Abstract
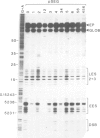
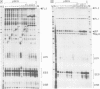
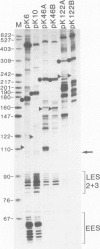
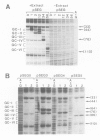
Recombinants in which the six GC-motifs (I-VI) present in the upstream element of the SV40 early promoter region have been point mutated either individually or in pairs were used to determine the possible contribution of each GC-motif to the function of the overlapping early-early and late-early SV40 promoters. GC-motif I, and to a lesser extent, GC-motifs II and III, are critical for initiation at the early-early start sites. GC-motifs IV-VI play a subsidiary role. Mutations in GC-motifs I and II do not decrease the activity of the late-early promoter, whereas mutations in the GC-motifs III-VI have a moderate effect on it. The in vivo phenotype of the GC-motif mutants can be almost fully reproduced in vitro using a nuclear extract. DNase I protection footprinting experiments using wild-type or mutated templates and nuclear extracts indicate that each GC-motif behaves principally as an independent protein-binding site, presumably for transcription factor Sp1. The effect of changing the position of the 21-bp repeat region on initiation from the early-early and late-early start sites indicates that there is little flexibility in the position in which this upstream element can efficiently activate initiation of transcription from these start sites.
Full text
PDF
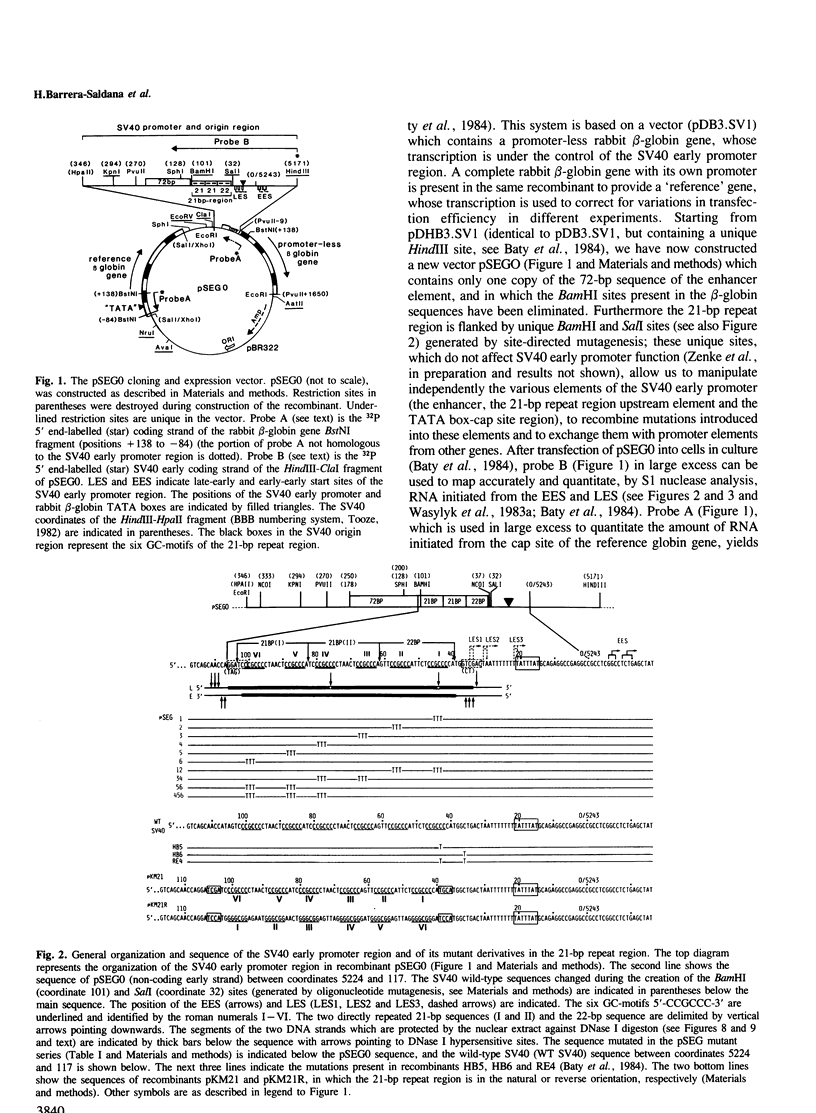

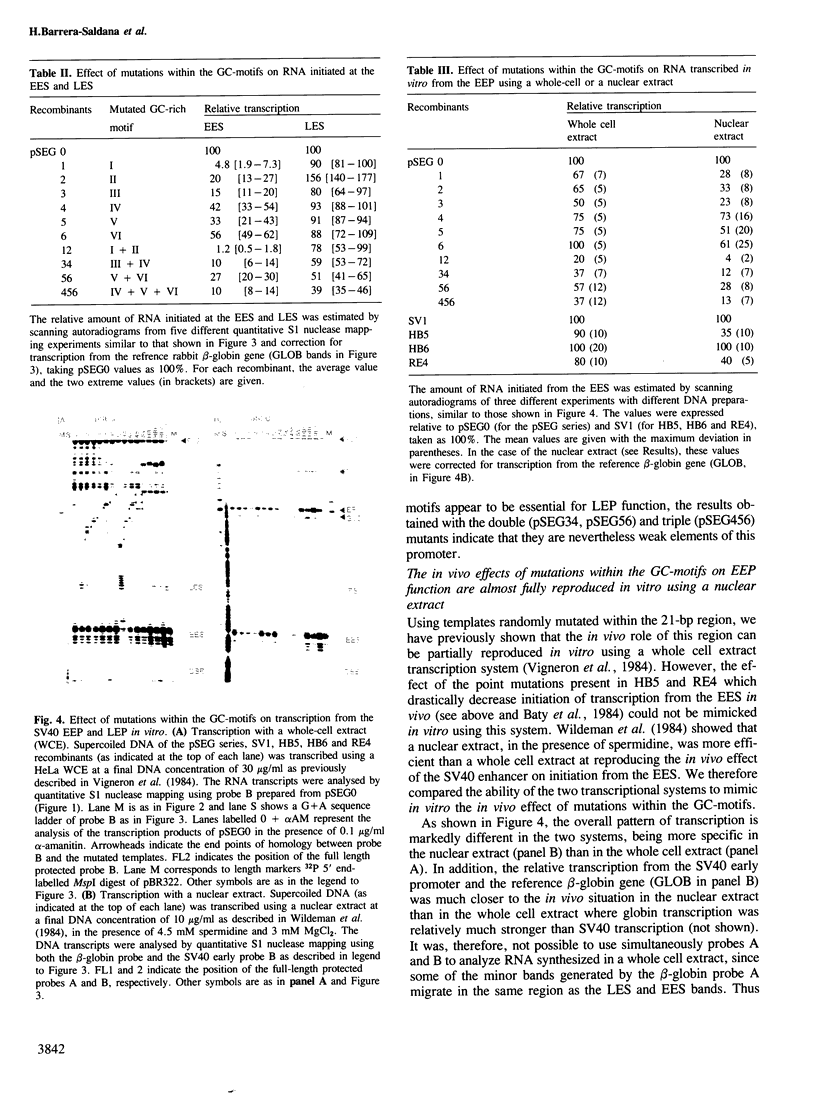

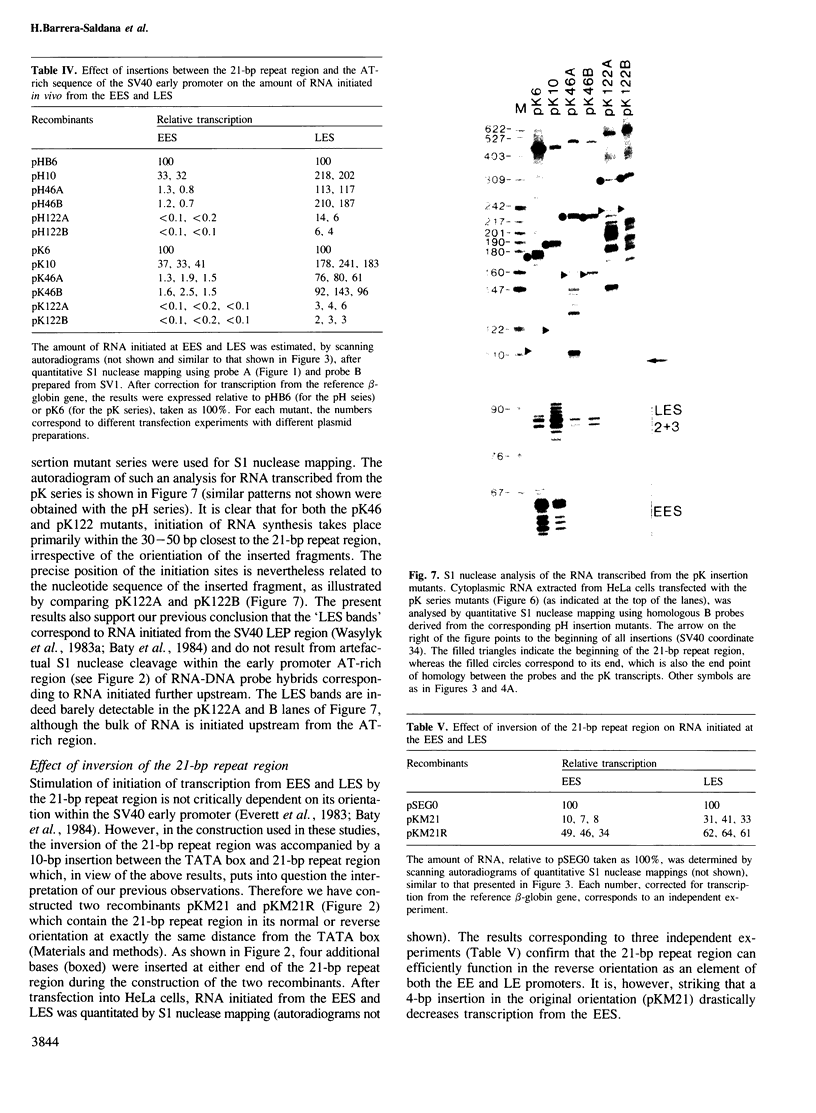
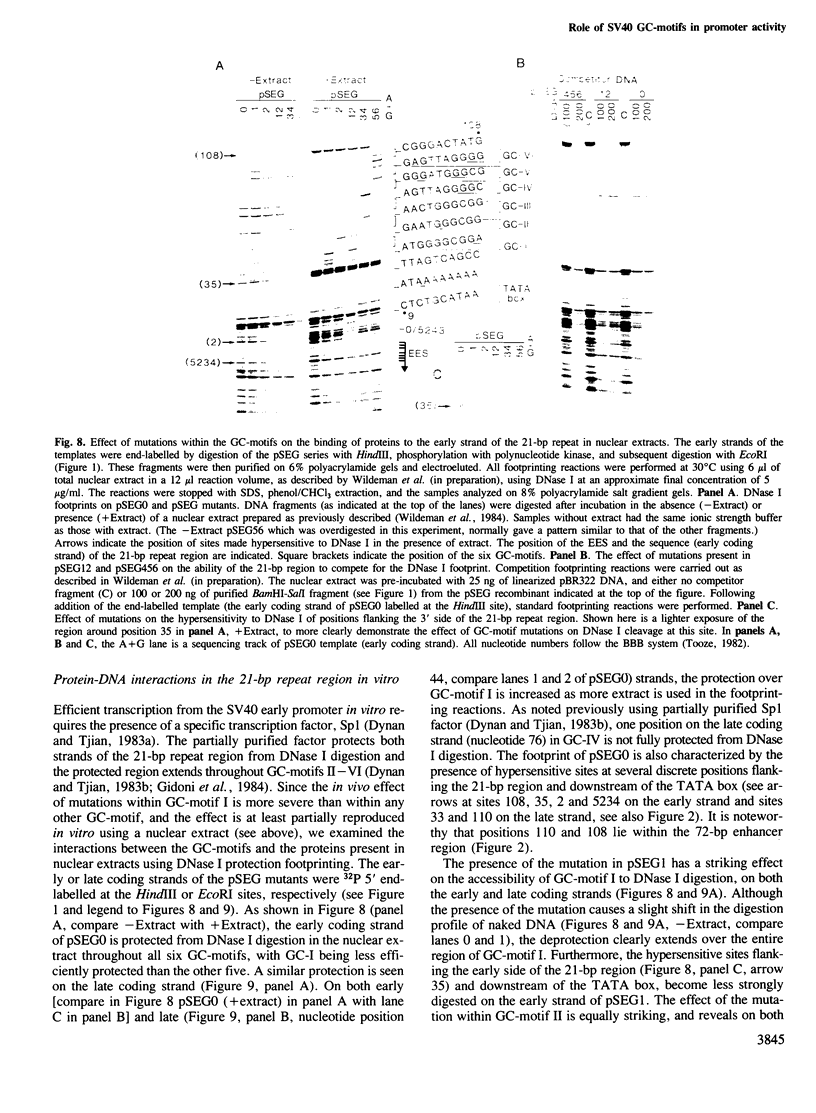




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augereau P., Wasylyk B. The MLV and SV40 enhancers have a similar pattern of transcriptional activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8801–8818. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baty D., Barrera-Saldana H. A., Everett R. D., Vigneron M., Chambon P. Mutational dissection of the 21 bp repeat region of the SV40 early promoter reveals that it contains overlapping elements of the early-early and late-early promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):915–932. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Fromm M., Berg P. Complex regulation of simian virus 40 early-region transcription from different overlapping promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1900–1914. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costlow N. A., Simon J. A., Lis J. T. A hypersensitive site in hsp70 chromatin requires adjacent not internal DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):147–149. doi: 10.1038/313147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. A detailed analysis of an HSV-1 early promoter: sequences involved in trans-activation by viral immediate-early gene products are not early-gene specific. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3037–3056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Baty D., Chambon P. The repeated GC-rich motifs upstream from the TATA box are important elements of the SV40 early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2447–2464. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. DNA structural variations produced by actinomycin and distamycin as revealed by DNAase I footprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9271–9285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström T., Zenke W. M., Wintzerith M., Matthes H. W., Staub A., Chambon P. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis by microscale 'shot-gun' gene synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3305–3316. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Sharp P. A. Sequences controlling in vitro transcription of SV40 promoters. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2293–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongstra J., Reudelhuber T. L., Oudet P., Benoist C., Chae C. B., Jeltsch J. M., Mathis D. J., Chambon P. Induction of altered chromatin structures by simian virus 40 enhancer and promoter elements. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):708–714. doi: 10.1038/307708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthes H. W., Zenke W. M., Grundström T., Staub A., Wintzerith M., Chambon P. Simultaneous rapid chemical synthesis of over one hundred oligonucleotides on a microscale. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):801–805. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. Functional relationships between transcriptional control signals of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Basu S. K., Osborne T. F., Chin D. J., Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Luskey K. L. HMG CoA reductase: a negatively regulated gene with unusual promoter and 5' untranslated regions. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigneron M., Barrera-Saldana H. A., Baty D., Everett R. E., Chambon P. Effect of the 21-bp repeat upstream element on in vitro transcription from the early and late SV40 promoters. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2373–2382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Suggs S. V., Miyoshi K., Bhatt R., Itakura K. A set of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers for DNA sequencing in the plasmid vector pBR322. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Chambon P. Short and long range activation by the SV40 enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5589–5608. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Chambon P. Transcription from the SV40 early-early and late-early overlapping promoters in the absence of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1605–1611. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Sassone-Corsi P., Grundström T., Zenke M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription from the SV40 early promoter by the enhancer involves a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3129–3133. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]