Abstract
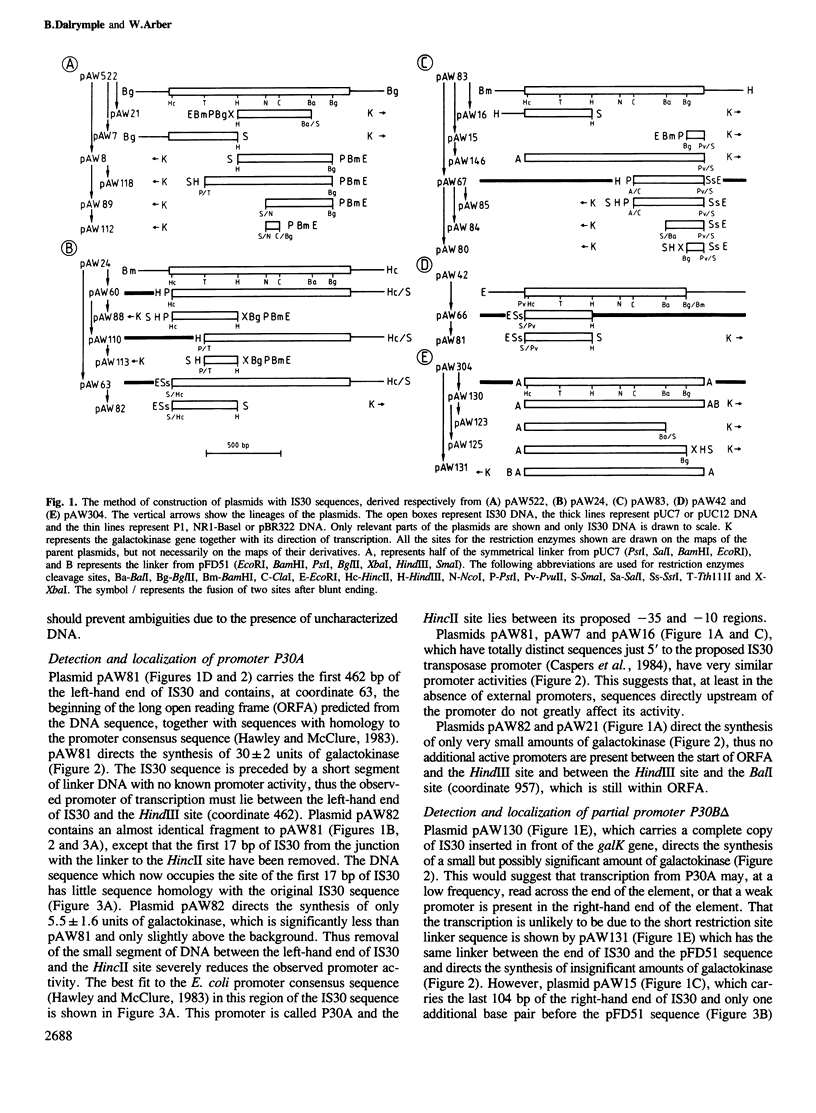
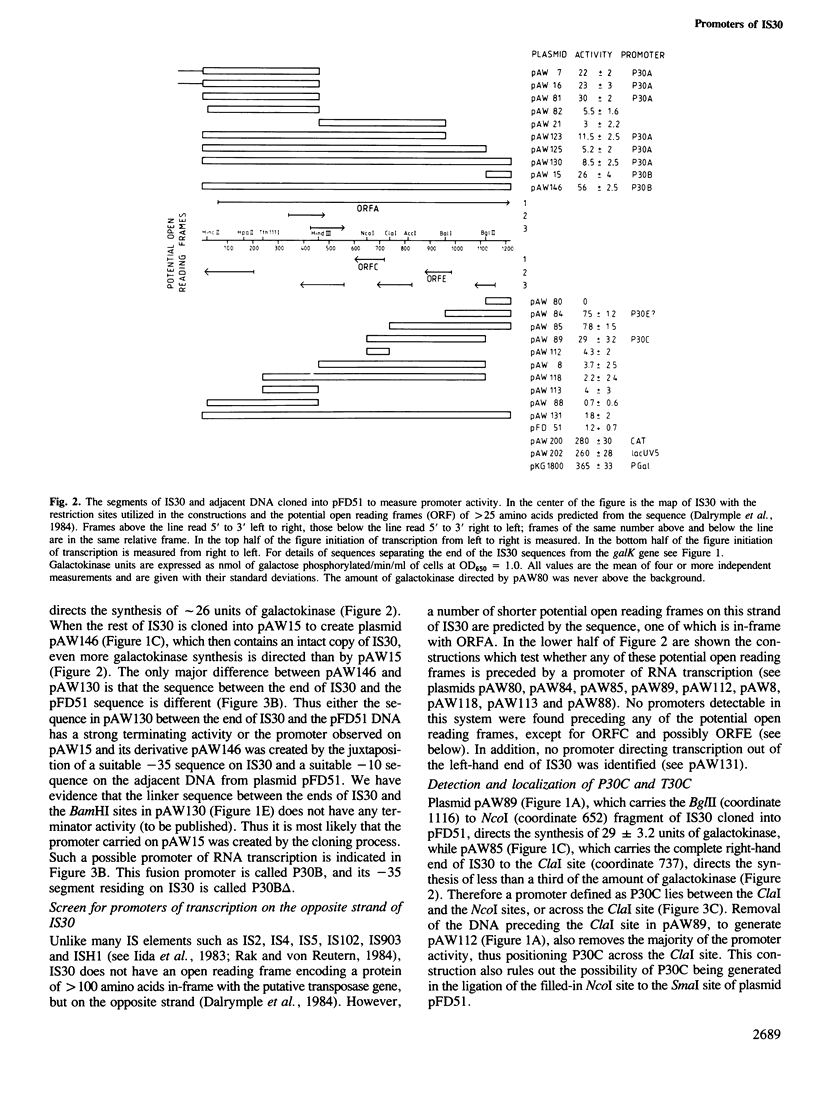
Two promoters of RNA transcription have been identified on IS30 by an in vivo assay, in which various DNA fragments with IS30 sequences were inserted in front of the promoterless galK gene of plasmid pFD51. Both promoters have a similar activity of approximately 10% of the activity of the lacUV5 promoter. Promoter P30A precedes the long open reading frame (ORFA), and its proposed -35 region lies within the left-hand terminal inverted repeat of IS30. However, the apparent activity of promoter P30A is significantly reduced when measured in the 3' region of ORFA. Thus, either the activity of promoter P30A is controlled by an IS30-encoded product from the same element, or some termination of transcription from P30A occurs within the coding region of ORFA. Promoter P30C precedes a short open reading frame (ORFC) in-frame with ORFA, but in the opposite strand. Reading frame ORFC is closely followed by a terminator of RNA transcription, T30C. None of the other potential open reading frames predicted from the DNA sequence, with one possible exception, are preceded by a promoter of RNA transcription active in the assay. No significant transcription was detected out of the left-hand end of the complete element. However, a small amount, probably due to read-through from promoter P30A, was detected out of the right-hand end of a complete copy of IS30. In addition the right-hand end of IS30 has been shown to have the potential to create promoters by insertion.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arber W., Iida S., Jütte H., Caspers P., Meyer J., Hänni C. Rearrangements of genetic material in Escherichia coli as observed on the bacteriophage P1 plasmid. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1197–1208. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Smith D. M. Conformational change in the DNA associated with an unusual promoter mutation in a tRNA operon of Salmonella. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):643–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90471-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bräu B., Pilz U., Piepersberg W. Genes for gentamicin-(3)-N-acetyltransferases III and IV: I. Nucleotide sequence of the AAC(3)-IV gene and possible involvement of an IS140 element in its expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(1):179–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00327434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspers P., Dalrymple B., Iida S., Arber W. IS30, a new insertion sequence of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(1):68–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00334094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. T., Lebowitz J. Mapping of RNA polymerase binding sites in R12 derived plasmids carrying the replication-incompatibility region and the insertion element IS1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7295–7311. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlier D., Piette J., Glansdorff N. IS3 can function as a mobile promoter in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5935–5948. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple B., Caspers P., Arber W. Nucleotide sequence of the prokaryotic mobile genetic element IS30. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2145–2149. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02104.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debouck C., Riccio A., Schumperli D., McKenney K., Jeffers J., Hughes C., Rosenberg M., Heusterspreute M., Brunel F., Davison J. Structure of the galactokinase gene of Escherichia coli, the last (?) gene of the gal operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1841–1853. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glansdorff N., Charlier D., Zafarullah M. Activation of gene expression by IS2 and IS3. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):153–156. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton D. M., Musso R. E. Specific in vitro transcription of the insertion sequence IS2. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):53–81. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton D. M., Musso R. E. Transcription initiation sites within an IS2 insertion in a Gal-constitutive mutant of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):5015–5031. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.5015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Normark S. Insertion of IS2 creates a novel ampC promoter in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):809–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Reznikoff W. S. Localization of the Tn5 transposase promoter using the cycling reaction of RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1873–1883. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Morisato D., Roberts D., Bender J. Mechanism and regulation of Tn10 transposition. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:235–244. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida C., Machida Y., Ohtsubo E. Both inverted repeat sequences located at the ends of IS1 provide promoter functions. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 5;177(2):247–267. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90455-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney K., Shimatake H., Court D., Schmeissner U., Brady C., Rosenberg M. A system to study promoter and terminator signals recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:383–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rak B., Lusky M., Hable M. Expression of two proteins from overlapping and oppositely oriented genes on transposable DNA insertion element IS5. Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):124–128. doi: 10.1038/297124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rak B., von Reutern M. Insertion element IS5 contains a third gene. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):807–811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01889.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Chepelinsky A. B., McKenney K. Studying promoters and terminators by gene fusion. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):734–739. doi: 10.1126/science.6356355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. Purification of genomic sequences from bacteriophage libraries by recombination and selection in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2427–2445. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Hoopes B. C., McClure W. R., Kleckner N. Three promoters near the termini of IS10: pIN, pOUT, and pIII. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90400-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Kleckner N. Translational control of IS10 transposition. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):683–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmerman K. P., Tu C. P. Complete sequence of IS3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2127–2139. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Lamond A. I., Mace H. A., Berman M. L. RNA polymerase interactions with the upstream region of the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90229-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



