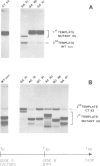
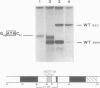
Abstract
To study the fine structure of the Xenopus laevis somatic 5S gene internal control region, we have created 15 different transversions using mutagenic oligonucleotide primers. The effects of these mutations on 5S DNA transcription in vitro as well as on stable complex formation with transcription factor TF III A and TF III C in crude nuclear extracts were analyzed. Mutations in the common class III 5' promoter element (nucleotides 50-61 in the 5S gene) interfere with transcription activity and stable complex formation whenever they contradict the tDNA box A consensus sequence. The second promoter element is defined by a major sequence block (nucleotides 80-89, box C) and two additional internal residues (70 and 71) at a distance of roughly one helical turn from both the major 3' and 5' control sequences; these two 3' elements contain the primary TF III A binding domain. The remaining nucleotides (62-69 and 71-79) when mutated do not interfere with transcription activity or factor binding and thus they constitute two spacer elements within a symmetrically structured 5S gene promoter. An increase in the relative spacing of box A and box C by insertion of 3 bp between nucleotides 66 and 67 leads to a drastic reduction in transcription activity and the ability to form a stable complex with TF III A and/or TF III C. Thus, accurate spacing is essential for the proper orientation of TF III A on 5S DNA and/or TF III C binding.
Full text
PDF
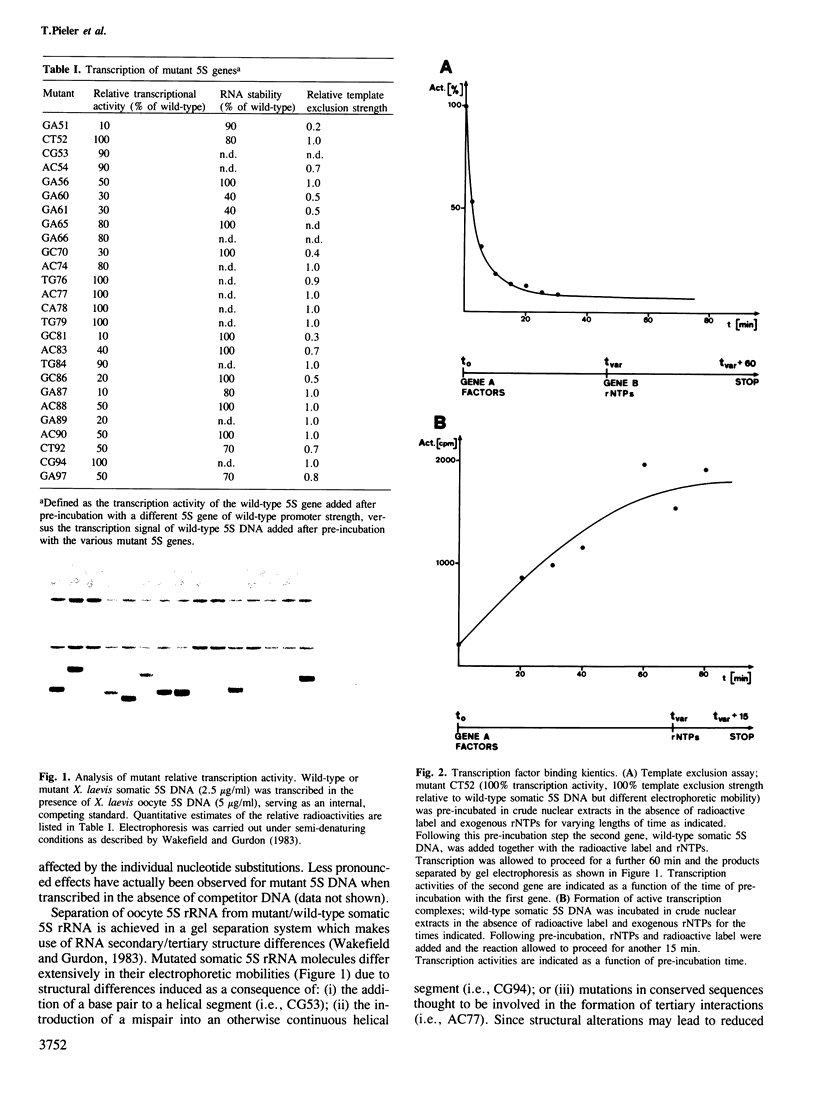
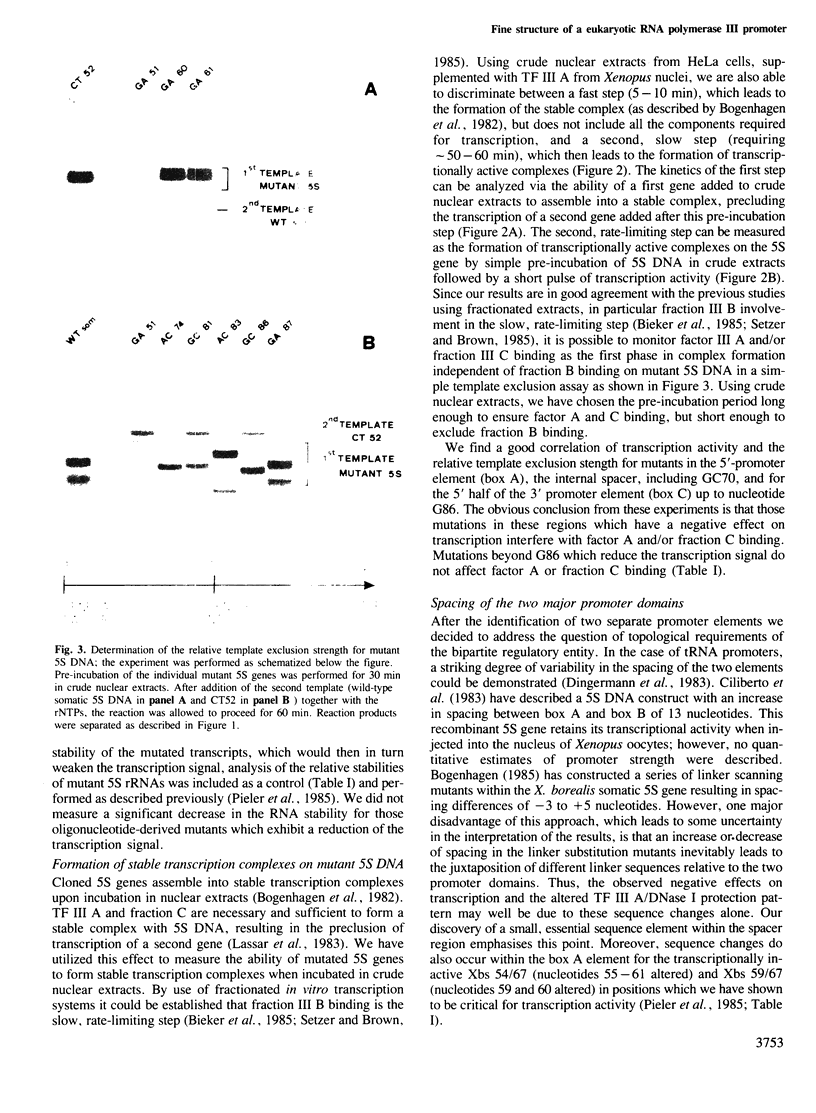



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieker J. J., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Formation of a rate-limiting intermediate in 5S RNA gene transcription. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F. The intragenic control region of the Xenopus 5 S RNA gene contains two factor A binding domains that must be aligned properly for efficient transcription initiation. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6466–6471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Raugei G., Costanzo F., Dente L., Cortese R. Common and interchangeable elements in the promoters of genes transcribed by RNA polymerase iii. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):725–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Sharp S., Schaack J., Söll D. Stable transcription complex formation of eukaryotic tRNA genes is dependent on a limited separation of the two intragenic control regions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10395–10402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Roeder R. G. DNA sequences and transcription factor interactions of active and inactive forms of mammalian 5 S RNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7926–7935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargiulo G., Razvi F., Worcel A. Assembly of transcriptionally active chromatin in Xenopus oocytes requires specific DNA binding factors. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):511–521. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90506-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Hazuda D. J., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu F. Y., Wu C. W. Xenopus transcription factor A requires zinc for binding to the 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14120–14125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladiges W. C., Raff R. F., Brown S., Deeg H. J., Storb R. The canine major histocompatibility complex. Supertypic specificities defined by the primed lymphocyte test (PLT). Immunogenetics. 1984;19(4):359–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00345410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. G., Sprague K. U. In vitro transcription of a silkworm 5S RNA gene requires an upstream signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5519–5522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Appel B., Oei S. L., Mentzel H., Erdmann V. A. Point mutational analysis of the Xenopus laevis 5S gene promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1847–1853. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D. Contact points between a positive transcription factor and the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D., Engelke D., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. The binding of a transcription factor to deletion mutants of a 5S ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):665–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Brown D. D. The transcriptional regulation of Xenopus 5s RNA genes in chromatin: the roles of active stable transcription complexes and histone H1. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., Brown D. D. Formation and stability of the 5 S RNA transcription complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2483–2492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S., DeFranco D., Dingermann T., Farrell P., Söll D. Internal control regions for transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6657–6661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors involved in the transcription of class III genes in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12979–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Jackson I. J., Brown D. D. Domains of the positive transcription factor specific for the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L., Gurdon J. B. Cytoplasmic regulation of 5S RNA genes in nuclear-transplant embryos. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1613–1619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01632.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M., Bogenhagen D. F., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A quantitative assay for Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):809–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]