Abstract
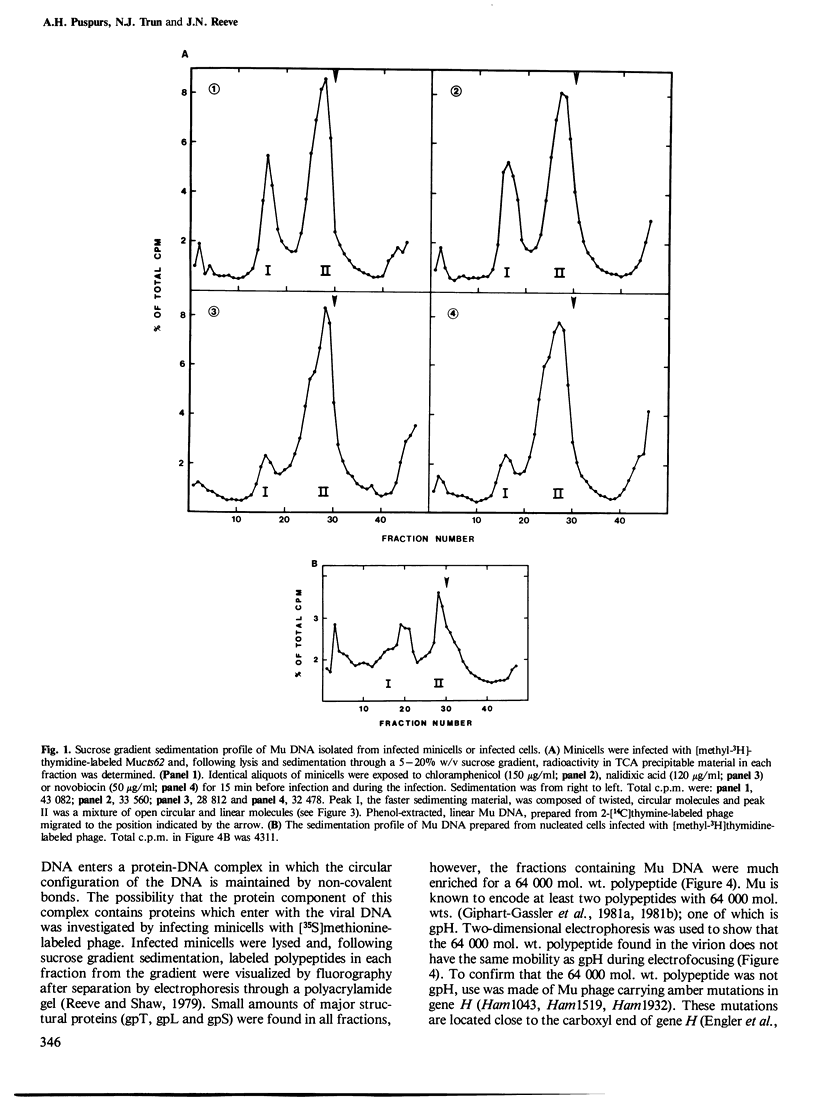
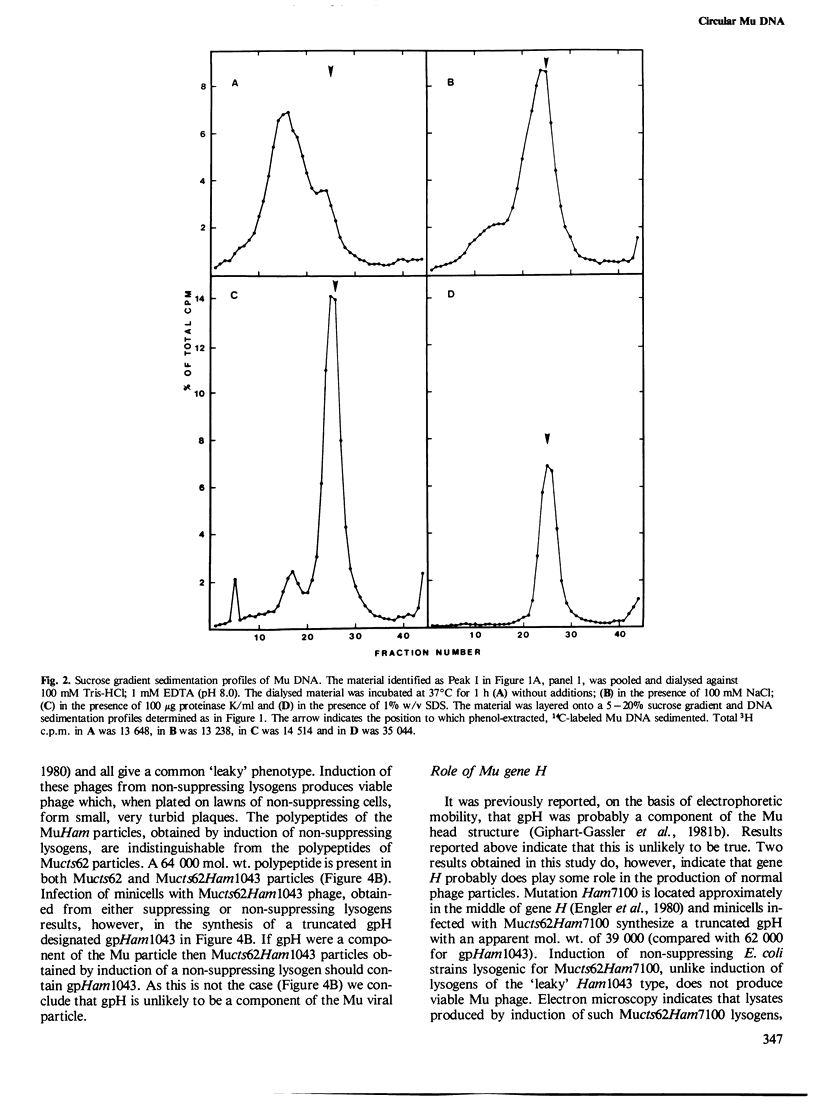
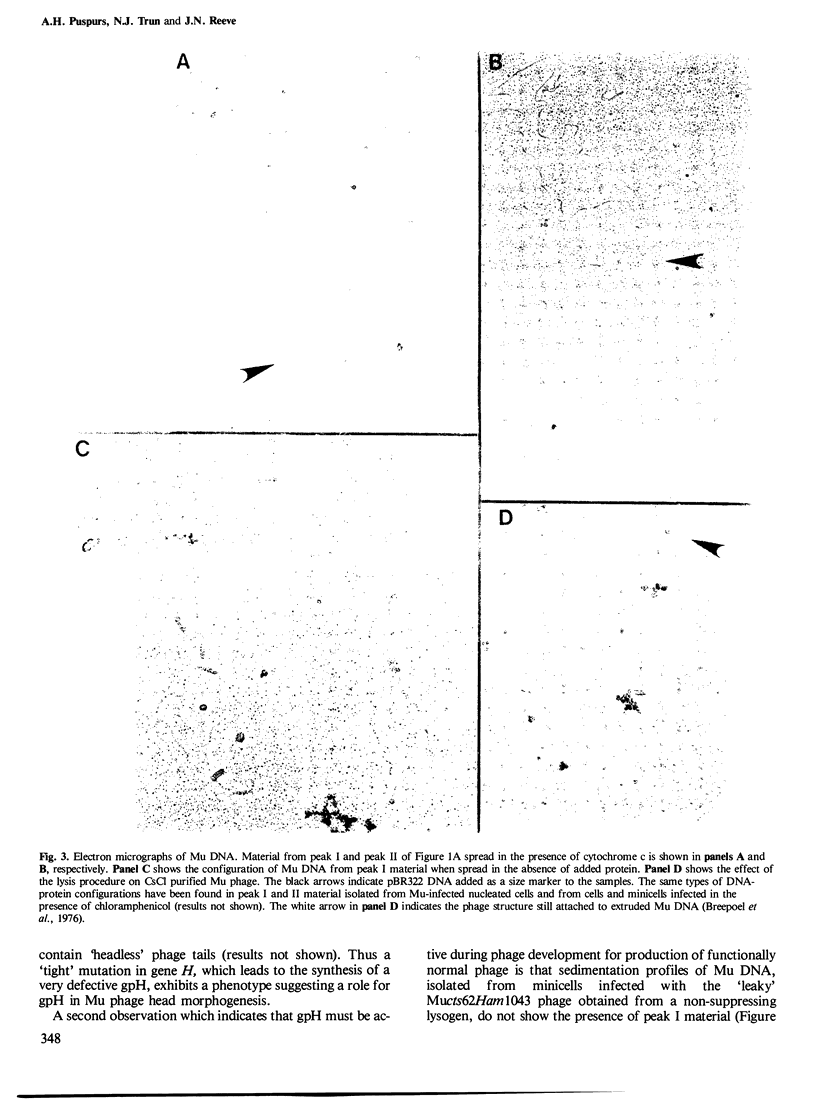
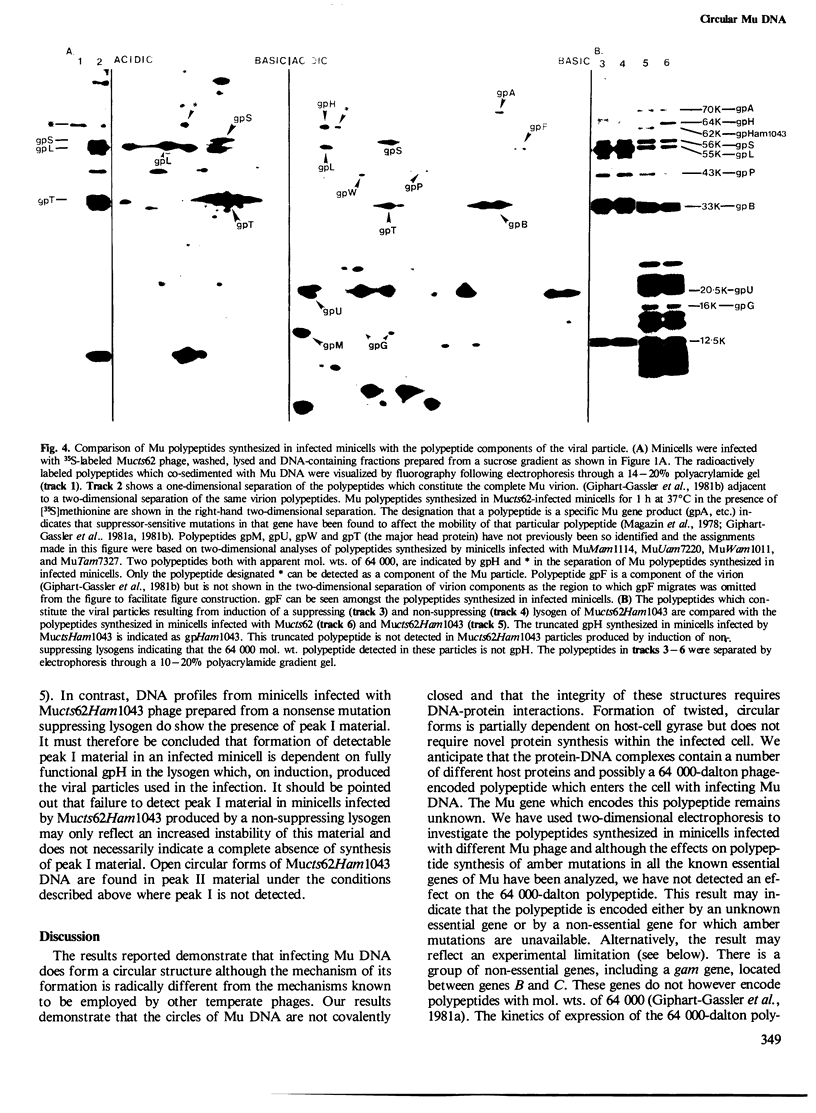
Mu DNA, isolated from infected cells or minicells, has been shown to be held by proteins in twisted and open circular forms. Circularization does not require protein synthesis in the infected cells. A 64,000-dalton polypeptide is injected into the infected cell with Mu DNA and co-sediments with Mu DNA through sucrose gradients. Circularization of the infecting Mu DNA does not require removal of the Escherichia coli DNA sequences which are attached to both ends of the Mu genome in the viral particle.
Full text
PDF
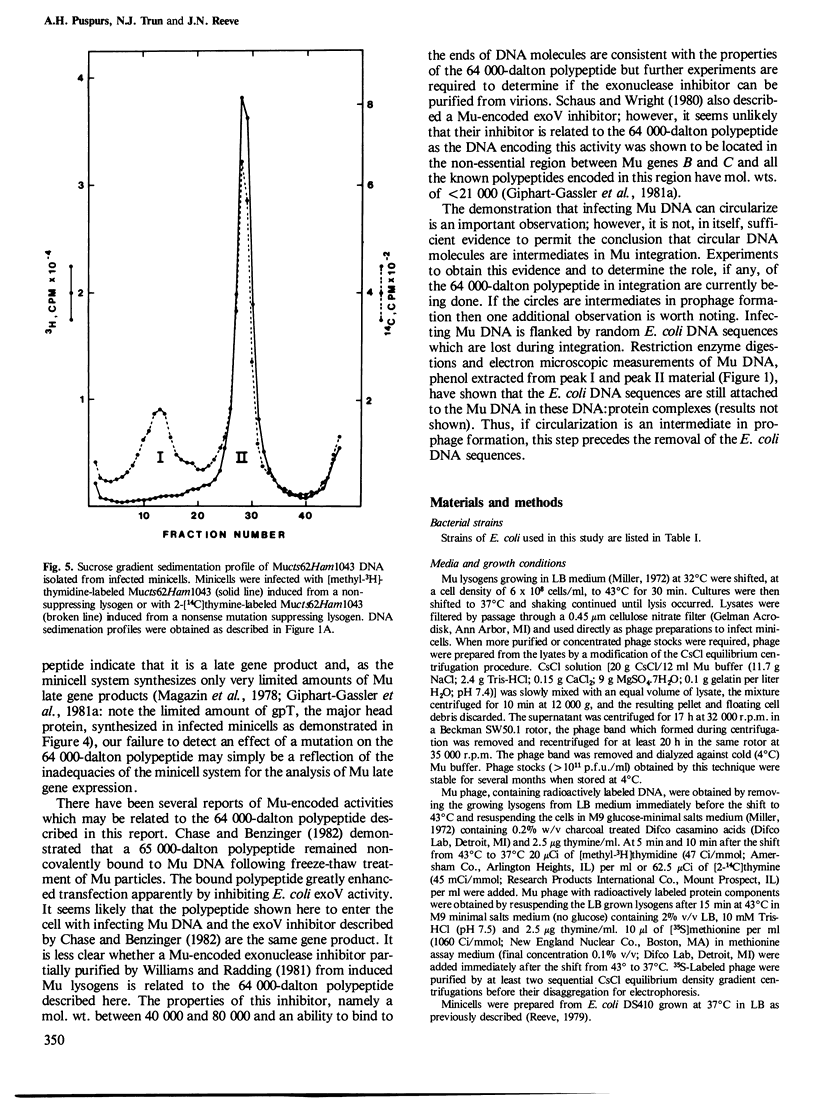


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abermann R., Salpeter M. M. Visualization of deoxyribonucleic acid molecules by protein film adsorption and tantalum-tungsten shadowing. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Sep;22(9):845–855. doi: 10.1177/22.9.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breepoel H., Hoogendorp J., Mellema J. E., Wijffelman C. Linkage of the variable end of the bacteriophage mu DNA to the tail. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):279–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90335-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase C. D., Benzinger R. H. Transfection of Escherichia coli spheroplasts with a bacteriophage Mu DNA-protein complex. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):176–185. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.176-185.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler J. A., Forgie R. A., Howe M. M. Restriction endonuclease BamHI cleaves bacteriophage Mu DNA within cistrons E and F. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):79–83. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giphart-Gassler M., Reeve J., van de Putte P. Polypeptides encoded by the early region of bacteriophage Mu synthesized in minicells of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):165–191. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giphart-Gassler M., Wijffelman C., Reeve J. Structural polypeptides and products of late genes of bacteriophage Mu: characterization and functional aspects. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):139–163. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90338-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harford A. G., Beer M. Electron-microscopic localization of the binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymease to T7 DNA in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 21;69(2):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann H., Burkardt H. J., Pühler A., Reeve J. N. Transposon mutagenesis of the gene encoding the bacteriophage P1 restriction endonuclease. Co-linearity of the gene and gene product. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 15;144(3):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90097-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey A. D., Burgi E., Ingraham L. COHESION OF DNA MOLECULES ISOLATED FROM PHAGE LAMBDA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):748–755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Tomizawa J. Prophage P1, and extrachromosomal replication unit. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:791–798. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahmann R., Kamp D. Nucleotide sequences of the attachment sites of bacteriophage Mu DNA. Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):247–250. doi: 10.1038/280247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungquist E., Bukhari A. I. Behavior of bacteriophage Mu DNA upon infecton of Escherichia coli cells. J Mol Biol. 1979 Sep 25;133(3):339–357. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90397-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens G., Amann E., Reeve J. N. Bacteriophage SPP1 polypeptides synthesized in infected minicells and in vitro. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;172(3):271–279. doi: 10.1007/BF00271726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Day K., Schultz D., Ericsen W., Rawluk L., Howe M. Correction and refinement of the genetic map of bacteriophage Mu. Virology. 1979 Mar;93(2):320–328. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J. Use of minicells for bacteriophage-directed polypeptide synthesis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:493–503. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaus N. A., Wright A. Inhibition of Escherichia coli exonuclease V by bacteriophage Mu. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):214–217. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. A., Jr, Kelly T. J., Jr, Rhoades M. The intracellular forms of T7 and P22 DNA molecules. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:417–424. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Radding C. M. Partial purification and properties of an exonuclease inhibitor induced by bacteriophage Mu-1. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):548–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.548-558.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




