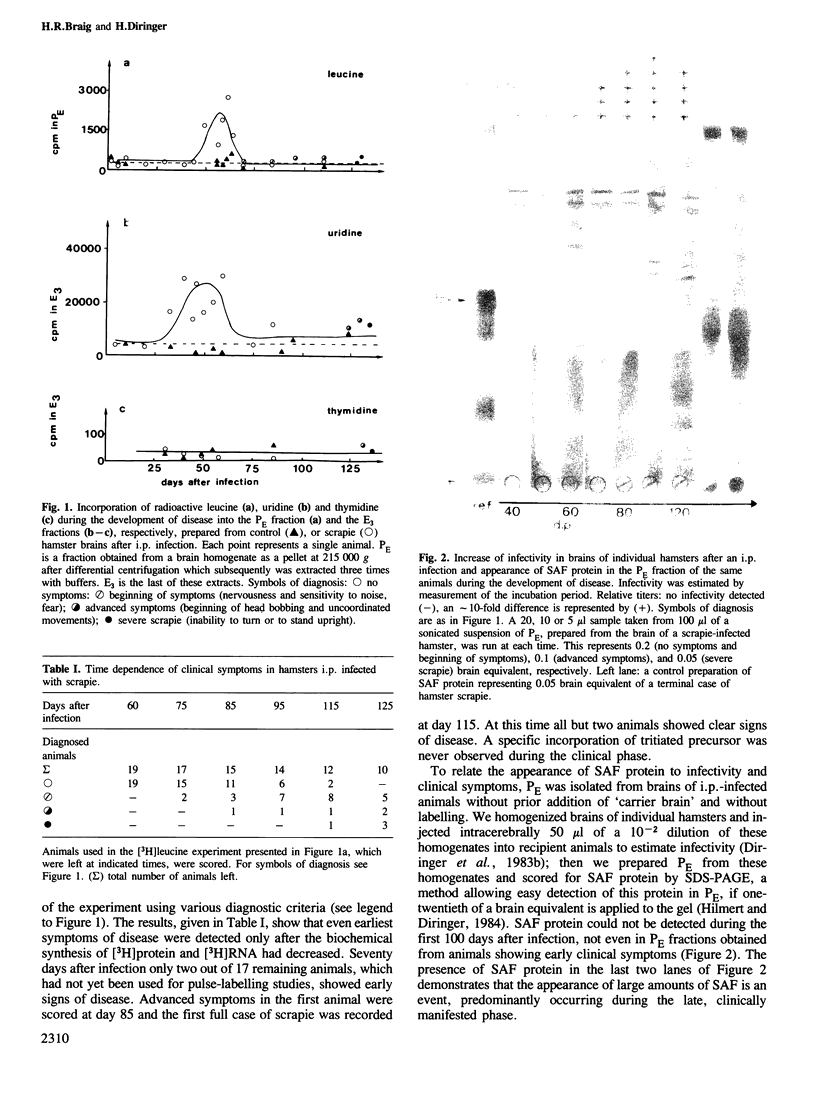
After an intraperitoneal infection disease-specific incorporation of [3H]leucine into protein and [3H]uridine into RNA in the brain precede clinical scrapie in hamsters. Onset of both incorporations are the earliest measurable events in the disease. Infectivity and subsequent clinical symptoms appear only after this biochemical activity has ceased. The disease-specific [3H]protein co-purifies with scrapie-associated fibrils (SAF) and infectivity during differential centrifugation and buffer extraction. SDS-PAGE shows that the [3H]protein is not SAF protein but a protein with an apparently higher mol. wt. The [3H]RNA is metabolically stable and separates from SAF and the main portion of infectivity in the last step of the purification. The appearance of SAF-protein is a late event and correlates with severe clinical symptoms. SAF seems to be derived from a brain protein turning over slowly. Our data are consistent with early pre-clinical virus replication. In this case treatment aimed at suppressing virus replication in the clinical phase of the human Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is unlikely to produce any beneficial effect.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baringer J. R., Bowman K. A., Prusiner S. B. Replication of the scrapie agent in hamster brain precedes neuronal vacuolation. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1983 Sep;42(5):539–547. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198309000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendheim P. E., Barry R. A., DeArmond S. J., Stites D. P., Prusiner S. B. Antibodies to a scrapie prion protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):418–421. doi: 10.1038/310418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Identification of a protein that purifies with the scrapie prion. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1309–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.6815801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce M. E. Serial studies on the development of cerebral amyloidosis and vacuolar degeneration in murine scrapie. J Comp Pathol. 1981 Oct;91(4):589–597. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(81)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David A. S., Grant R., Ballantyne J. P. Unsuccessful treatment of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with acyclovir. Lancet. 1984 Mar 3;1(8375):512–513. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92880-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Gelderblom H., Hilmert H., Ozel M., Edelbluth C., Kimberlin R. H. Scrapie infectivity, fibrils and low molecular weight protein. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):476–478. doi: 10.1038/306476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Hilmert H., Simon D., Werner E., Ehlers B. Towards purification of the scrapie agent. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 15;134(3):555–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Kimberlin R. H. Infectious scrapie agent is apparently not as small as recent claims suggest. Biosci Rep. 1983 Jun;3(6):563–568. doi: 10.1007/BF01120701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Rahn H. C., Bode L. Antibodies to protein of scrapie-associated fibrils. Lancet. 1984 Aug 11;2(8398):345–345. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92708-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H. Sustained viremia in experimental hamster scrapie. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1984;82(1-2):105–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01309373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund C. M., Kennedy R. C., Hadlow W. J. Pathogenesis of scrapie virus infection in the mouse. J Infect Dis. 1967 Feb;117(1):15–22. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser H., Bruce M. Argyrophilic plaques in mice inoculated with scrapie from particular sources. Lancet. 1973 Mar 17;1(7803):617–618. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90775-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis. The beta-fibrilloses (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1283–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilmert H., Diringer H. A rapid and efficient method to enrich SAF-protein from scrapie brains of hamsters. Biosci Rep. 1984 Feb;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1007/BF01120313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H., Walker C. Characteristics of a short incubation model of scrapie in the golden hamster. J Gen Virol. 1977 Feb;34(2):295–304. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Rohwer R. G., Kascsak R., Wisniewski H. M., Somerville R. A., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Infection-specific particle from the unconventional slow virus diseases. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):437–440. doi: 10.1126/science.6377496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Somerville R. A., Wisniewski H. M., Iqbal K. Abnormal fibrils from scrapie-infected brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;54(1):63–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00691333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Somerville R. A., Wisniewski H. M., Manuelidis L., Manuelidis E. E. Scrapie-associated fibrils in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):474–476. doi: 10.1038/306474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman P. K. Acyclovir in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet. 1984 Apr 7;1(8380):793–793. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91302-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Groth D. F., Glenner G. G. Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):136–144. doi: 10.1126/science.6801762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H. M., Bruce M. E., Fraser H. Infectious etiology of neuritic (senile) plaques in mice. Science. 1975 Dec 12;190(4219):1108–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.1237933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]