Abstract
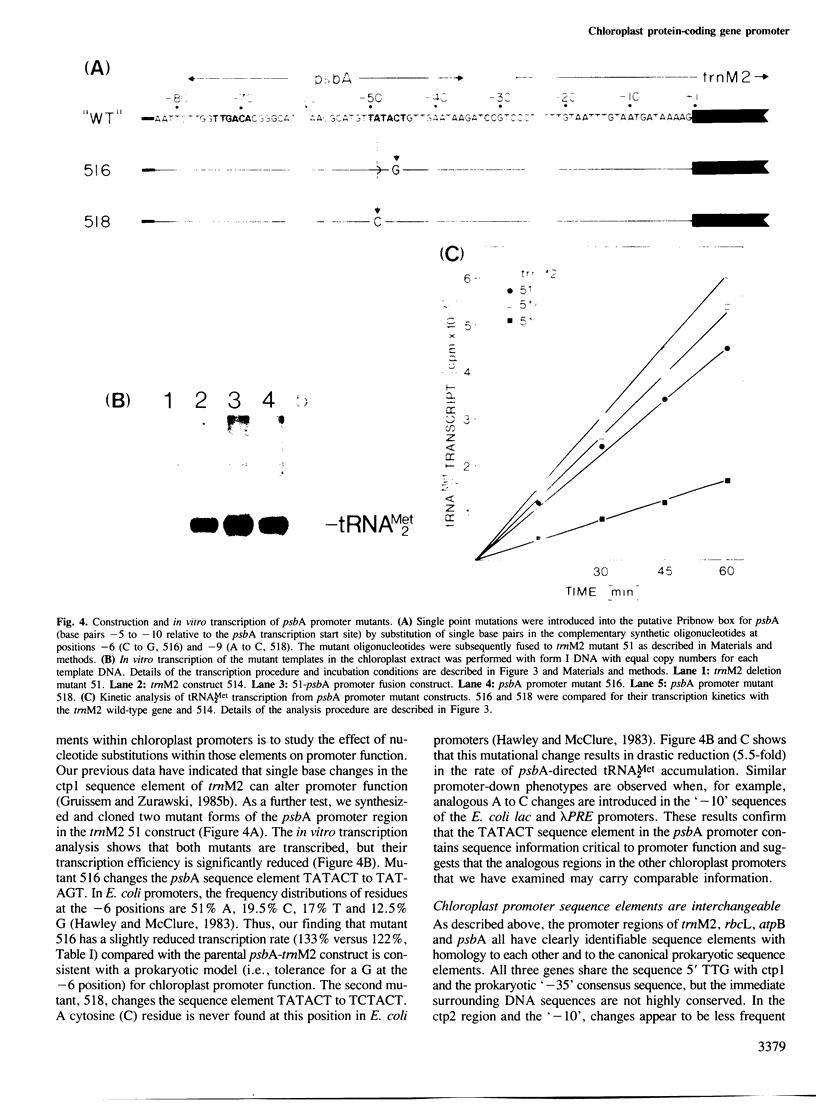
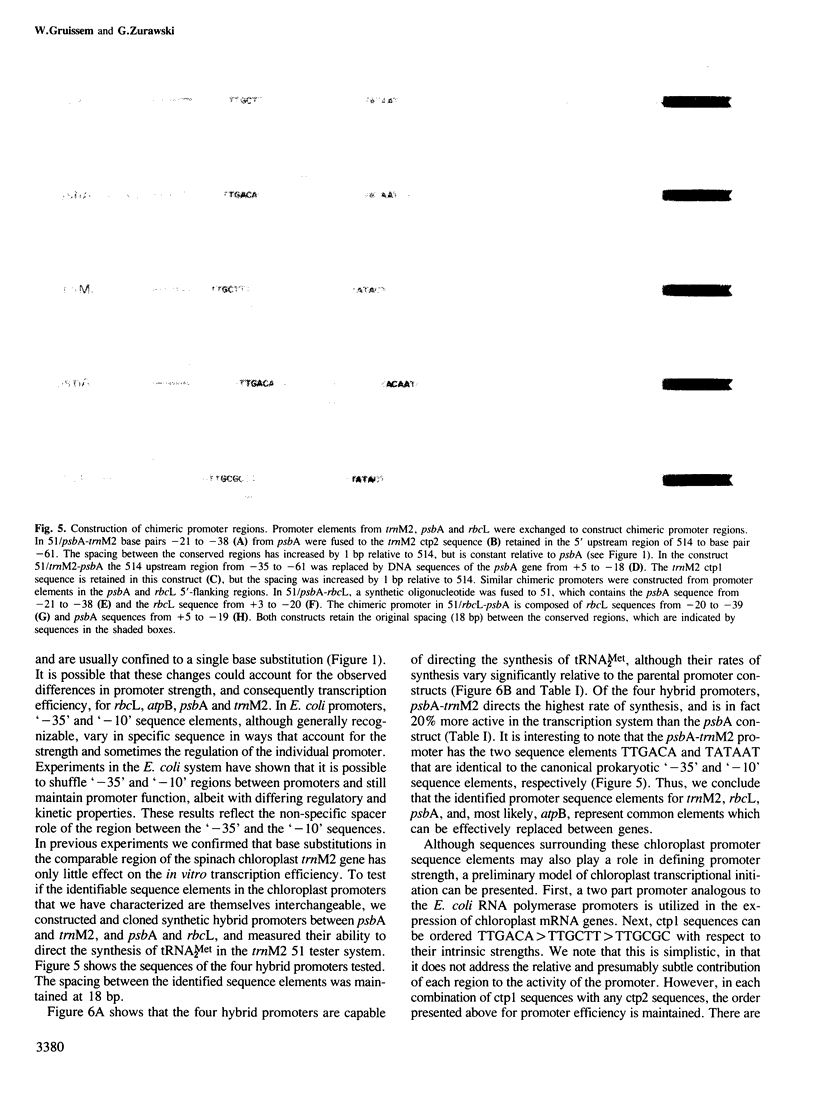
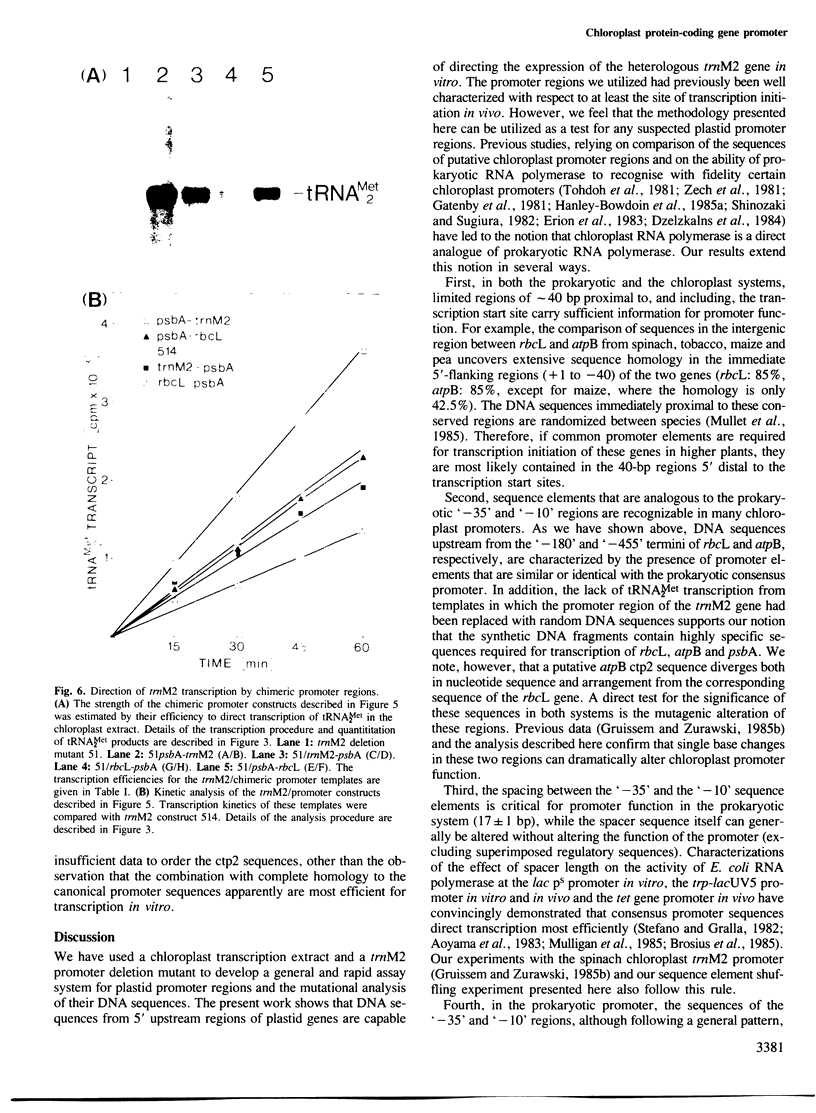
A promoter-deletion derivative of the spinach trnM2 gene was used for the identification and characterization of the promoter regions for the spinach chloroplast RuBisCo large subunit (rbcL), ATPase beta-subunit (atpB) and QB-polypeptide (psbA) genes. The DNA sequences 5' upstream from the transcriptional start sites of these genes share homology with the ctp1 and ctp2 arrangement found for the trnM2 transcription unit and the canonical Escherichia coli '-10' and '-35' promoter regions. Synthetic DNA fragments of approximately 40-bp regions, including the defined transcriptional start sites and proximal residues, from rbcL, atpB and psbA, were fused to the trnM2 deletion mutant 51. The promoter-fusion constructs direct the correct transcription of tRNAMet2 in the chloroplast extract with distinct efficiencies. The ctp1- and ctp2-like elements in the trnM2, rbcL and psbA promoter regions can be interchanged to yield functional chimeric promoters of varying strengths. As a result, ctp1 sequences from atpB and psbA, trnM2 and rbcL, respectively, can be ordered TTGACA greater than TTGCTT greater than TTGCGC with respect to their intrinsic strengths. Single base pair changes were introduced into the ctp2-like element in the psbA promoter region. In analogy to similar base pair changes which lower promoter efficiency in E. coli, these mutations result in reduced transcription levels in the chloroplast extract. The data are consistent with a prokaryotic model for chloroplast promoter function.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyama T., Takanami M., Ohtsuka E., Taniyama Y., Marumoto R., Sato H., Ikehara M. Essential structure of E. coli promoter: effect of spacer length between the two consensus sequences on promoter function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5855–5864. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedbrook J. R., Link G., Coen D. M., Bogorad L. Maize plastid gene expressed during photoregulated development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley W., Smith H. J., Bogorad L. RNA polymerases of maize: partial purification and properties of the chloroplast enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Erfle M., Storella J. Spacing of the -10 and -35 regions in the tac promoter. Effect on its in vivo activity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3539–3541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzelzkalns V. A., Owens G. C., Bogorad L. Chloroplast promoter driven expression of the chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene in a cyanobacterium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8917–8925. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatenby A. A., Castleton J. A., Saul M. W. Expression in E. coli of maize and wheat chloroplast genes for large subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase. Nature. 1981 May 14;291(5811):117–121. doi: 10.1038/291117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Greenberg B. M., Zurawski G., Hallick R. B. Chloroplast gene expression and promoter identification in chloroplast extracts. Methods Enzymol. 1986;118:253–270. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)18077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Greenberg B. M., Zurawski G., Prescott D. M., Hallick R. B. Biosynthesis of chloroplast transfer RNA in a spinach chloroplast transcription system. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):815–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Narita J. O., Greenberg B. M., Prescott D. M., Hallick R. B. Selective in vitro transcription of chloroplast genes. J Cell Biochem. 1983;22(1):31–46. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240220104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Prescott D. M., Greenberg B. M., Hallick R. B. Transcription of E. coli and Euglena chloroplast tRNA gene clusters and processing of polycistronic transcripts in a HeLa cell-free system. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Zurawski G. Identification and mutational analysis of the promoter for a spinach chloroplast transfer RNA gene. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1637–1644. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03831.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley-Bowdoin L., Orozco E. M., Jr, Chua N. H. In vitro synthesis and processing of a maize chloroplast transcript encoded by the ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase large subunit gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2733–2745. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. In vitro comparison of initiation properties of bacteriophage lambda wild-type PR and x3 mutant promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6381–6385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Mechanism of activation of transcription initiation from the lambda PRM promoter. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 25;157(3):493–525. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90473-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holschuh K., Bottomley W., Whitfeld P. R. Structure of the spinach chloroplast genes for the D2 and 44 kd reaction-centre proteins of photosystem II and for tRNASer (UGA). Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8819–8834. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebbers E. T., Larrinua I. M., McIntosh L., Bogorad L. The maize chloroplast genes for the beta and epsilon subunits of the photosynthetic coupling factor CF1 are fused. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):4985–5002. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.4985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link G. DNA sequence requirements for the accurate transcription of a protein-coding plastid gene in a plastid in vitro system from mustard (Sinapis alba L.). EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1697–1704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Rate-limiting steps in RNA chain initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5634–5638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Brosius J., McClure W. R. Characterization in vitro of the effect of spacer length on the activity of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase at the TAC promoter. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3529–3538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T., Harpster M. H., Mayfield S. P., Taylor W. C. Light-regulated gene expression during maize leaf development. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):558–564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco E. M., Jr, Mullet J. E., Chua N. H. An in vitro system for accurate transcription initiation of chloroplast protein genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1283–1302. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodermel S. R., Bogorad L. Maize plastid photogenes: mapping and photoregulation of transcript levels during light-induced development. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):463–476. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Deno H., Kato A., Sugiura M. Overlap and cotranscription of the genes for the beta and epsilon subunits of tobacco chloroplast ATPase. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. Sequence of the intercistronic region between the ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit and coupling factor beta subunit gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):4923–4934. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.4923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Hoopes B. C., McClure W. R., Kleckner N. Three promoters near the termini of IS10: pIN, pOUT, and pIII. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90400-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Ellis R. J. Light-stimulated accumulation of transcripts of nuclear and chloroplast genes for ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(2):127–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielmann A., Stutz E. Nucleotide sequence of soybean chloroplast DNA regions which contain the psb A and trn H genes and cover the ends of the large single copy region and one end of the inverted repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7157–7167. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E., Gralla J. D. Spacer mutations in the lac ps promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1069–1072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohdoh N., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. Sequence of a putative promoter region for the rRNA genes of tobacco chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5399–5406. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Bohnert H. J., Whitfeld P. R., Bottomley W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the M(r) 32,000 thylakoid membrane protein from Spinacia oleracea and Nicotiana debneyi predicts a totally conserved primary translation product of M(r) 38,950. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7699–7703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Bottomley W., Whitfeld P. R. Junctions of the large single copy region and the inverted repeats in Spinacia oleracea and Nicotiana debneyi chloroplast DNA: sequence of the genes for tRNAHis and the ribosomal proteins S19 and L2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6547–6558. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Bottomley W., Whitfeld P. R. Structures of the genes for the beta and epsilon subunits of spinach chloroplast ATPase indicate a dicistronic mRNA and an overlapping translation stop/start signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6260–6264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Clegg M. T. The barley chloroplast DNA atpBE, trnM2, and trnV1 loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2549–2559. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Perrot B., Bottomley W., Whitfeld P. R. The structure of the gene for the large subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from spinach chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3251–3270. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









