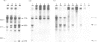Abstract
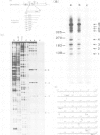
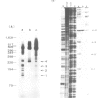
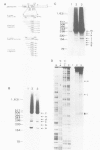
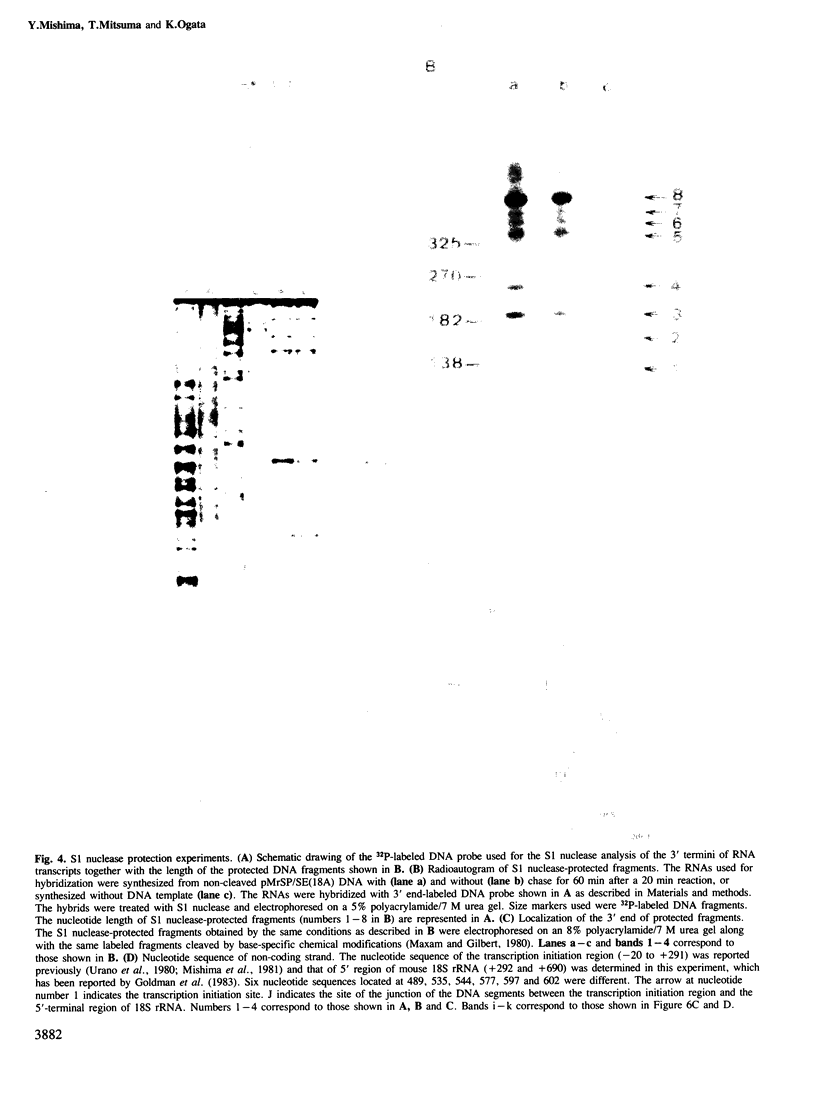
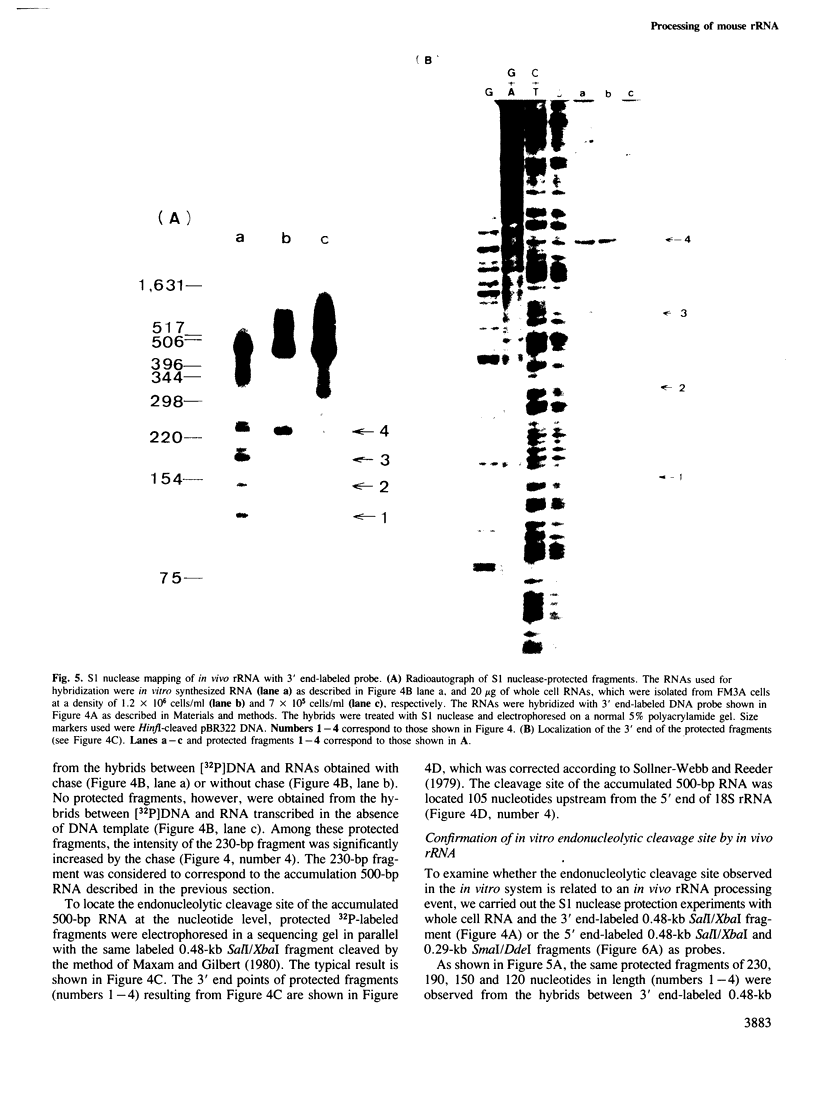
An in vitro processing system of mouse rRNA was achieved using an RNA polymerase I-specific transcription system, (S100) and recombinant plasmids consisting of mouse rRNA gene (rDNA) segments containing the transcription initiation and 5'-terminal region of 18S (or 41S) rRNA. Pulse-chase experiments showed that a specific processing occurred with transcripts of the plasmid DNAs when the direction of transcription was the correct orientation relative to the 18S rRNA coding sequence, but not with transcripts of the DNA templates in which this coding sequence was in the opposite orientation. From the S1 nuclease protection analyses, we concluded that there are several steps of endonucleolytic cleavage including one 105 nucleotides upstream from the 5' end of 18S rRNA. Intermediates cleaved at this site were identified in in vivo processing of rRNA. This result indicates that endonucleolytic cleavage takes place 105 nucleotides upstream from the 5' terminus of 18S rRNA prior to the formation of mature 18S rRNA. Trimming or cleavage of the 105 nucleotides may be involved in the formation of the 5' terminus of mature 18S rRNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman L. H., Goldman W. E., Goldberg G. I., Hebert M. B., Schlessinger D. Location of the initial cleavage sites in mouse pre-rRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1501–1510. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman L. H., Rabin B., Schlessinger D. Multiple ribosomal RNA cleavage pathways in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):4951–4966. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Mizumoto K., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. Human ribosomal RNA gene: nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region and comparison of three mammalian genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman W. E., Goldberg G., Bowman L. H., Steinmetz D., Schlessinger D. Mouse rDNA: sequences and evolutionary analysis of spacer and mature RNA regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1488–1500. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Mapping of a mouse ribosomal DNA promoter by in vitro transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6093–6102. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Nucleotide sequence requirements for specific initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6908–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Heterogeneity of 5' -termini of nucleolar 45S, 32S and 28S RNA in mouse hepatoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jan;4(1):229–240. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maderious A., Chen-Kiang S. Pausing and premature termination of human RNA polymerase II during transcription of adenovirus in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5931–5935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Kominami R., Honjo T., Muramatsu M. Cloning and determination of a putative promoter region of a mouse ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid fragment. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 5;19(16):3780–3786. doi: 10.1021/bi00557a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Yamamoto O., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. In vitro transcription of a cloned mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6773–6785. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M. Preparation of RNA from animal cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1973;7:23–51. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61770-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N. Studies on the 5' termini of Novikoff ascites hepatoma ribosomal precursor RNA. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3215–3219. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. Processing of RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:605–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urano Y., Kominami R., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. The nucleotide sequence of the putative transcription initiation site of a cloned ribosomal RNA gene of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6043–6058. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Secondary structure maps of ribosomal RNA. II. Processing of mouse L-cell ribosomal RNA and variations in the processing pathway. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 25;89(2):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90527-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto O., Takakusa N., Mishima Y., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Determination of the promoter region of mouse ribosomal RNA gene by an in vitro transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):299–303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Cech T. R. The intervening sequence excised from the ribosomal RNA precursor of Tetrahymena contains a 5-terminal guanosine residue not encoded by the DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2823–2838. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]