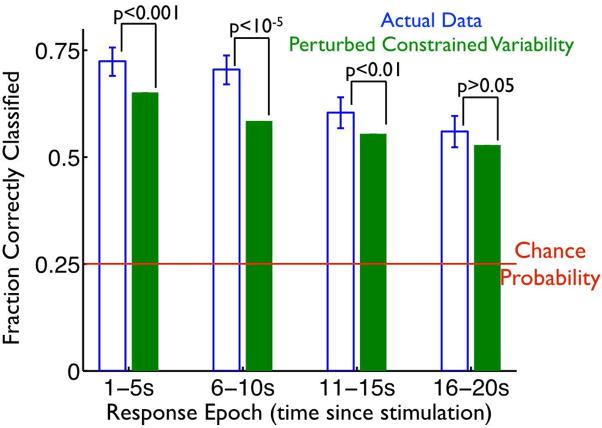
Fig. 5. Variability constrained to lie near mean trajectories enhances pattern separability in the dentate gyrus.
We used our KNN classifier to identify the stimulus responsible for the neural responses (as in Fig. 2D). The classifier was applied to both the actual experimental data (blue bars), and the surrogate data (green bars) in which the structure of the trial-to-trial variability was perturbed (as in Fig. 4AB), reducing the tendency of fluctuations to lie along / near the mean stimulus-evoked trajectories. The classification was performed on the mean EPSP frequencies measured in 1s windows post-stimulation, and the bar heights indicate the fraction of successfully classified responses, in 4 different post-stimulation epochs. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. To generate the green bars, we repeated the random rotation procedure 10,000 times, yielding enough surrogate trials that the error bars associated with the performance values are vanishingly small. At each epoch, we show the p-values for comparisons between the performance obtained with the raw, and the surrogate, data; these p-values come from binomial tests.