Abstract
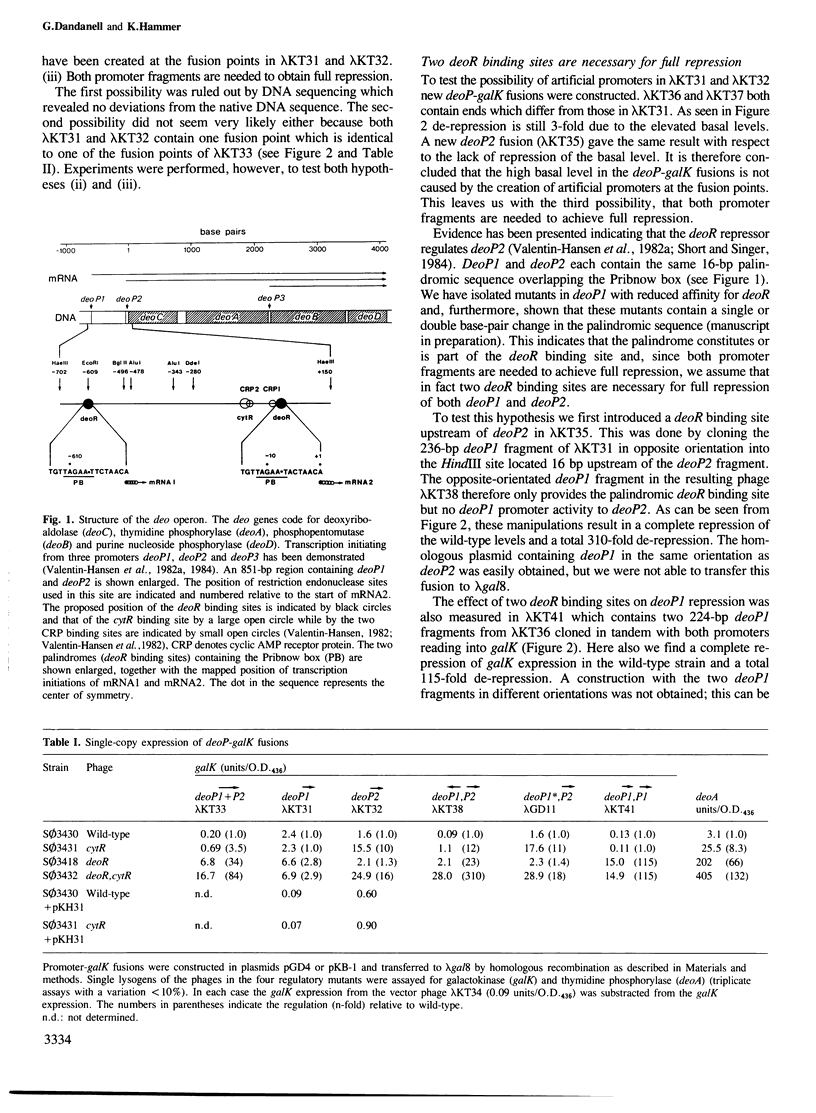
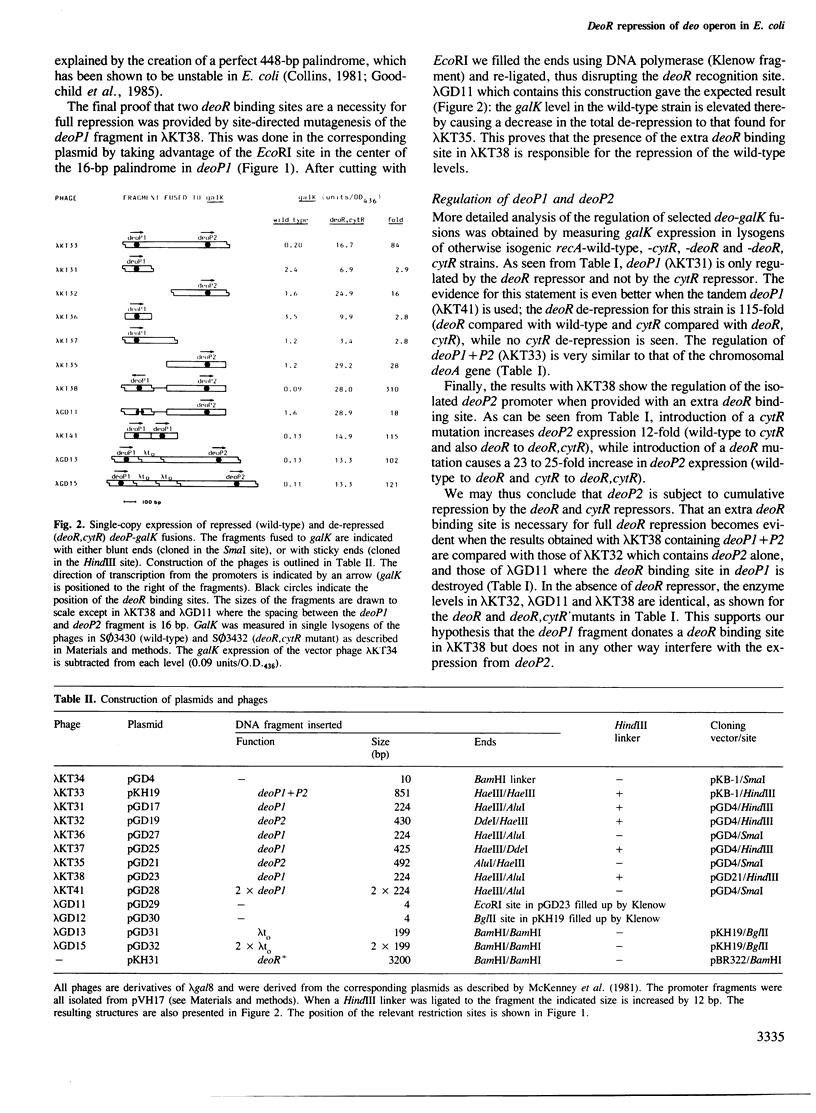
DeoP1 and deoP2 promoter fragments from the deo operon of Escherichia coli have been transcriptionally fused to the galactokinase gene. From single-copy expression of these fusions it is shown that the deoR binding site of both deoP1 and deoP2 are necessary to achieve full repression of the deo operon by the deoR repressor. Repression of the promoters can be achieved either by supplying extra deoR repressor in trans or by introduction of an extra deoR binding site at a position between 224 and 997 bp upstream of the promoter. Furthermore, the deoP2 promoter is shown to be regulated in a cumulative way by both the deoR and the cytR repressors, while deoP1 is only regulated by the deoR repressor. DeoP2 is a strong promoter being 20 times stronger than araPBAD and four times stronger than deoP1.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrechtsen H., Hammer-Jespersen K., Munch-Petersen A., Fiil N. Multiple regulation of nucleoside catabolizing enzymes: effects of a polar dra mutation on the deo enzymes. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jul 23;146(2):139–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00268082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. Instability of palindromic DNA in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):409–416. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. M., Hahn S., Ogden S., Schleif R. F. An operator at -280 base pairs that is required for repression of araBAD operon promoter: addition of DNA helical turns between the operator and promoter cyclically hinders repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5017–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Adyha S., Court D. L. Isolation of plaque-forming, galactose-transducing strains of phage lambda. Genetics. 1972 Jun;71(2):189–206. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild J., Michniewicz J., Seto-Young D., Narang S. A novel deletion found during cloning of a synthetic palindromic DNA. Gene. 1985;33(3):367–371. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90246-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Dunn T., Schleif R. Upstream repression and CRP stimulation of the Escherichia coli L-arabinose operon. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani M. H., Orosz L., Adhya S. A control element within a structural gene: the gal operon of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P., Collins J., Valentin-Hansen P. On the structure of the deo operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Sep 21;155(1):93–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00268565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A., Adhya S. Demonstration of two operator elements in gal: in vitro repressor binding studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6100–6104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munch-Petersen A. On the catabolism of deoxyribonucleosides in cells and cell extracts of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Nov;6(3):432–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00465.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Weisberg R. A., Gottesman M. E. Prophage lambda at unusual chromosomal locations. I. Location of the secondary attachment sites and the properties of the lysogens. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):483–503. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., Singer J. T. Studies on deo operon regulation in Escherichia coli: cloning and expression of the deoR structural gene. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Hansen P., Aiba H., Schümperli D. The structure of tandem regulatory regions in the deo operon of Escherichia coli K12. EMBO J. 1982;1(3):317–322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01167.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Hansen P., Hammer K., Løve Larsen J. E., Svendsen I. The internal regulated promoter of the deo operon of Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5211–5224. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Hansen P., Svenningsen B. A., Munch-Petersen A., Hammer-Jespersen K. Regulation of the deo operon in Escherichia coli: the double negative control of the deo operon by the cytR and deoR repressors in a DNA directed in vitro system. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Feb 16;159(2):191–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00270893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin-Hansen P. Tandem CRP binding sites in the deo operon of Escherichia coli K-12. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1049–1054. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Bear D. G., Morgan W. D., McSwiggen J. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions in transcription: a molecular analysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:389–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



