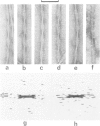
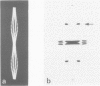
Abstract
The paired helical filament (PHF) is the principal constituent of the neurofibrillary tangles that occur in the brain in senile dementias of the Alzheimer type. We have previously shown from fragmentation patterns of isolated PHFs that they consist of a regularly repeating subunit, which is axially compact and not an extended fibrous molecule or protofilament. Here we present diffraction patterns of PHFs and an objective reconstruction of the cross-sectional density of the PHF computed from the diffraction patterns. We demonstrate the presence of an axial periodicity (3 nm) in PHFs. These results establish conclusively that the PHF is made up of a double helical stack of transversely oriented subunits, each of which has three domains, and precludes purely descriptive models based on helical rearrangements of preformed cytoskeletal polymers or protofilaments. The structure is of the type that might arise by the de novo assembly of a single structural subunit, which appears to be produced in considerable abundance in those neurons where tangles form.
Full text
PDF
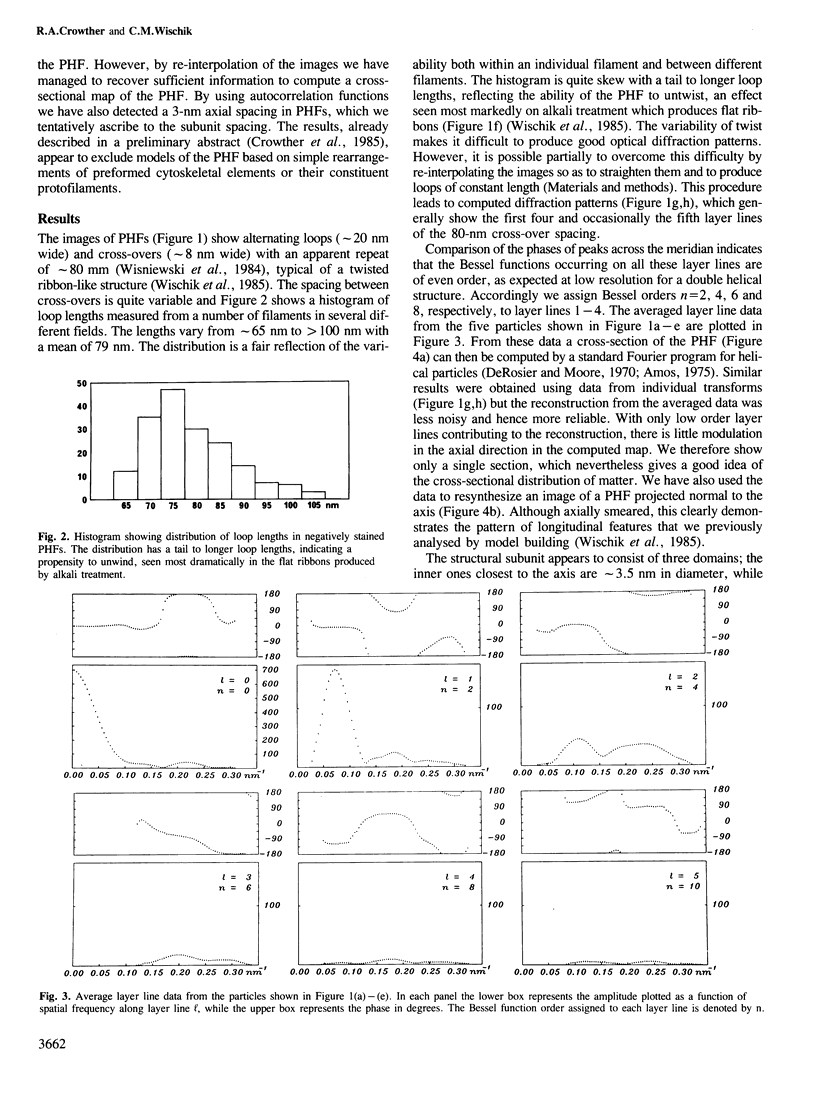


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi U., Fowler W. E., Rew P., Sun T. T. The fibrillar substructure of keratin filaments unraveled. J Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;97(4):1131–1143. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.4.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderton B. H., Breinburg D., Downes M. J., Green P. J., Tomlinson B. E., Ulrich J., Wood J. N., Kahn J. Monoclonal antibodies show that neurofibrillary tangles and neurofilaments share antigenic determinants. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):84–86. doi: 10.1038/298084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami A., Selkoe D. J., Dahl D. Amyloid-like (Congophilic) neurofibrillary tangles do not react with neurofilament antisera in Alzheimer's cerebral cortex. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;64(3):243–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00688115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blessed G., Tomlinson B. E., Roth M. The association between quantitative measures of dementia and of senile change in the cerebral grey matter of elderly subjects. Br J Psychiatry. 1968 Jul;114(512):797–811. doi: 10.1192/bjp.114.512.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRosier D. J., Moore P. B. Reconstruction of three-dimensional images from electron micrographs of structures with helical symmetry. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 14;52(2):355–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott A., Lowy J., Squire J. M. Convolution camera to reveal periodicities in electron micrographs. Nature. 1968 Sep 21;219(5160):1224–1226. doi: 10.1038/2191224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambetti P., Shecket G., Ghetti B., Hirano A., Dahl D. Neurofibrillary changes in human brain. An immunocytochemical study with a neurofilament antiserum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1983 Jan;42(1):69–79. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198301000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D., Chojnacki B., Goldman A. E., Starger J., Steinert P., Talian J., Whitman M., Zackroff R. Aspects of the cytoskeleton and cytomusculature of nonmuscle cells. Neurosci Res Program Bull. 1981 Feb;19(1):59–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal K., Wiśniewski H. M., Shelanski M. L., Brostoff S., Liwnicz B. H., Terry R. D. Protein changes in senile dementia. Brain Res. 1974 Sep 6;77(2):337–343. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90798-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal K., Zaidi T., Thompson C. H., Merz P. A., Wisniewski H. M. Alzheimer paired helical filaments: bulk isolation, solubility, and protein composition. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;62(3):167–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00691849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIDD M. ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE--AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPICAL STUDY. Brain. 1964 Jun;87:307–320. doi: 10.1093/brain/87.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIDD M. Paired helical filaments in electron microscopy of Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1963 Jan 12;197:192–193. doi: 10.1038/197192b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Multhaup G., Simms G., Pottgiesser J., Martins R. N., Beyreuther K. Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metuzals J., Montpetit V., Clapin D. F. Organization of the neurofilamentous network. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;214(3):455–482. doi: 10.1007/BF00233488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Rizzuto N., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P. Paired helical filaments from Alzheimer disease patients contain cytoskeletal components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3916–3920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M., Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G. The relationship between quantitative measures of dementia and of degenerative changes in the cerebral grey matter of elderly subjects. Proc R Soc Med. 1967 Mar;60(3):254–260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Abraham C., Ihara Y. Brain transglutaminase: in vitro crosslinking of human neurofilament proteins into insoluble polymers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6070–6074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Ihara Y., Salazar F. J. Alzheimer's disease: insolubility of partially purified paired helical filaments in sodium dodecyl sulfate and urea. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1243–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.6120571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson B. E. Plaques, tangles and Alzheimer's disease. Psychol Med. 1982 Aug;12(3):449–459. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700055549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcock G. K., Esiri M. M. Plaques, tangles and dementia. A quantitative study. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Nov;56(2-3):343–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wischik C. M., Crowther R. A., Stewart M., Roth M. Subunit structure of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1905–1912. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Merz P. A., Iqbal K. Ultrastructure of paired helical filaments of Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangle. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1984 Nov;43(6):643–656. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198411000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski K., Jervis G. A., Moretz R. C., Wisniewski H. M. Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles in diseases other than senile and presenile dementia. Ann Neurol. 1979 Mar;5(3):288–294. doi: 10.1002/ana.410050311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H. M., Narang H. K., Terry R. D. Neurofibrillary tangles of paired helical filaments. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Feb;27(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]