Abstract
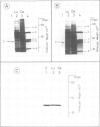
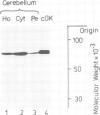
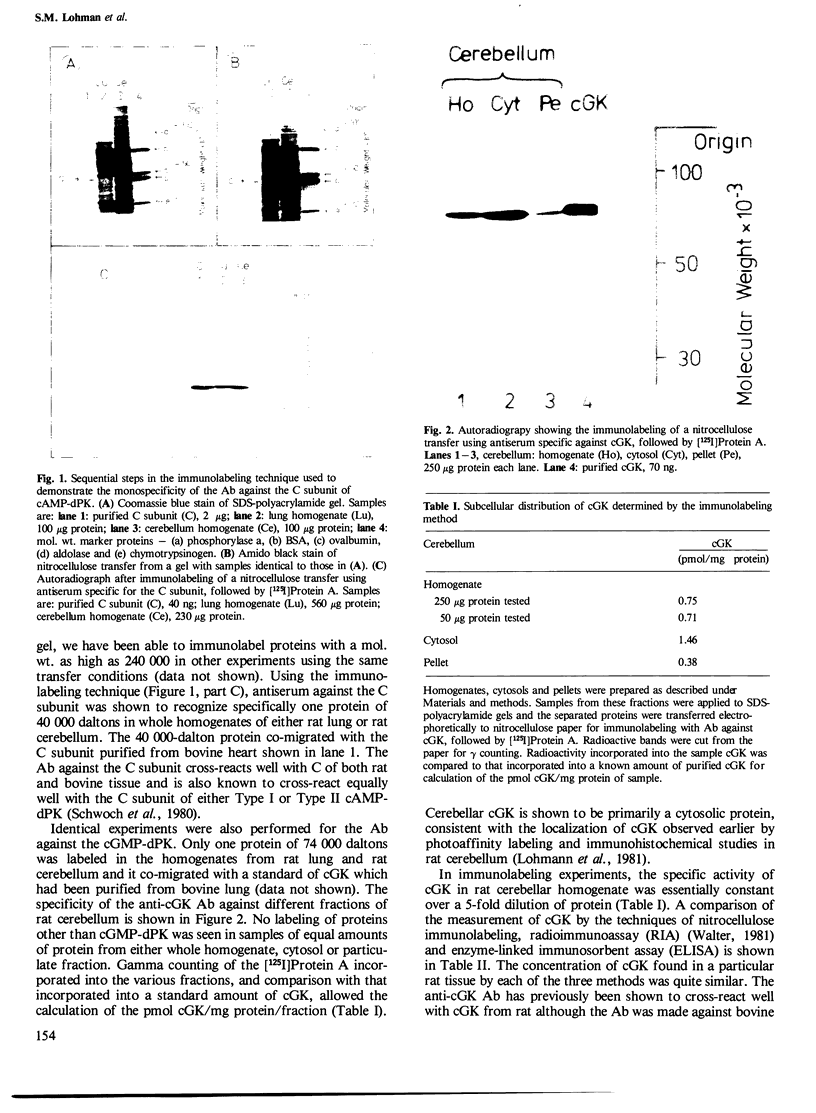
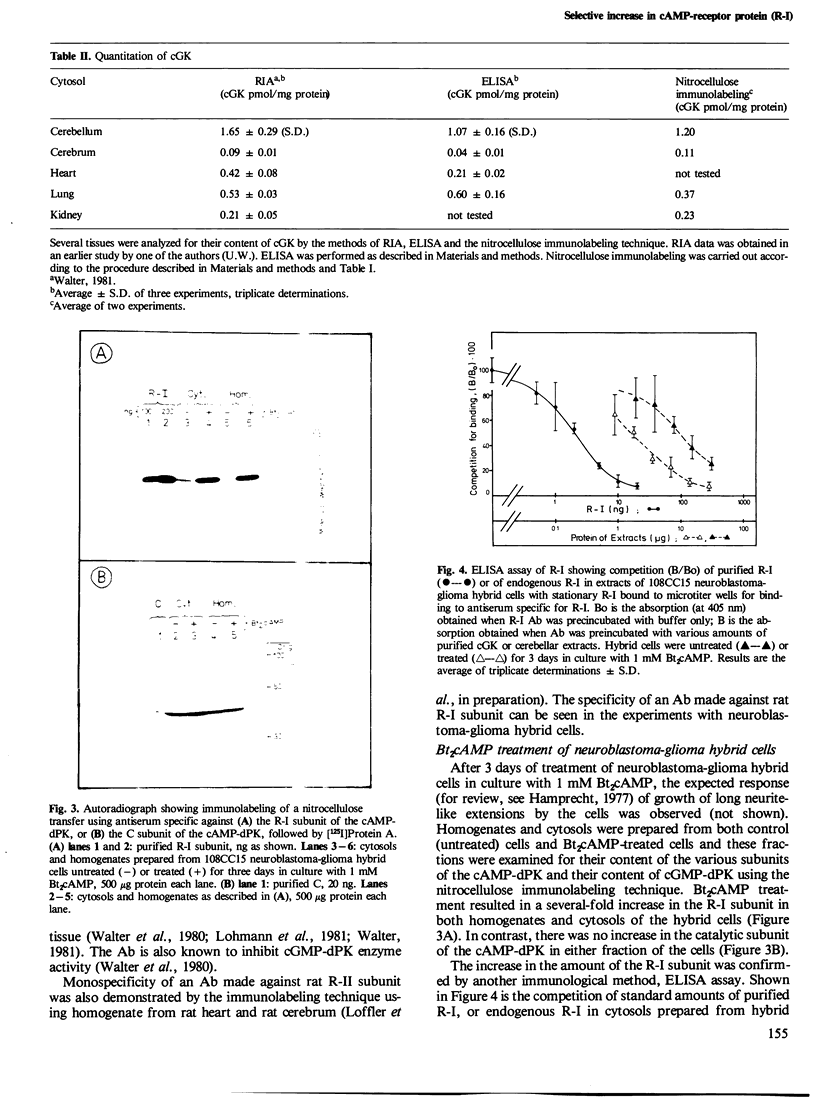
The absolute levels of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (cAMP-dPK) subunits (R-I, R-II and C) and cGMP-dependent protein kinase (cGMP-dPK) holoenzyme were studied in neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells before and after dibutyryl-cAMP (Bt2cAMP) treatment which results in differentiation of these cells. The levels were determined by two different techniques utilizing antibodies which had been raised against each individual purified protein kinase subunit (or the holoenzyme in the case of the cGMP-dPK). Electrophoretic transfer of samples from SDS-polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose paper, followed by immunolabeling of protein kinase subunits with their respective antibodies and [125I]Protein A, demonstrated the monospecific nature of the antibodies, and a selective, several-fold increase in the R-I subunit in Bt2cAMP-treated cells, with no change in the level of R-II or C subunits. A simple enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) capable of measuring nanogram amounts of the various subunits confirmed the selective increase in the R-I subunit. ELISA assay results also indicated that the R-I subunits present before and after Bt2cAMP treatment are antigenically homologous. In conclusion, the specific, sensitive immunological methods described here demonstrate the capacity of neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells to regulate separately the levels of the two distinct subunits (R-I and C) of the Type I cAMP-dPK.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beale E. G., Hartley J. L., Granner D. K. N6,O2'-dibutyryl cycle AMP and glucose regulate the amount of messenger RNA coding for hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):2022–2028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., Lincoln T. M., Keely S. L. Compartmentalization of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in heart tissue. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3854–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., West L., Flockhart D. A., Lincoln T. M., McCarthy D. Studies on the properties and mode of action of the purified regulatory subunit of bovine heart adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3997–4003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. J., Tsao J., Schimmer B. P., Mumby M. C., Beavo J. A. Alteration of the regulatory subunit of type 1 cAMP-dependent protein kinase in mutant Y1 adrenal cells resistant to 8-bromoadenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5877–5883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlichman J., Rosenfeld R., Rosen O. M. Phosphorylation of a cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):5000–5003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer N., Rosen O. M., Reichlin M. Radioimmunoassay of bovine heart protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):54–58. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geahlen R. L., Krebs E. G. Regulatory subunit of the type I cAMP-dependent protein kinase as an inhibitor and substrate of the cGMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1164–1169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geahlen R. L., Krebs E. G. Studies on the phosphorylation of the type I cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9375–9379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Holdy K. E., Walton G. M., Kanstein C. B. Purification and characterization of 3':5'-cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3918–3922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granot J., Mildvan A. S., Hiyama K., Kondo H., Kaiser E. T. Magnetic resonance studies of the effect of the regulatory subunit on metal and substrate binding to the catalytic subunit of bovine heart protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4569–4573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamprecht B. Structural, electrophysiological, biochemical, and pharmacological properties of neuroblastoma-glioma cell hybrids in cell culture. Int Rev Cytol. 1977;49:99–170. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61948-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Concentrations of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase subunits in various tissues. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1441–1447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor C. L., Beavo J. A., Steiner A. L. Radioimmunoassay of the regulatory subunit of type I cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12427–12432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlavage A. R., Taylor S. S. Site-specific cyclic nucleotide binding and dissociation of the holoenzyme of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1749–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln T. M., Dills W. L., Jr, Corbin J. D. Purification and subunit composition of guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine lung. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4269–4275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y., Chan T., Chen K. Y. Induction of the regulatory subunit of type I adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in differentiated N-18 mouse neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4579–4587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y. Differentiation-specific increase of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in the 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):298–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Greengard P. Identification of endogenous substrate proteins for cAMP-dependent protein kinase in bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9985–9992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Greengard P. Protein kinases in developing rat brain. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978 Dec;4(6):445–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Miller P. E., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Immunohistochemical localization of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase in mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prashad N., Rosenberg R. N., Wischmeyer B., Ulrich C., Sparkman D. Induction of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate binding proteins by N6,O2'-dibutyryladenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in mouse neuroblastoma cells. Analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2717–2725. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannels S. R., Corbin J. D. Two different intrachain cAMP binding sites of cAMP-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7085–7088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser G., Hamprecht B. Differential effects of various cAMP derivatives on the morphological and electrical maturation of neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Oct;141(2):498–503. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90243-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. S., Rolfes A. I. Hormonal regulation of cyclic AMP binding to specific receptor proteins in rat ovarian follicles. Characterization by photoaffinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5481–5489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Frazier G. R. Statistical analysis of radioligand assay data. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:3–22. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G., Schmid W., Strange C. M., Röwekamp W., Schütz G. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for rat tyrosine aminotransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7205–7208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwoch G., Hamann A. Determination and comparative analysis of the catalytic subunit of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate-dependent protein kinase by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Biochem J. 1982 Oct 15;208(1):109–117. doi: 10.1042/bj2080109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwoch G., Hamann A., Hilz H. Antiserum against the catalytic subunit of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Reactivity towards various protein kinases. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):223–230. doi: 10.1042/bj1920223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh T. J., Roth C., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. H. Characterization of cyclic AMP-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants lacking type I protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):926–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Agard D. A. Studies on the phosphorylation and synthesis of type I regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in intact S49 mouse lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11356–11364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., van Daalen Wetters T., Coffino P. Kinase-negative mutants of S49 mouse lymphoma cells carry a trans-dominant mutation affecting expression of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1351–1361. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. I. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5155–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Costa M. R., Breakefield X. O., Greengard P. Presence of free cyclic AMP receptor protein and regulation of its level by cyclic AMP in neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3251–3255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U. Distribution of cyclic-GMP-dependent protein kinase in various rat tissues and cell lines determined by a sensitive and specific radioimmunoassay. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(2):339–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Greengard P. Cyclic AMP-dependent and cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinases of nervous tissue. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;19:219–256. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152819-5.50023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Greengard P. Quantitative labeling of the regulatory subunit of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine heart by a photoaffinity analog. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978 Dec;4(6):437–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Miller P., Wilson F., Menkes D., Greengard P. Immunological distinction between guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3757–3762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]