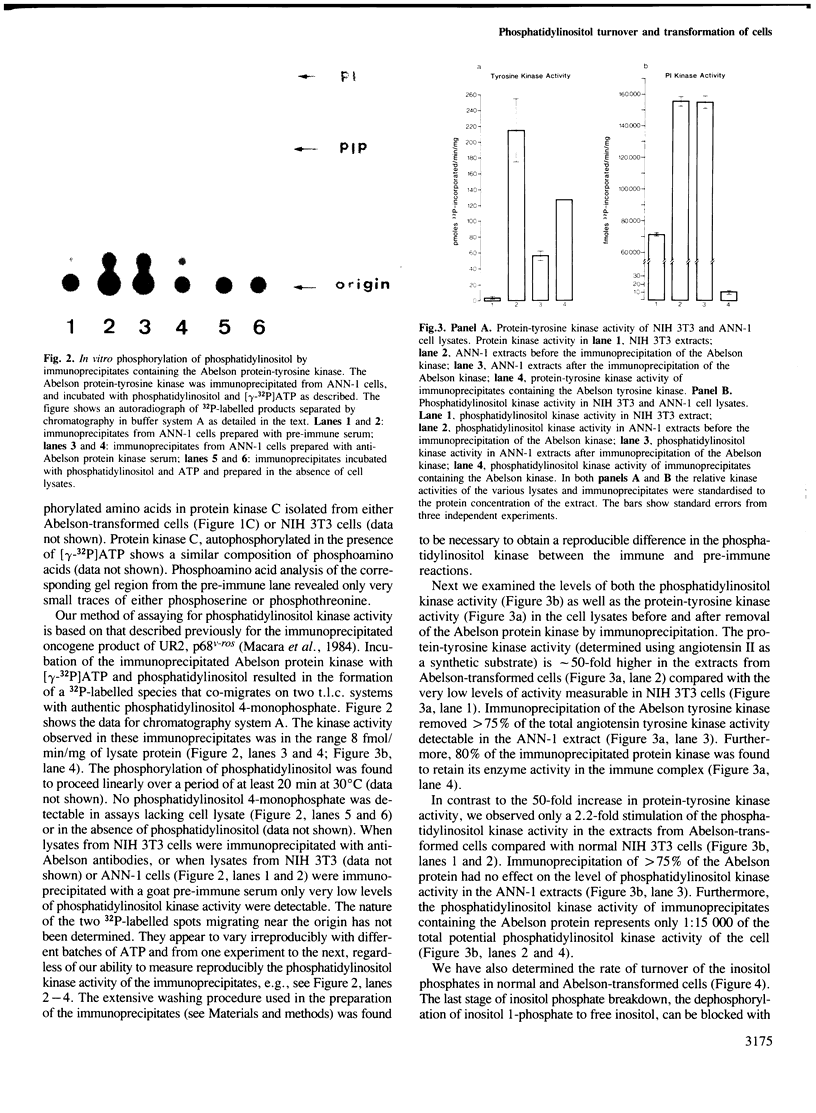
Abstract
The transforming protein of the Abelson murine leukaemia virus encodes a protein-tyrosine kinase. Previously, we have shown that in Abelson-transformed cells, the Abelson kinase regulates the phosphoserine content of ribosomal protein S6. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (TPA), which activates protein kinase C, induces the phosphorylation of S6 at the same five phosphopeptides as found in S6 isolated from Abelson-transformed cells. We have investigated three models whereby the Abelson kinase might regulate S6 phosphorylation via the activation of protein kinase C. First, the Abelson kinase could phosphorylate protein kinase C on tyrosine. However, we do not detect significant amounts of phosphotyrosine in protein kinase C in vivo. Second, it has been suggested that protein-tyrosine kinases might phosphorylate phosphatidylinositol. This could increase the intracellular levels of diacylglycerol and thereby activate protein kinase C. Our data strongly suggest that direct phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol by the Abelson protein-tyrosine kinase has no physiological role. Third, an indirect activation of protein kinase C may occur via an increase in the rate of phosphoinositide breakdown. We have found that phosphoinositide breakdown appears to be constitutively activated in Abelson-transformed cells. The implications of these observations are discussed with regard to S6 phosphorylation and the mechanism of Abelson-induced transformation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. H., Blisner M. E., Holland W. H., Hipps P. P., Sherman W. R. Increased brain myo-inositol 1-phosphate in lithium-treated rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 26;71(2):664–670. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90839-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison J. H., Blisner M. E. Inhibition of the effect of lithium on brain inositol by atropine and scopolamine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 23;68(4):1332–1338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Blay J., Irvine R. F., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. Reduction of epidermal growth factor receptor affinity by heterologous ligands: evidence for a mechanism involving the breakdown of phosphoinositides and the activation of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 30;123(1):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Identification and characterization of cellular targets for tyrosine protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1108–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Regulation of cell growth and transformation by tyrosine-specific protein kinases: the search for important cellular substrate proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;107:125–161. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69075-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in avian sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4112–4115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Friis R. R. Changes in phosphatidylinositol metabolism correlated to growth state of normal and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed Japanese quail cells. Cancer Res. 1977 Sep;37(9):2979–2984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Michell R. H. The polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1980133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Wusteman M. M. Breakdown of polyphosphoinositides and not phosphatidylinositol accounts for muscarinic agonist-stimulated inositol phospholipid metabolism in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):633–640. doi: 10.1042/bj2160633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., McConkey E. H. Preferential utilization of phosphorylated 40-S ribosomal subunits during initiation complex formation. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):535–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Heldin C. H. Characterization of a tyrosine-specific kinase activity in human fibroblast membranes stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10486–10492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Westermark B., Wasteson A., Heldin C. H. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific phosphorylation by platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):419–420. doi: 10.1038/295419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes J. G., Chow M., Gorka C., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Baltimore D. Purification and characterization of a protein-tyrosine kinase encoded by the Abelson murine leukemia virus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8070–8077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes J. G. Phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatases. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;107:163–180. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69075-4_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V. Heat shock induces rapid dephosphorylation of a ribosomal protein in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht A. J., Glomset J. A., King W. C., Nist C., Mitchell C. D., Ross R. Early changes in phosphatidylinositol and arachidonic acid metabolism in quiescent swiss 3T3 cells stimulated to divide by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12329–12335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbacher G. K., Humbel R. E., Thomas G. Insulin-like growth factor: insulin or serum increase phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during transition of stationary chick embryo fibroblasts into early G1 phase of the cell cycle. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 1;100(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Brown K. D., Berridge M. J. Specificity of inositol trisphosphate-induced calcium release from permeabilized Swiss-mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):269–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2220269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blith D. L., Karlsson F. A., Häring H. U., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulation of phosphorylation of the beta subunit of the insulin receptor. Formation of both phosphoserine and phosphotyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):9891–9894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Peuch C. J., Ballester R., Rosen O. M. Purified rat brain calcium- and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6858–6862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G., Marinetti G. V., Balduzzi P. C. Transforming protein of avian sarcoma virus UR2 is associated with phosphatidylinositol kinase activity: possible role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2728–2732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Foulkes J. G., Erikson E., Baltimore D. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 on serine after microinjection of the Abelson murine leukemia virus tyrosine-specific protein kinase into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):272–276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 30;156(1):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Kikkawa U., Kaibuchi K. Phospholipid turnover in hormone action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1984;40:301–345. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571140-1.50012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Katan M., Waterfield M. D., Leader D. P. The phosphorylation of eukaryotic ribosomal protein S6 by protein kinase C. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):579–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Stabel S., Waterfield M. D. Purification to homogeneity of protein kinase C from bovine brain--identity with the phorbol ester receptor. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):953–959. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebecchi M. J., Gershengorn M. C. Thyroliberin stimulates rapid hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate by a phosphodiesterase in rat mammotropic pituitary cells. Evidence for an early Ca2+-independent action. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 15;216(2):287–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2160287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. B., Shia M. A., Pilch P. F. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific phosphorylation in vitro by insulin-like growth factor I. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):438–440. doi: 10.1038/305438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D., Siegler R. Direct transformation of 3T3 cells by Abelson murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1975 Feb 27;253(5494):729–731. doi: 10.1038/253729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Whitman M., Cantley L. C., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swergold G. D., Rosen O. M., Rubin C. S. Hormonal regulation of the phosphorylation of ATP citrate lyase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Effects of insulin and isoproterenol. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4207–4215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Otto A. M. The effect of serum, EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin on S6 phosphorylation and the initiation of protein and DNA synthesis. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevillyan J. M., Kulkarni R. K., Byus C. V. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters stimulate the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in quiescent Reuber H35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):897–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D. R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):239–242. doi: 10.1038/315239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]