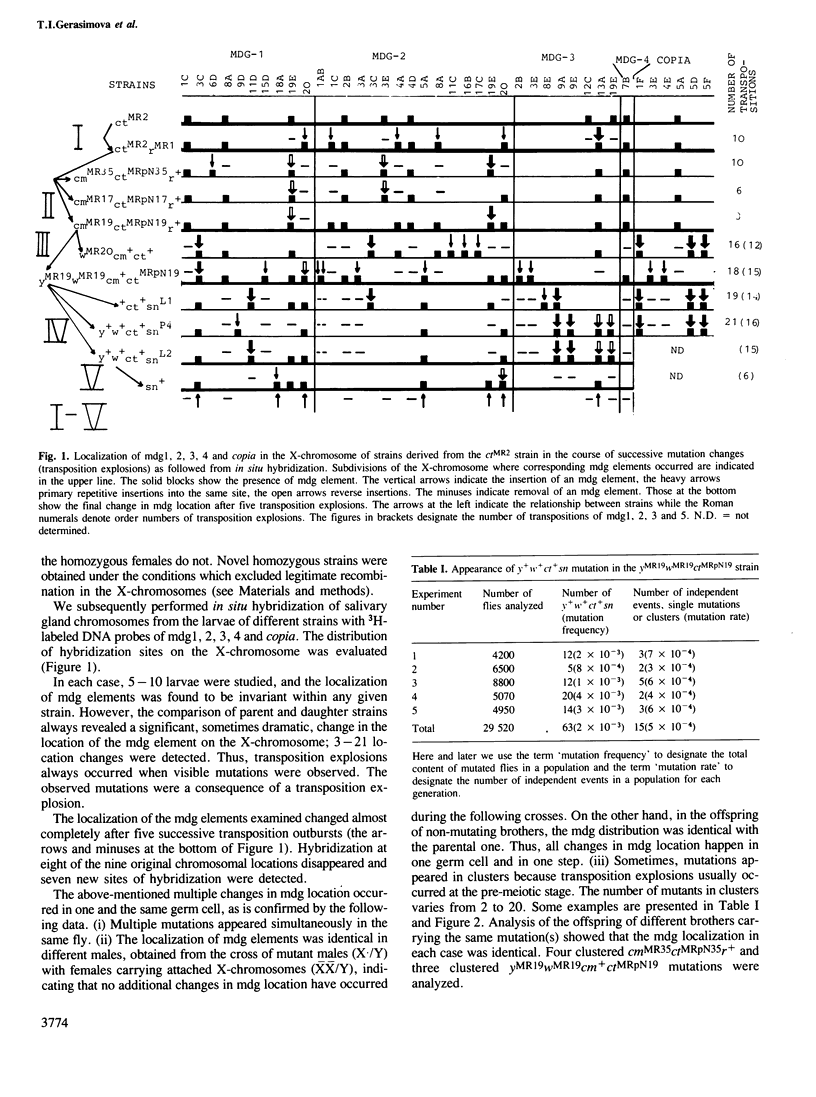
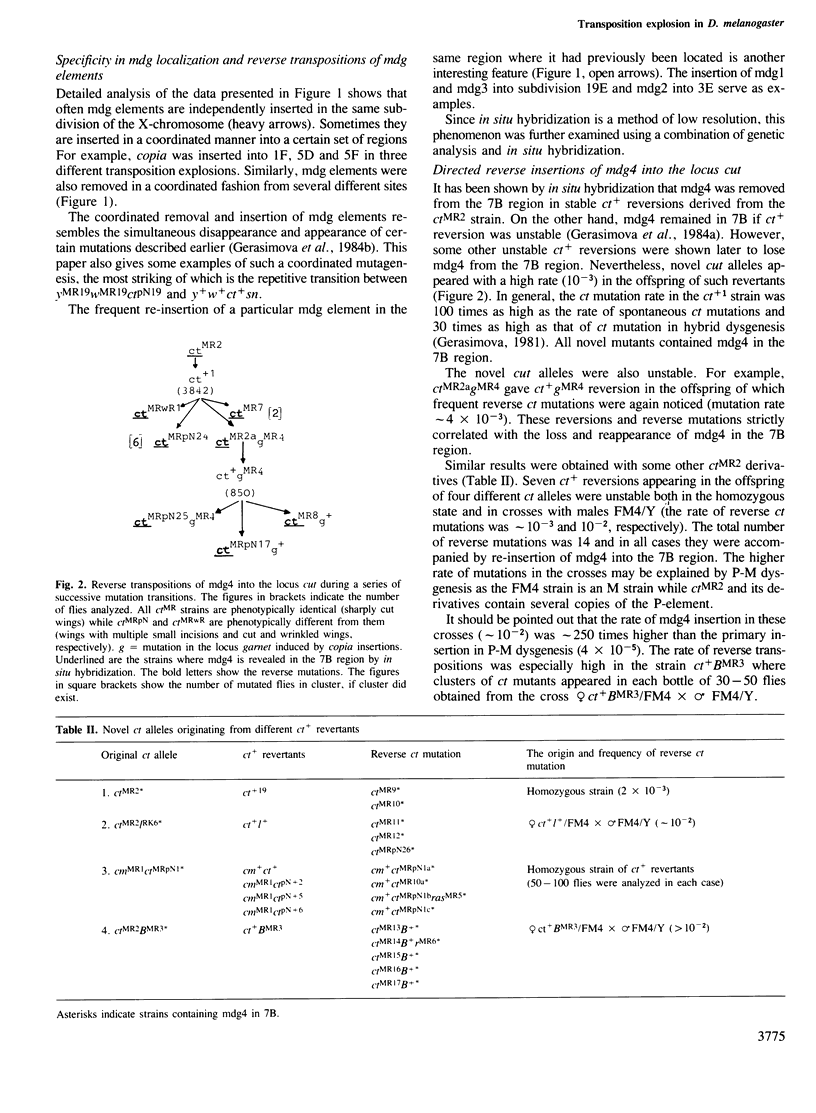
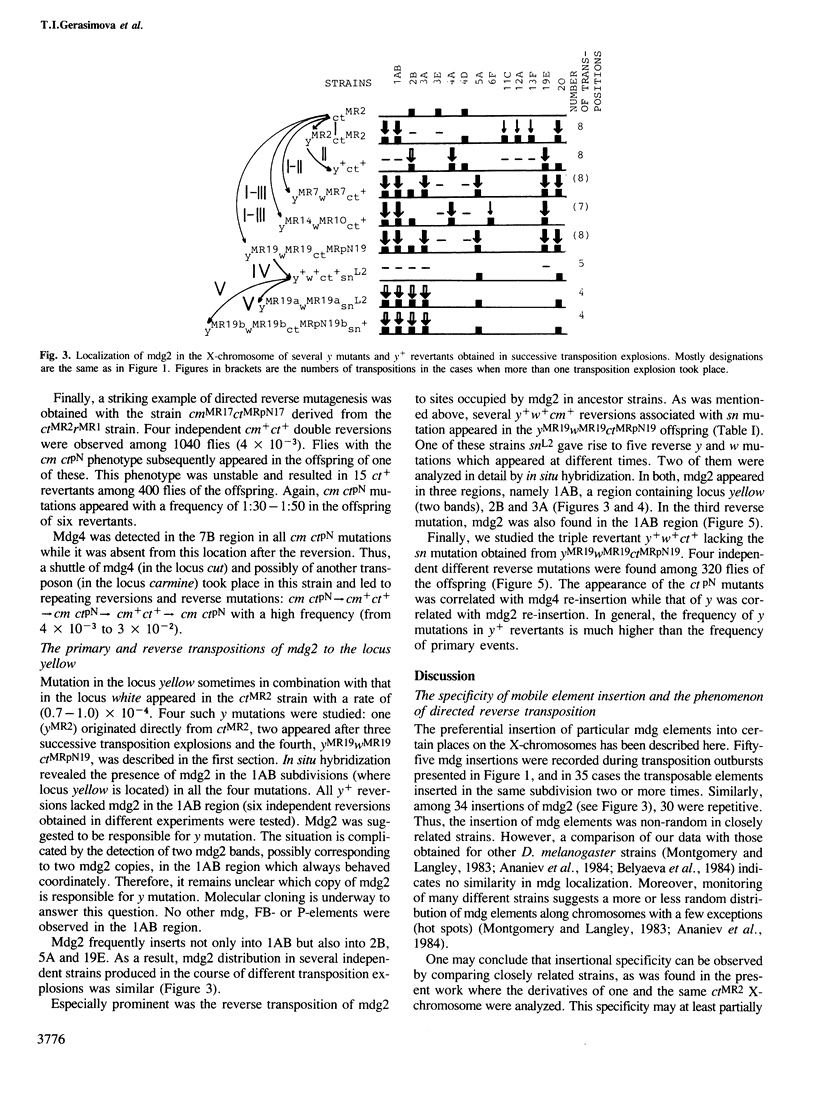
Abstract
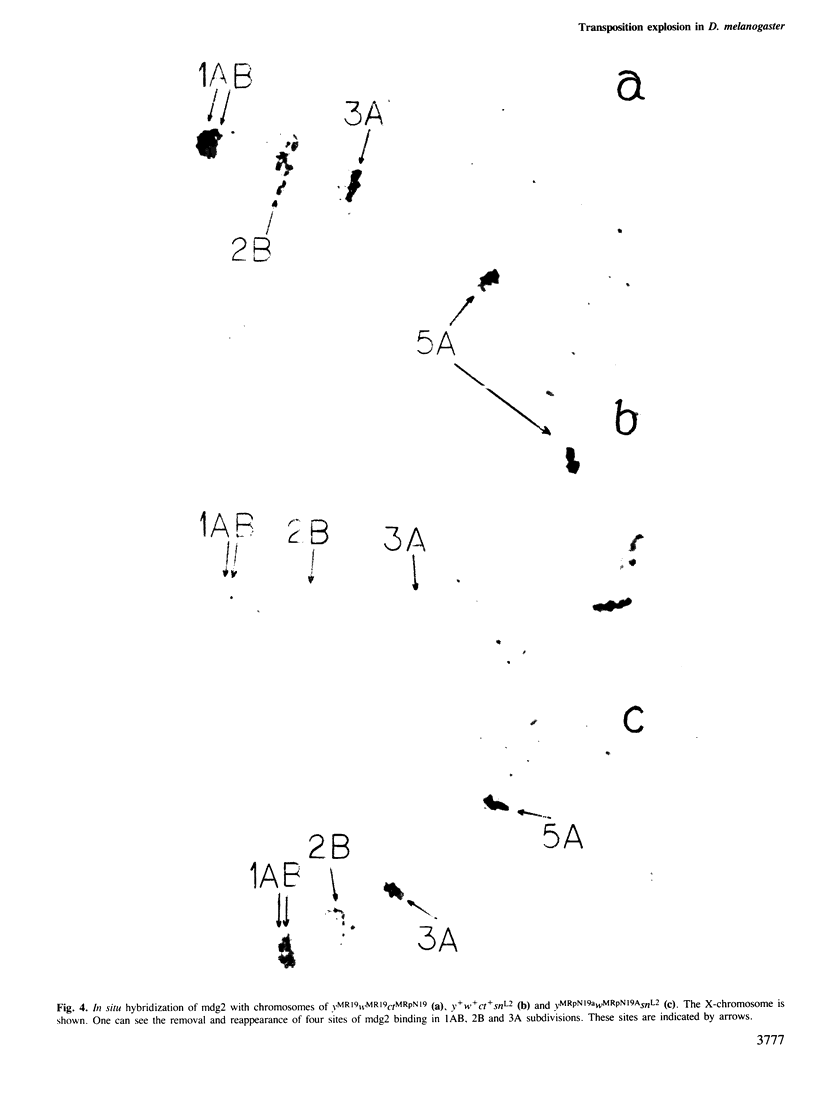
Transposition outbursts occur in the destabilized Drosophila melanogaster strain ctMR2 carrying a mutation in the locus cut induced by an insertion of mdg4. While the distribution of mobile genetic elements remained unchanged in the great majority of germ cells, in a few cells numerous transpositions had occurred involving mdg (copia-like), fold-back and P-elements. We used in situ hybridization to analyze the distribution of five families of mdg elements in the X-chromosome during several consequent mutational changes in D. melanogaster. Each of them was accompanied by many changes in mdg localization, all of which occurred in one and the same cell. Thus, we could observe the series consisting of up to five successive transposition explosions leading to an almost complete change in the distribution of the mdg elements tested. We also found that in the course of successive transposition explosions, mdg elements often inserted into those sub-sections of the X-chromosome where they had previously been located. This phenomenon, designated as reverse directed transposition, was studied in more detail on insertion into the locus yellow. The rate of reverse transposition of the same mdg element to the corresponding locus was 10–100 times as high as that of primary insertion. In some cases, `the transposon shuttle' into and out of the locus was observed. The existence of `transposition memory' partially explains the specificity of mdg localization in closely related strains as well as the co-ordinated behaviour of different mdg elements in independent transposition explosions. The evolutionary significance of transposition explosions and directed reverse transposition (transposon shuttle) is discussed.
Keywords: transposition explosions (outbursts); mdg elements; in situ hydridization; loci cut, yellow
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ananiev E. V., Gvozdev V. A., Ilyin Yu V., Tchurikov N. A., Georgiev G. P. Reiterated genes with varying location in intercalary heterochromatin regions of Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1978 Dec 21;70(1):1–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00292211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. J., Pardue M. L. Ecdysone-stimulated RNA synthesis in imaginal discs of Drosophila melanogaster. Assay by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1976 Oct 12;58(1):87–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00293443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucheton A., Paro R., Sang H. M., Pelisson A., Finnegan D. J. The molecular basis of I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: identification, cloning, and properties of the I factor. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90536-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan D. J., Rubin G. M., Young M. W., Hogness D. S. Repeated gene families in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1053–1063. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimova T. I. Genetic instability at the cut locus of Drosophila melanogaster induced by the MR-h12 chromosome. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):544–547. doi: 10.1007/BF00352537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimova T. I. Superunstable alleles at the cut locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(3):390–393. doi: 10.1007/BF00331064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaga H., Saigo K. Insertion of a movable genetic element, 297, into the T-A-T-A box for the H3 histone gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4143–4147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilyin Y. V., Tchurikov N. A., Ananiev E. V., Ryskov A. P., Yenikolopov G. N., Limborska S. A., Maleeva N. E., Gvozdev V. A., Georgiev G. P. Studies on the DNA fragments of mammals and Drosophila containing structural genes and adjacent sequences. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):959–969. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery E. A., Langley C. H. Transposable Elements in Mendelian Populations. II. Distribution of Three COPIA-like Elements in a Natural Population of DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1983 Jul;104(3):473–483. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Kidwell M. G., Bingham P. M. The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: the nature of induced mutations. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):987–994. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90462-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett M. A., Jones R. S., Potter S. S. Unusual structure of the FB family of transposable elements in Drosophila. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]