Abstract
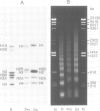
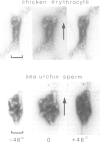
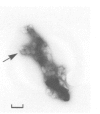
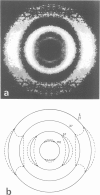
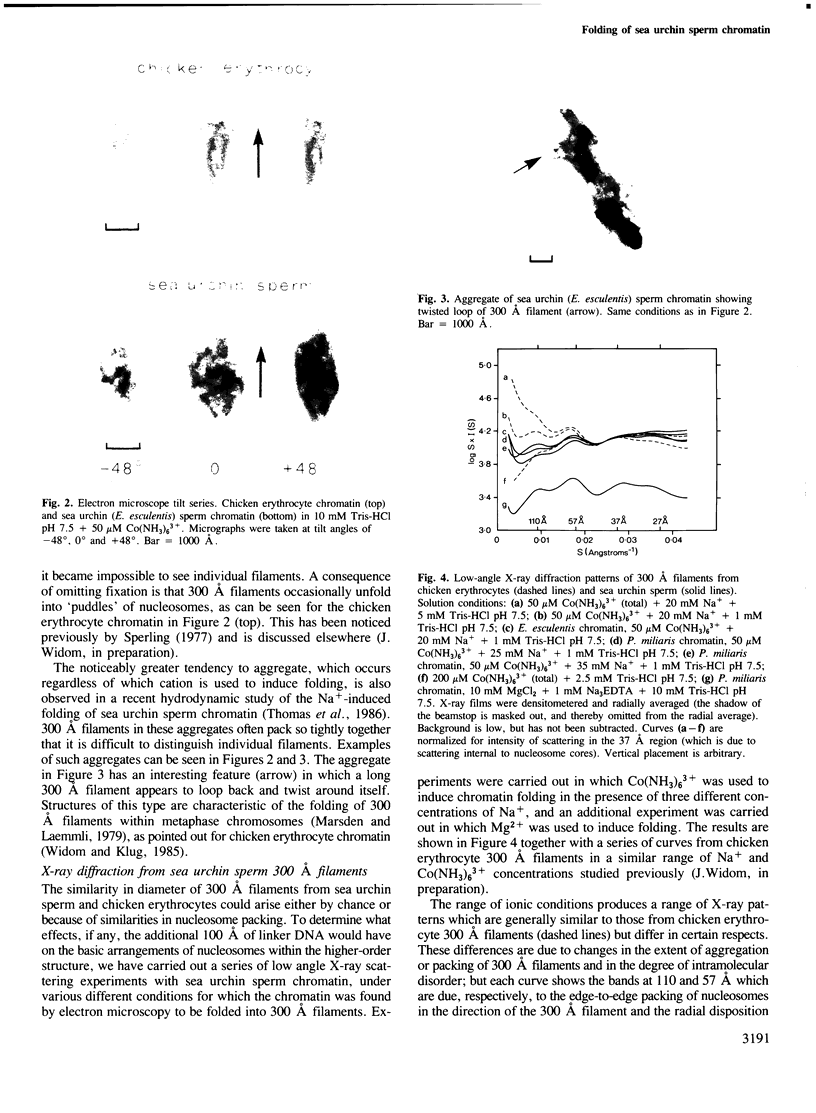
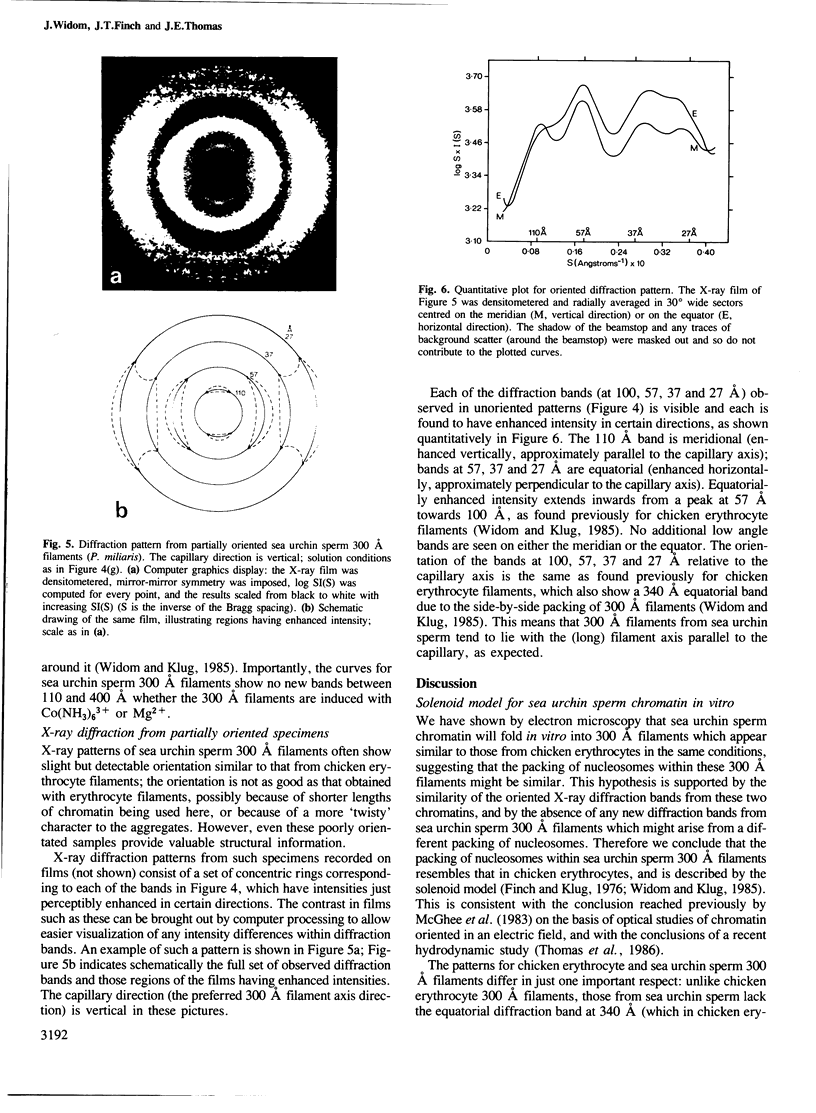
The higher-order structure of chromatin isolated from sea urchin sperm, which has a long nucleosomal DNA repeat length (approximately 240 bp), has been studied by electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. Electron micrographs show that this chromatin forms 300 A filaments which are indistinguishable from those of chicken erythrocytes (approximately 212 bp repeat); X-ray diffraction patterns from partially oriented samples show that the edge-to-edge packing of nucleosomes in the direction of the 300 A filament axis, and the radial disposition of nucleosomes around it, are both similar to those of the chicken erythrocyte 300 A filament, which is described by the solenoid model. The invariance of the structure with increased linker DNA length is inconsistent with many other models proposed for the 300 A filament and, furthermore, means that the linker DNA must be bent. The low-angle X-ray scattering in the 300-400 A region both in vitro and in vivo differs from that of chicken erythrocyte chromatin. The nature of the difference suggests that 300 A filaments in sea urchin sperm in vivo are packed so tightly together that electron-density contrast between individual filaments is lost; this is consistent with electron micrographs of the chromatin in vitro.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J., Rau D. C., Harborne N., Gould H. Higher order structure in a short repeat length chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1320–1327. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausio J., Borochov N., Seger D., Eisenberg H. Interaction of chromatin with NaCl and MgCl2. Solubility and binding studies, transition to and characterization of the higher-order structure. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 15;177(3):373–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90291-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. L., Butler P. J., Pearson E. C., Thomas J. O. Stability of the higher-order structure of chicken-erythrocyte chromatin in solution. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(3):469–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J. A defined structure of the 30 nm chromatin fibre which accommodates different nucleosomal repeat lengths. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2599–2604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J. The folding of chromatin. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;15(1):57–91. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J., Thomas J. O. Changes in chromatin folding in solution. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jul 15;140(4):505–529. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Klug A. Solenoidal model for superstructure in chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1897–1901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewish D. R., Burgoyne L. A. Chromatin sub-structure. The digestion of chromatin DNA at regularly spaced sites by a nuclear deoxyribonuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langmore J. P., Paulson J. R. Low angle x-ray diffraction studies of chromatin structure in vivo and in isolated nuclei and metaphase chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;96(4):1120–1131. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.4.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langmore J. P., Schutt C. The higher order structure of chicken erythrocyte chromosomes in vivo. Nature. 1980 Dec 11;288(5791):620–622. doi: 10.1038/288620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden M. P., Laemmli U. K. Metaphase chromosome structure: evidence for a radial loop model. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):849–858. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G., Rau D. C. Higher order structure of chromatin: orientation of nucleosomes within the 30 nm chromatin solenoid is independent of species and spacer length. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):831–841. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Rau D. C., Charney E., Felsenfeld G. Orientation of the nucleosome within the higher order structure of chromatin. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra S., Sen D., Crothers D. M. Orientation of nucleosomes and linker DNA in calf thymus chromatin determined by photochemical dichroism. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):247–250. doi: 10.1038/308247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris N. R. A comparison of the structure of chicken erythrocyte and chicken liver chromatin. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 1):627–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. Preparation of native chromatin and damage caused by shearing. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1203–1206. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson E. C., Butler P. J., Thomas J. O. Higher-order structure of nucleosome oligomers from short-repeat chromatin. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1367–1372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadafora C., Bellard M., Compton J. L., Chambon P. The DNA repeat lengths in chromatins from sea urchin sperm and gastrule cells are markedly different. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 15;69(1):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80704-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strätling W. H., Klingholz R. Supranucleosomal structure of chromatin: digestion by calcium/magnesium endonuclease proceeds via a discrete size class of particles with elevated stability. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1386–1392. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suau P., Bradbury E. M., Baldwin J. P. Higher-order structures of chromatin in solution. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;97(2):593–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Butler P. J. Size-dependence of a stable higher-order structure of chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1980 Nov 25;144(1):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. The study of histone--histone associations by chemical cross-linking. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;18:429–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Rees C., Pearson E. C. Histone H5 promotes the association of condensed chromatin fragments to give pseudo-higher-order structures. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):143–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley M. E., Davies H. G. Ultrastructural and biochemical observations on interphase nuclei isolated from chicken erythrocytes. J Cell Sci. 1975 Jan;17(1):113–139. doi: 10.1242/jcs.17.1.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock C. L., Frado L. L., Rattner J. B. The higher-order structure of chromatin: evidence for a helical ribbon arrangement. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):42–52. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Strogatz S., Riley D. Structure of chromatin and the linking number of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1461–1465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabuki H., Dattagupta N., Crothers D. M. Orientation of nucleosomes in the thirty-nanometer chromatin fiber. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):5015–5020. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zentgraf H., Franke W. W. Differences of supranucleosomal organization in different kinds of chromatin: cell type-specific globular subunits containing different numbers of nucleosomes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):272–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]