Abstract
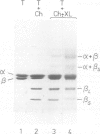
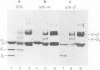
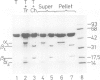
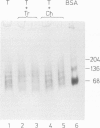
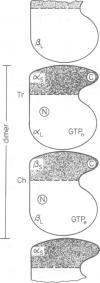
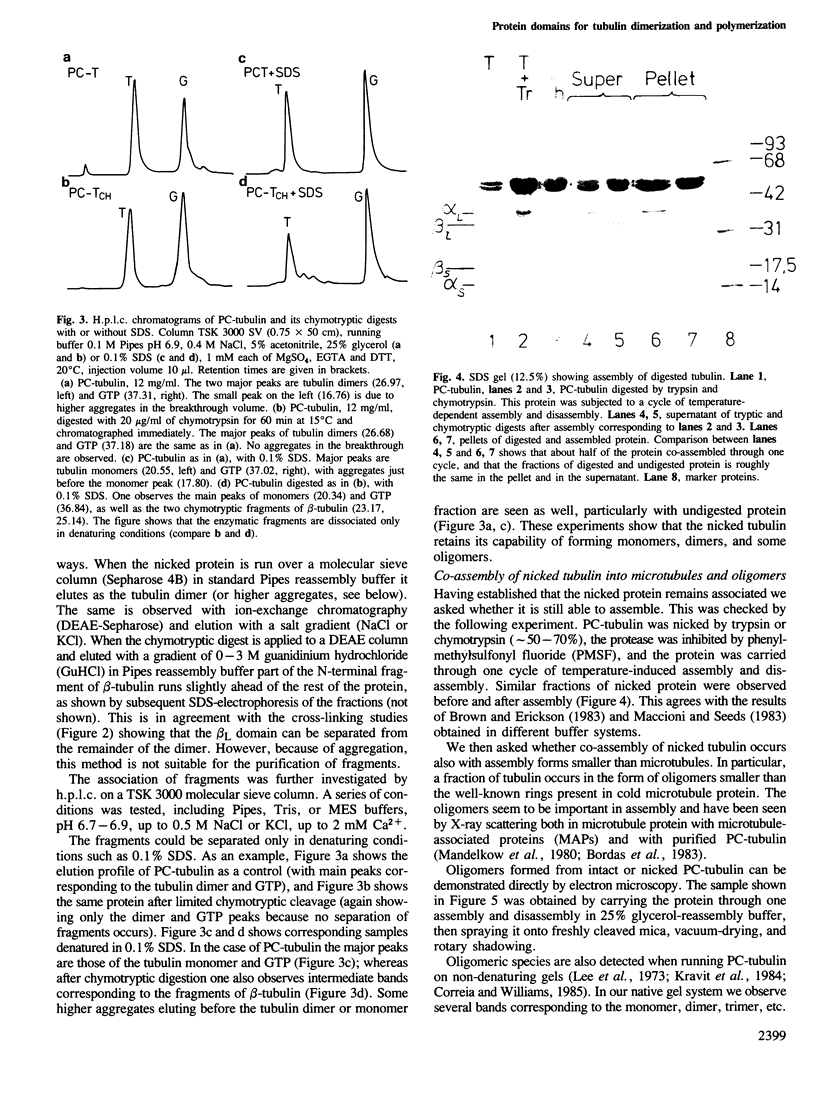
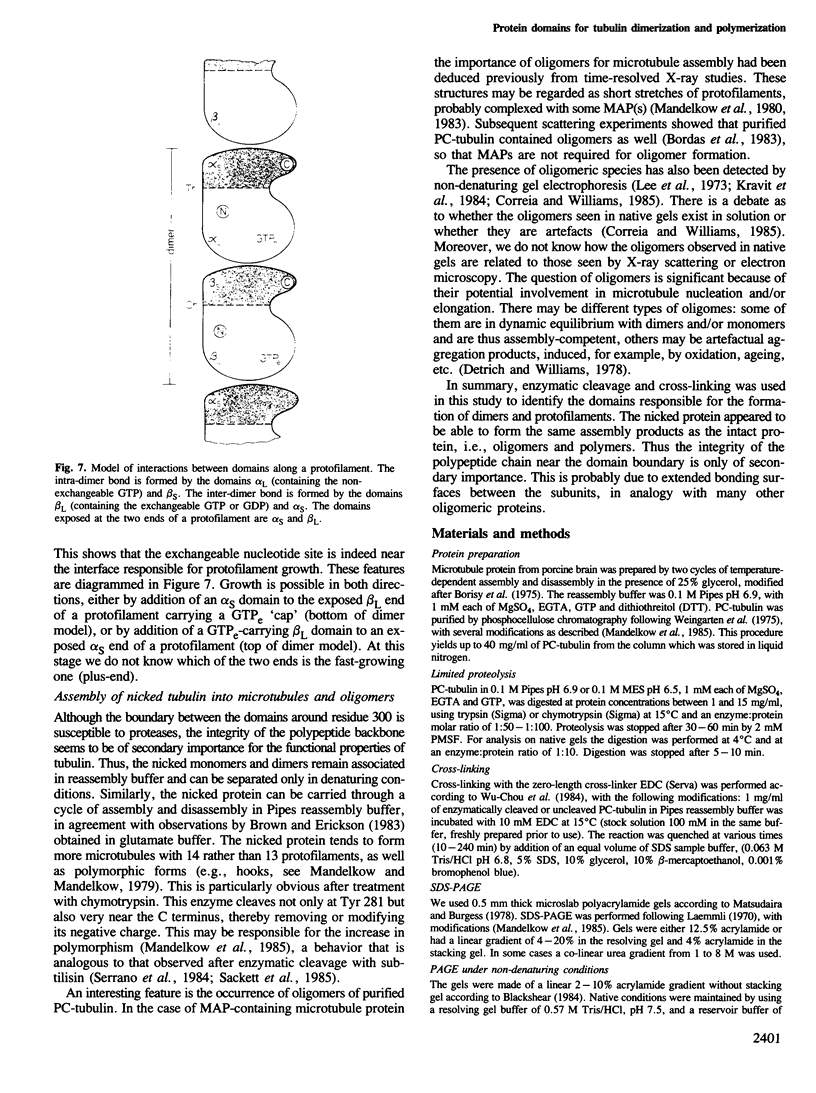
The protein domains responsible for the dimerization and polymerization of tubulin have been determined using chemical cross-linking and limited proteolysis. The intra-dimer bond is formed by the N-terminal domain of alpha-tubulin and the C-terminal domain of beta-tubulin. Conversely, the inter-dimer bond along protofilaments is formed by the N-terminal domain of beta-tubulin (carrying the exchangeable GTP) and the C-terminal domain of alpha-tubulin. The domains of proteolytically cleaved tubulin remain tightly associated in solution. Apart from the monomer, tubulin shows three levels of assembly: the dimer, oligomer and polymer. Several oligomeric species can be visualized by electron microscopy of rotary shadowed phosphocellulose-tubulin, h.p.l.c. and non-denaturing gel electrophoresis. Tubulin's capacity to form the higher level aggregates is not destroyed by enzymatic nicking.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bittner M., Kupferer P., Morris C. F. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins and nucleic acids from slab gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or nitrocellulose sheets. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J. Systems for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:237–255. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordas J., Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E. Stages of tubulin assembly and disassembly studied by time-resolved synchrotron X-ray scattering. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 15;164(1):89–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisy G. G., Marcum J. M., Olmsted J. B., Murphy D. B., Johnson K. A. Purification of tubulin and associated high molecular weight proteins from porcine brain and characterization of microtubule assembly in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:107–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. R., Erickson H. P. Assembly of proteolytically cleaved tubulin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jan;220(1):46–51. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90385-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correia J. J., Williams R. C., Jr Characterization of oligomers of tubulin by two-dimensional native electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 May 15;239(1):120–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90818-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detrich H. W., 3rd, Williams R. C. Reversible dissociation of the alpha beta dimer of tubulin from bovine brain. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):3900–3907. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott A., Offer G. Shape and flexibility of the myosin molecule. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 25;123(4):505–519. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geahlen R. L., Haley B. E. Interactions of a photoaffinity analog of GTP with the proteins of microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4375–4377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J., Maruta H., Isenberg G. Monoclonal antibodies localize the exchangeable GTP-binding site in beta- and not alpha-tubulins. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 1;179(1):91–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M., Smith H., Taylor E. W. Tublin: nucleotide binding and enzymic activity. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 5;89(3):455–468. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90475-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kravit N. G., Regula C. S., Berlin R. D. A reevaluation of the structure of purified tubulin in solution: evidence for the prevalence of oligomers over dimers at room temperature. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):188–198. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Frigon R. P., Timasheff S. N. The chemical characterization of calf brain microtubule protein subunits. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7253–7262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maccioni R. B., Seeds N. W. Limited proteolysis of tubulin: nucleotide stabilizes an active conformation. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1567–1572. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Harmsen A., Mandelkow E., Bordas J. X-ray kinetic studies of microtubule assembly using synchrotron radiation. Nature. 1980 Oct 16;287(5783):595–599. doi: 10.1038/287595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Herrmann M., Rühl U. Tubulin domains probed by limited proteolysis and subunit-specific antibodies. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):311–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90406-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E. Junctions between microtubule walls. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E., Mandelkow E. M., Bordas J. Structure of tubulin rings studied by X-ray scattering using synchrotron radiation. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):179–196. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. T., Burgess D. R. SDS microslab linear gradient polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jul 1;87(2):386–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90688-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Bertrand R., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Structure of the actin-myosin interface. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):301–306. doi: 10.1038/292301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath J. P., Eagle G. R., Himes R. H. Direct photoaffinity labeling of tubulin with guanosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1555–1560. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackett D. L., Bhattacharyya B., Wolff J. Tubulin subunit carboxyl termini determine polymerization efficiency. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):43–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano L., de la Torre J., Maccioni R. B., Avila J. Involvement of the carboxyl-terminal domain of tubulin in the regulation of its assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5989–5993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Chou S., Robinson A. E., Hrabeta E., Packer L. Cross-linking of bacteriorhodopsin using specific carboxyl modifications and proteolytic cleavage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91591-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]