Abstract
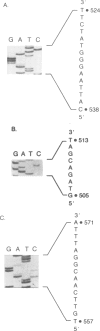
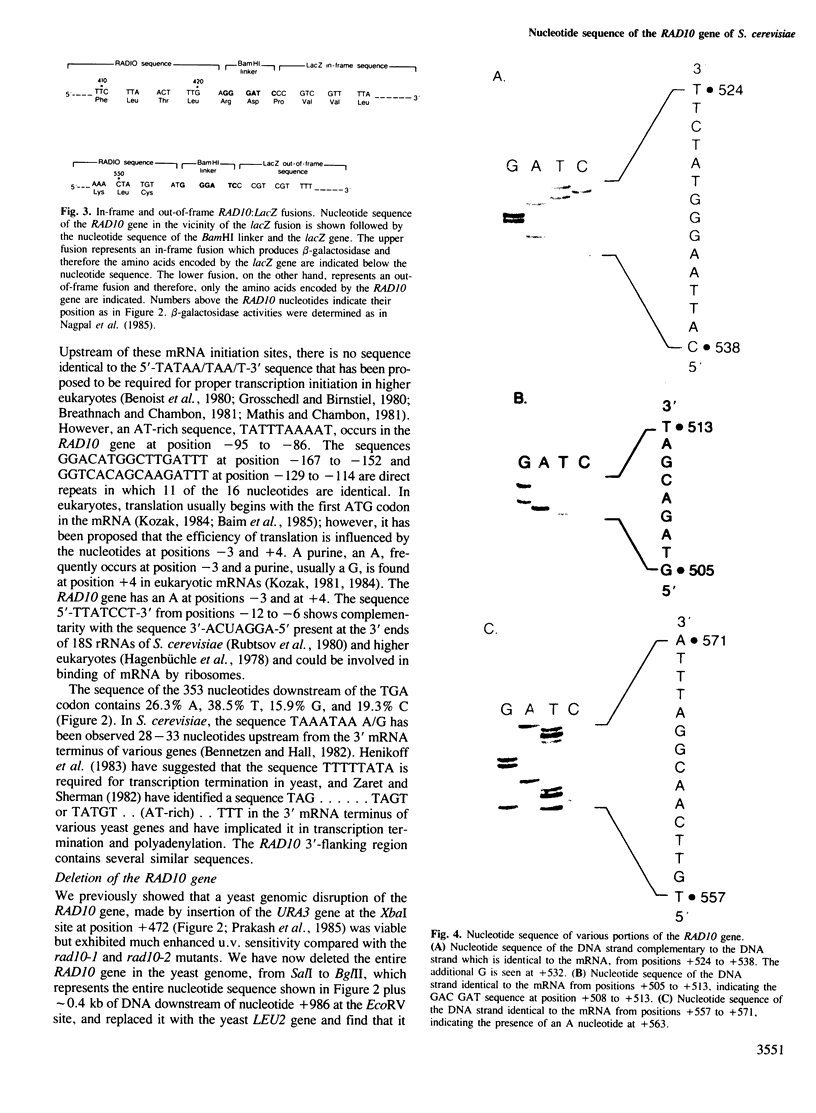
The RAD10 gene is one of several genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae required for incision of u.v.-irradiated or cross-linked DNA. We have determined the nucleotide sequence of the RAD10 gene and its flanking regions. The RAD10 nucleotide sequence presented here differs significantly from that recently reported. The RAD10 protein predicted from the nucleotide sequence contains 210 amino acids with a calculated mol. wt. of 24 310. The middle portion of the RAD10 protein, which is highly basic and also contains eight of the total of 10 tyrosine residues present in the protein, may be involved in DNA binding by ionic interactions and tyrosine intercalation between the bases of DNA. A genomic deletion of the entire RAD10 gene does not affect viability; however, the rad10 deletion mutant is highly u.v. sensitive.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. A., Coleman J. E. Physiochemical properties of DNA binding proteins: gene 32 protein of T4 and Escherichia coli unwinding protein. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5485–5491. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. A., Nakashima Y., Coleman J. E. Chemical modifications of functional residues of fd gene 5 DNA-binding protein. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 11;14(5):907–917. doi: 10.1021/bi00676a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Kelly J. D., Cohen E. H. Transcription terminates in yeast distal to a control sequence. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):607–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. R., Prakash L., Reynolds P., Prakash S. Isolation and characterization of the RAD2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. R., Prakash S., Reynolds P., Polakowska R., Weber S., Prakash L. Isolation and characterization of the RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and inviability of rad3 deletion mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5680–5684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. R., Prakash S., Reynolds P., Prakash L. Molecular cloning and characterization of the RAD1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jachymczyk W. J., von Borstel R. C., Mowat M. R., Hastings P. J. Repair of interstrand cross-links in DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires two systems for DNA repair: the RAD3 system and the RAD51 system. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):196–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00269658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magaña-Schwencke N., Henriques J. A., Chanet R., Moustacchi E. The fate of 8-methoxypsoralen photoinduced crosslinks in nuclear and mitochondrial yeast DNA: comparison of wild-type and repair-deficient strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1722–1726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Chambon P. The SV40 early region TATA box is required for accurate in vitro initiation of transcription. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):310–315. doi: 10.1038/290310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson A., Jurnak F. A., Wang A. H., Molineux I., Rich A. Structure at 2.3 A resolution of the gene 5 product of bacteriophage fd: a DNA unwinding protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 5;134(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90359-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. D., Prakash L., Prakash S. Defective excision of pyrimidine dimers and interstrand DNA crosslinks in rad7 and rad23 mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(2):235–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00332681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. D., Prakash L., Prakash S. Genetic control of excision of Saccharomyces cerevisiae interstrand DNA cross-links induced by psoralen plus near-UV light. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;2(8):939–948. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.8.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagpal M. L., Higgins D. R., Prakash S. Expression of the RAD1 and RAD3 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is not affected by DNA damage or during the cell division cycle. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(1):59–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00327510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. A DNA repair gene required for the incision of damaged DNA is essential for viability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4818–4821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD2 gene: isolation, subcloning, and partial characterization. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):290–295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash L., Dumais D., Polakowska R., Perozzi G., Prakash S. Molecular cloning of the RAD10 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1985;34(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P., Higgins D. R., Prakash L., Prakash S. The nucleotide sequence of the RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a potential adenine nucleotide binding amino acid sequence and a nonessential acidic carboxyl terminal region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2357–2372. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R. J., Friedberg E. C. Molecular mechanisms of pyrimidine dimer excision in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: incision of ultraviolet-irradiated deoxyribonucleic acid in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):692–704. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.692-704.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubtsov P. M., Musakhanov M. M., Zakharyev V. M., Krayev A. S., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. I. The complete nucleotide sequence of the 18S ribosomal RNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5779–5794. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss W. A., Friedberg E. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of the yeast RAD10 gene and expression of RAD10 protein in E. coli. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1575–1582. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03819.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox D. R., Prakash L. Incision and postincision steps of pyrimidine dimer removal in excision-defective mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):618–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.618-623.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. R., LoPresti M. B., Setoguchi M. Primary structure of the bacteriophage T4 DNA helix-destabilizing protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1754–1762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]