Abstract
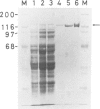
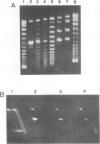
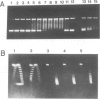
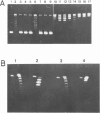
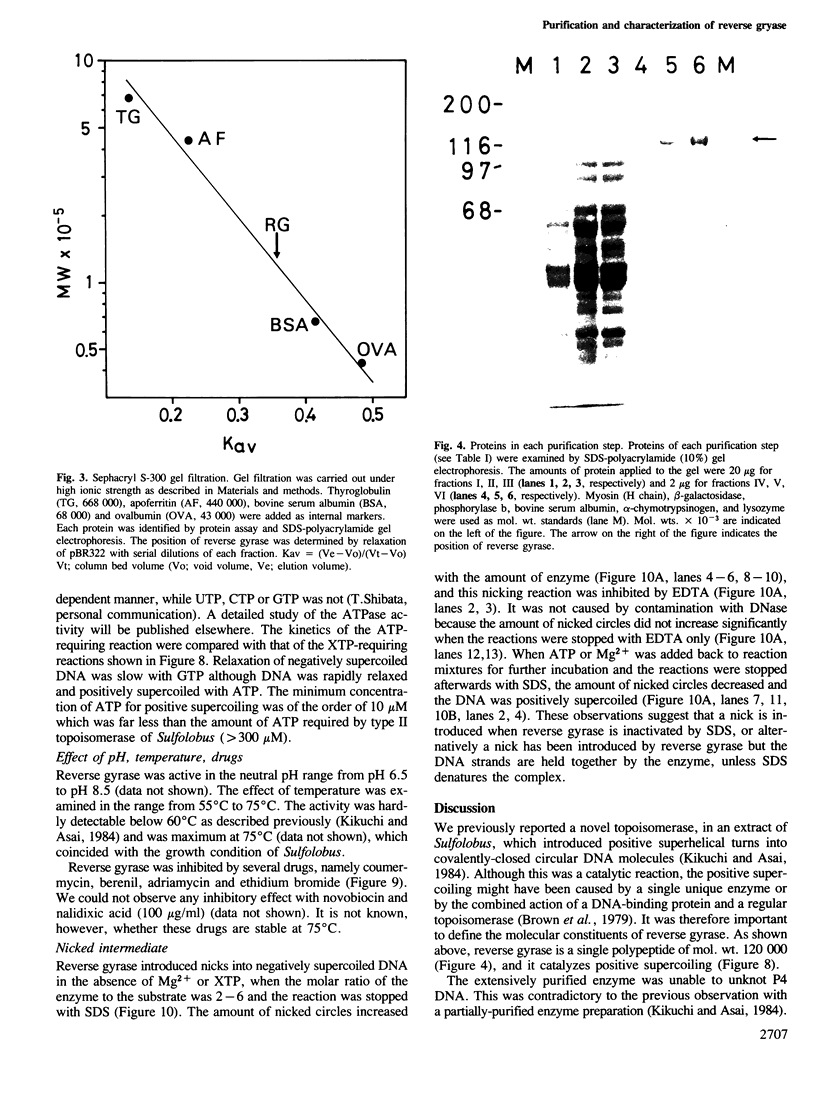
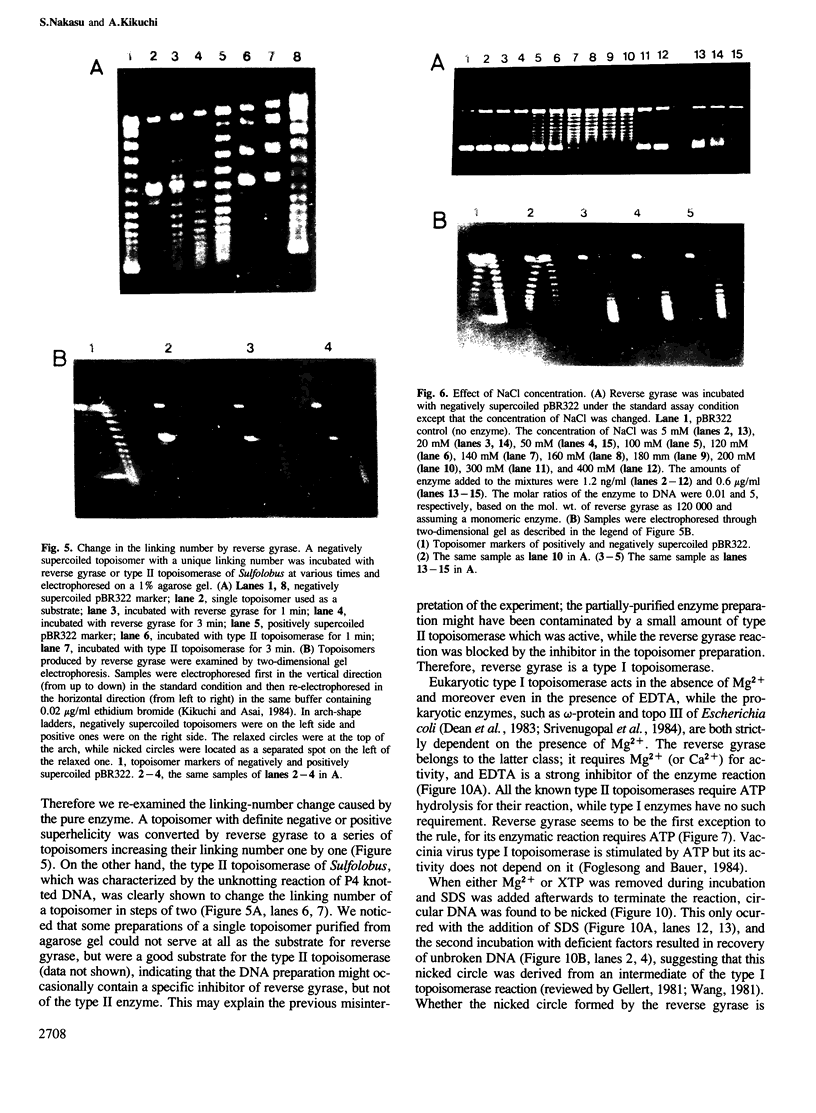
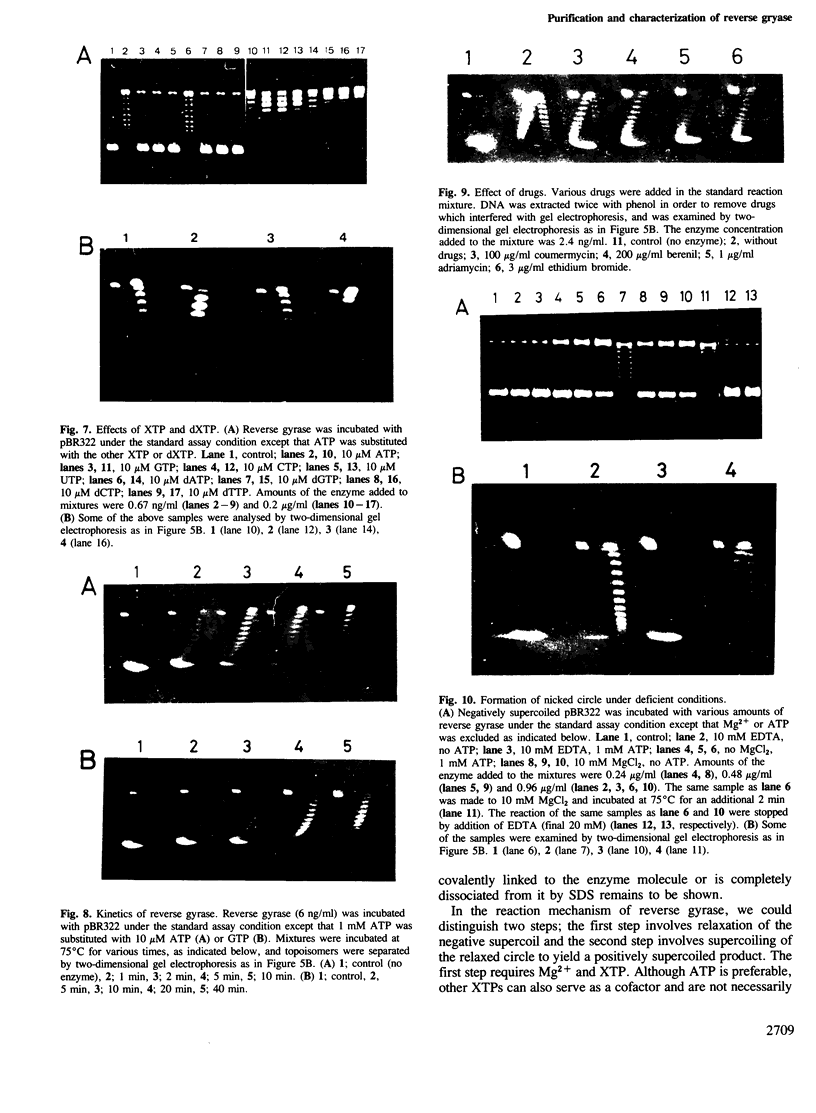
Reverse gyrase, a topoisomerase which introduces positive superhelical turns into DNA, has been purified from Sulfolobus to near homogeneity. It is a single polypeptide with a mol. wt. of 120 000 as determined by denaturing gel electrophoresis. Contrary to a previous report, it is a type I topoisomerase as judged by the linking-number change of closed circular DNA topoisomer. Unlike other known type I topoisomerases, ATP or dATP is required for introducing positive superhelical turns. In order to relax negatively supercoiled DNA, other nucleotide triphosphates (XTP) are also effective with low efficiency. In the absence of either XTP or divalent cations, the enzyme introduces nicks into closed circular DNA when the reaction is stopped by SDS. This suggests that reverse gyrase cuts one of the two strands of DNA in the course of its enzymatic reaction.
Keywords: ATP requirement, nicked intermediate, positive supercoiling, Sulfolobus, type I topoisomerase
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Cozzarelli N. R. A sign inversion mechanism for enzymatic supercoiling of DNA. Science. 1979 Nov 30;206(4422):1081–1083. doi: 10.1126/science.227059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Peebles C. L., Cozzarelli N. R. A topoisomerase from Escherichia coli related to DNA gyrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6110–6114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R. DNA gyrase and the supercoiling of DNA. Science. 1980 Feb 29;207(4434):953–960. doi: 10.1126/science.6243420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F., Krasnow M. A., Otter R., Matzuk M. M., Spengler S. J., Cozzarelli N. R. Escherichia coli type-1 topoisomerases: identification, mechanism, and role in recombination. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):769–777. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Biology of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid topoisomerases. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):273–289. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.273-289.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foglesong P. D., Bauer W. R. Effects of ATP and inhibitory factors on the activity of vaccinia virus type I topoisomerase. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.1-8.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto T., Wang J. C. Yeast DNA topoisomerase II. An ATP-dependent type II topoisomerase that catalyzes the catenation, decatenation, unknotting, and relaxation of double-stranded DNA rings. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5866–5872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Asai K. Reverse gyrase--a topoisomerase which introduces positive superhelical turns into DNA. Nature. 1984 Jun 21;309(5970):677–681. doi: 10.1038/309677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Davis J. L., Calendar R. Novel topologically knotted DNA from bacteriophage P4 capsids: studies with DNA topoisomerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3979–3989. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Micrococcus luteus DNA gyrase: active components and a model for its supercoiling of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2098–2102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivenugopal K. S., Lockshon D., Morris D. R. Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase III: purification and characterization of a new type I enzyme. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 24;23(9):1899–1906. doi: 10.1021/bi00304a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]