Abstract
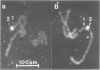
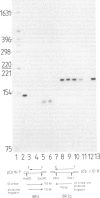
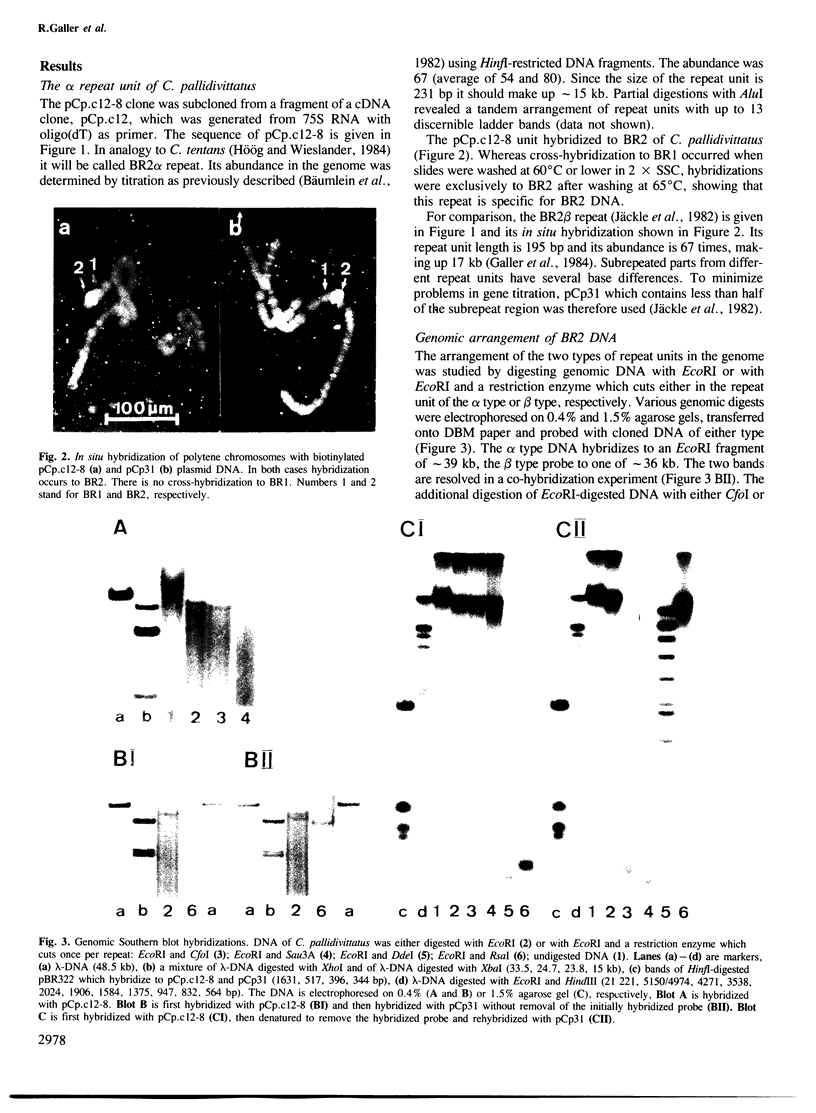
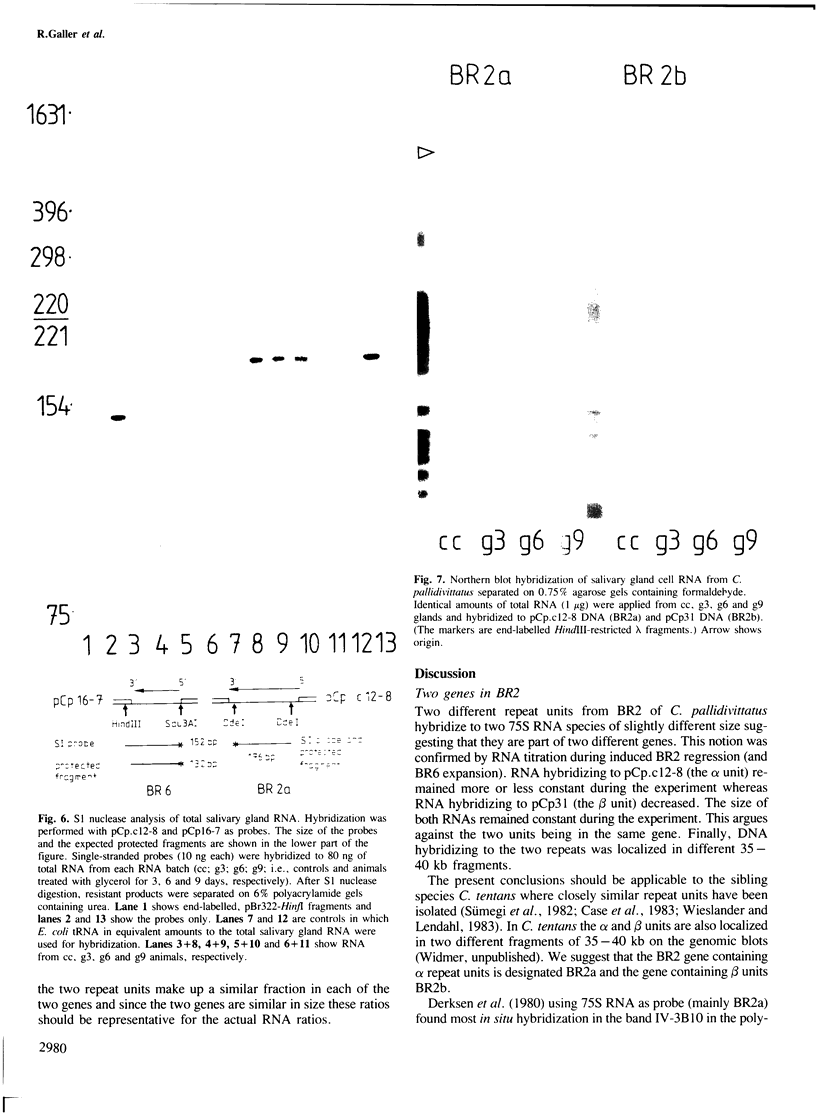
Balbiani ring 2 (BR2) in salivary glands of Chironomus pallidivittatus and C. tentans (two sibling species of the subgenus Camptochironomus) is a favoured model system for studies of gene organization and transcript formation. Here we show that BR2 is more complex than hitherto believed, containing two 75S RNA-producing genes, BR2a and BR2b, present in different 35–40 kb blocks of DNA. The transcripts hybridizing to two different repeat units originating in BR2 differ in size. Further support for the presence of two genes comes from RNA studies during experimentally induced BR2 regression. The amounts of BR2a RNA per cell remain more or less constant throughout the course of the experiment, whereas the BR2b RNA decreases considerably. Under normal conditions there is 5–6 times more BR2a RNA than BR2b RNA. This ratio increases ˜3-fold under experimental conditions. BR2a and BR2b, although partially homologous, contain repeat units with characteristic differences. BR2a contains a repeat unit that is much more similar to a BR1 repeat than it is to the BR2b repeat. The possibility is discussed that a Balbiani ring in general represents an integrated set of active genes rather than a singe gene.
Keywords: Balbianbi ring, Chironomus, gene structure, giant transcript, repetitive sequences
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beermann W. Directed changes in the pattern of Balbiani ring puffing in Chironomus: effects of a sugar treatment. Chromosoma. 1973;41(3):297–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00344024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case S. T., Daneholt B. The size of the transcription unit in Balbiani ring 2 of Chironomus tentans as derived from analysis of the primary transcript and 75 S RNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):223–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case S. T., Summers R. L., Jones A. G. A variant tandemly repeated nucleotide sequence in Balbiani ring 2 of Chironomus tentans. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):555–562. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90436-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneholt B., Anderson K., Fagerlind M. Large-sized polysomes in Chironomus tentans salivary glands and their relation to Balbiani ring 75S RNA. J Cell Biol. 1977 Apr;73(1):149–160. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneholt B., Edström J. E., Egyházi E., Lambert B., Ringborg U. RNA synthesis in a Balbiani ring in Chironomus tentans salivary gland cells. Chromosoma. 1969;28(4):418–429. doi: 10.1007/BF00284258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneholt B. Giant RNA transcript in a Balbiani ring. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 20;240(103):229–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio240229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneholt B., Hosick H. Evidence for transport of 75S RNA from a discrete chromosome region via nuclear sap to cytoplasm in Chironomus tentans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen J., Wieslander L., van der Ploeg M., Daneholt B. Identification of the Balbiani ring 2 chromomere and determination of the content and compaction of its DNA. Chromosoma. 1980;81(1):65–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00292423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström J. E., Rydlander L., Francke C. Concomitant induction of a Balbiani ring and a giant secretory protein in Chironomus salivary glands. Chromosoma. 1980;81(1):115–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00292426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström J. E., Sierakowska H., Burvall K. Dependence of Balbiani ring induction in Chironomus salivary glands on inorganic phosphate. Dev Biol. 1982 May;91(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galler R., Rydlander L., Riedel N., Kluding H., Edström J. E. Balbiani ring induction in phosphate metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1448–1452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hög C., Wieslander L. Different evolutionary behavior of structurally related, repetitive sequences occurring in the same Balbiani ring gene in Chironomus tentans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5165–5169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäckle H., Almeida J. C., Galler R., Kluding H., Lehrach H., Edström J. E. Constant and variable parts in the Balbiani ring 2 repeat unit and the translation termination region. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):883–888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb M. M., Daneholt B. Characterization of active transcription units in Balbiani rings of Chironomus tentans. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):835–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert B. Tracing of RNA from a puff in the polytene chromosomes to the cytoplasm in Chironomus tentans salivary gland cells. Nature. 1973 Mar 2;242(5392):51–53. doi: 10.1038/242051a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer-Safer P. R., Levine M., Ward D. C. Immunological method for mapping genes on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PELLING C. RIBONUKLEINSAEURE-SYNTHESE DER RIESENCHROMOSOMEN. AUTORADIOGRAPHISCHE UNTERSUCHUNGEN AN CHIRONOMUS TENTANS. Chromosoma. 1964 Apr 1;15:71–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00326915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydlander L., Edström J. E. Large sized nascent protein as dominating component during protein synthesis in Chironomus salivary glands. Chromosoma. 1980;81(1):85–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00292424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydlander L., Pigon A., Edström J. E. Sequences translated by Balbiani ring 75S RNA in vitro are present in giant secretory protein from Chironomus tentans. Chromosoma. 1980;81(1):101–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00292425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiga H., Edström J. E. Long tandem arrays of complex repeat units in Chironomus telomeres. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):799–804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sümegi J., Wieslander L., Daneholt B. A hierarchic arrangement of the repetitive sequences in the Balbiani ring 2 gene of Chironomus tentans. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer R. M., Lucchini R., Lezzi M., Meyer B., Sogo J. M., Edström J. E., Koller T. Chromatin structure of a hyperactive secretory protein gene (in Balbiani ring 2) of Chironomus. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1635–1641. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L., Lendahl U. The Balbiani ring 2 gene in Chironomus tentans is built from two types of tandemly arranged major repeat units with a common evolutionary origin. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1169–1175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L. Number and structure of Balbiani ring 75 S RNA transcription units in Chironomus tentans. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):347–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]