Telomerase can generate a novel telomere at a DNA break, with potentially lethal consequences for the cell. Ouenzar et al. reveal novel roles for Pif1, Rad52, and Siz1-dependent sumoylation in the spatial exclusion of telomerase from sites of DNA repair during the cell cycle.
Abstract
Telomerase can generate a novel telomere at DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), an event called de novo telomere addition. How this activity is suppressed remains unclear. Combining single-molecule imaging and deep sequencing, we show that the budding yeast telomerase RNA (TLC1 RNA) is spatially segregated to the nucleolus and excluded from sites of DNA repair in a cell cycle–dependent manner. Although TLC1 RNA accumulates in the nucleoplasm in G1/S, Pif1 activity promotes TLC1 RNA localization in the nucleolus in G2/M. In the presence of DSBs, TLC1 RNA remains nucleolar in most G2/M cells but accumulates in the nucleoplasm and colocalizes with DSBs in rad52Δ cells, leading to de novo telomere additions. Nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA depends on Cdc13 localization at DSBs and on the SUMO ligase Siz1, which is required for de novo telomere addition in rad52Δ cells. This study reveals novel roles for Pif1, Rad52, and Siz1-dependent sumoylation in the spatial exclusion of telomerase from sites of DNA repair.
Introduction
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are one of the most cytotoxic forms of DNA damage, and their repair is critical for maintenance of genome integrity and cell survival. Classically, two pathways of DSB repair have been defined: nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR). NHEJ, which occurs preferentially in G1, directly rejoins the DNA ends and often results in loss of genetic information at the break site (Moore and Haber, 1996; Takata et al., 1998). HR, which occurs during S and G2 phase, requires an homologous template for repair and generally preserves genetic information at the break site (Moore and Haber, 1996; Pâques and Haber, 1999). The choice of DSB repair by the HR or NHEJ pathway is dictated in part by the presence or absence of 5′-to-3′ resection, which generates 3′ single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) tails at the DSB ends and commits DSB repair to HR.
In addition to HR and NHEJ, DSBs can be repaired by the action of telomerase at the break site, a phenomenon referred to as telomere healing or de novo telomere addition, which often leads to gross chromosomal rearrangements (GCRs; Kramer and Haber, 1993; Pennaneach et al., 2006). Telomere healing has been particularly well studied in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In yeast, telomerase is composed of an RNA moiety called TLC1, which contains the template sequence and acts as scaffold on which the catalytic reverse transcription Est2 and associated proteins (Est1, Est3, and yKu70/80) bind (Singer and Gottschling, 1994; Counter et al., 1997; Lingner et al., 1997). Recruitment of telomerase to telomeres during S phase depends on the interaction between Est1 and the telomeric DNA single-strand binding protein Cdc13 (Pennock et al., 2001; Bianchi et al., 2004; Bianchi and Shore, 2008).
Telomere healing events in yeast are suppressed by numerous mechanisms. One includes the 5′–3′ DNA helicase Pif1 that acts as a potent inhibitor of telomere addition at telomeres and DSBs (Schulz and Zakian, 1994; Zhou et al., 2000). Pif1-deficient cells have overelongated telomeres and a rate of telomere healing that is dramatically increased compared with WT cells (Myung et al., 2001). Pif1 is phosphorylated upon DNA damage in a Mec1-dependent manner, and a phosphorylation-defective mutant of Pif1 (pif1-4A) displays an increased propensity to add telomeric repeats on an HO endonuclease–induced DSB (Makovets and Blackburn, 2009). In addition to Pif1, the Mec1 kinase phosphorylates Cdc13 on its S306 residue, a phosphorylation event suggested to suppress Cdc13 recruitment to DSB ends that have little or no telomere-like sequences (Zhang and Durocher, 2010). However, recent evidence shows that these mechanisms are not sufficient to repress all Cdc13 and telomerase recruitment events at DSBs because Cdc13 and telomerase subunits can be detected at a DSB by chromatin immunoprecipitation, even if no telomere is added to the break (Oza et al., 2009; Chung et al., 2010; McGee et al., 2010; Ribaud et al., 2012).
These results suggest a competition between de novo telomere addition and other repair pathways. Indeed, decreased resection by simultaneous deletion of SGS1 and EXO1 partially affects HR and increases de novo telomere formation via the recruitment of Cdc13 to the break site (Chung et al., 2010; Lydeard et al., 2010), suggesting that Cdc13 binding to DSB might be a limiting factor for telomere addition. In agreement with this, artificial binding of Cdc13 or Est1 subunit to an HO-induced DSB increases the repair of DSB by telomerase (Bianchi et al., 2004). Another factor involved in HR that affects de novo telomere addition is Rad52, although its role in this process is controversial. Indeed, deletion of RAD52 does not increase spontaneous telomere addition at HO-induced or spontaneous DSB in yeast (Kramer and Haber, 1993; Mangahas et al., 2001; Myung et al., 2001). However, deletion of RAD52 increases the frequency of telomere addition in subtelomeric regions (Ricchetti et al., 2003). Furthermore, the deletion of RAD52 acts synergistically with the pif1-m2 mutation, an allele that reduces the nuclear activity of Pif1, to increase de novo telomere addition (Myung et al., 2001), suggesting a specific but still unknown role for Rad52 in the suppression of telomere healing.
Previous studies on telomere healing were performed using methods that measure telomerase recruitment or de novo telomere elongation at a single unrepaired endonuclease-induced DSB (Ribeyre and Shore, 2013). Although these approaches revealed extensive mechanistic details on this process, they also showed that sequences surrounding the DNA break and location of the break in the chromosome affect the efficacy by which telomerase recruitment and telomere healing can occur (Ribeyre and Shore, 2013). However, novel approaches are needed to study the behavior, dynamics, and regulation of telomerase molecules in the presence of random breaks in the genome.
In this study, we address this question by visualizing the spatial distribution of telomerase molecules in the presence of random DSBs using single-molecule fluorescent in situ hybridization on endogenous TLC1 RNA. With this approach, we found that TLC1 RNA is engaged in an intranuclear trafficking during the cell cycle, as it accumulates in the nucleoplasm in G1/S, whereas it localizes preferentially in the nucleolus in G2/M. This trafficking depends on the helicase Pif1, suggesting a role for this process in the regulation of de novo telomere addition. Indeed, treatment with the radiomimetic drug bleomycin increases the presence of TLC1 RNA molecules in the nucleoplasm in G2/M cells. We show that Rad52 suppresses the nucleoplasmic localization of TLC1 RNA in G2/M by inhibiting Cdc13 accumulation at DSBs. Furthermore, we found that the SUMO E3 ligase Siz1 regulates the nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA and de novo telomere addition without affecting Cdc13 accumulation at DSBs. Altogether, our data show that Pif1, Rad52, and Siz1 act together to control the accumulation of TLC1 RNA and Cdc13 at DSBs and spatially exclude telomerase into the nucleolus, away from sites of DNA repair.
Results
TLC1 RNA nuclear distribution varies during the cell cycle
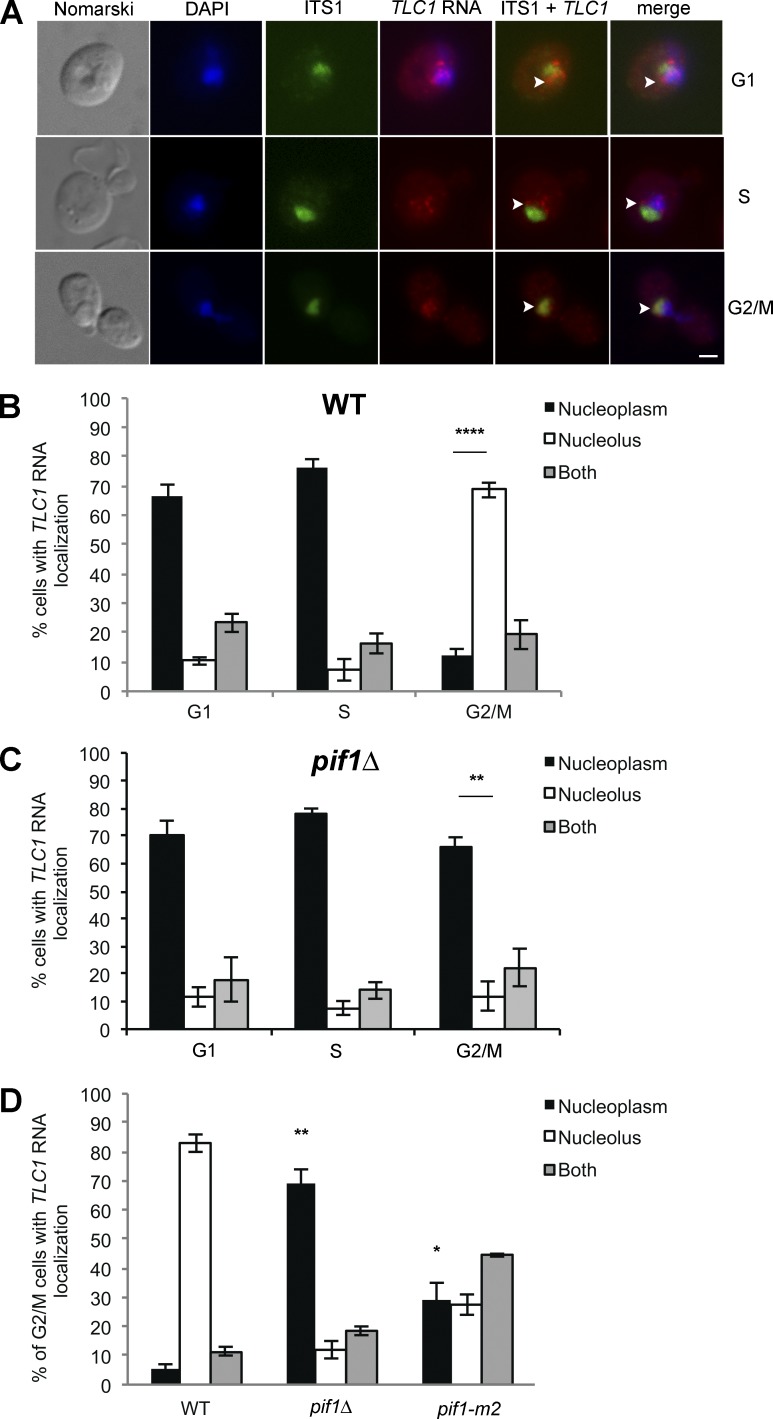
Previous studies used FISH to show that TLC1 RNA accumulates in the nucleoplasm in G1 and S phase, which is related to its function in telomere elongation (Teixeira et al., 2002; Gallardo et al., 2008). Because the telomerase RNA is the limiting component of the telomerase holoenzyme in yeast (Mozdy and Cech, 2006), its dynamics should reflect the dynamics of the active telomerase complex in vivo better than other telomerase components. However, a systematic analysis of the distribution of TLC1 RNA in each phase of the cell cycle has not yet been conducted. To do so, quantification of telomerase RNA in the nucleus of yeast cells at different phases of the cell cycle was performed using FISH on the endogenous TLC1 RNA. Budding index was used to determine the cell cycle phase of each cell. Beside TLC1 RNA, the yeast nucleolus was detected using a probe against the ITS1 ribosomal RNA spacer precursor, and the nucleoplasm was labeled using DAPI. We detected between 3 and 10 nuclear TLC1 RNA foci per cell, with each focus corresponding to a single TLC1 RNA molecule, as recently reported (Bajon et al., 2015). Although cells in G1 and S phase displayed a nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA foci, as previously shown (Gallardo et al., 2008), a predominantly nucleolar accumulation of TLC1 RNA foci was observed in G2/M cells, as shown by colocalization with the ITS1 ribosomal RNA precursor (Fig. 1, A and B). Accumulation of TLC1 RNA in the nucleolus in G2/M was further validated by cell synchronization with nocodazole (see Fig. 2 C).
Figure 1.
Intranuclear trafficking of TLC1 RNA during the cell cycle depends on Pif1. (A) Monitoring TLC1 RNA localization during the cell cycle by FISH. The nucleolus was stained with a probe against the ITS1 spacer of the rRNA precursor (labeled with Cy5). Arrowheads mark the position of the TLC1 RNA in selected cells. DAPI was used to stain DNA. Bar, 1 µm. (B) Quantification of TLC1 RNA localization during the cell cycle; n = 900 cells. (C) Quantification of TLC1 RNA localization during the cell cycle in pif1Δ cells; n = 900 cells. (D) Quantification of TLC1 RNA localization in G2/M in WT, pif1Δ, and pif1-m2 cells; n = 200–900 cells. Error bars represent ±SD. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.001 (two-tailed t test).
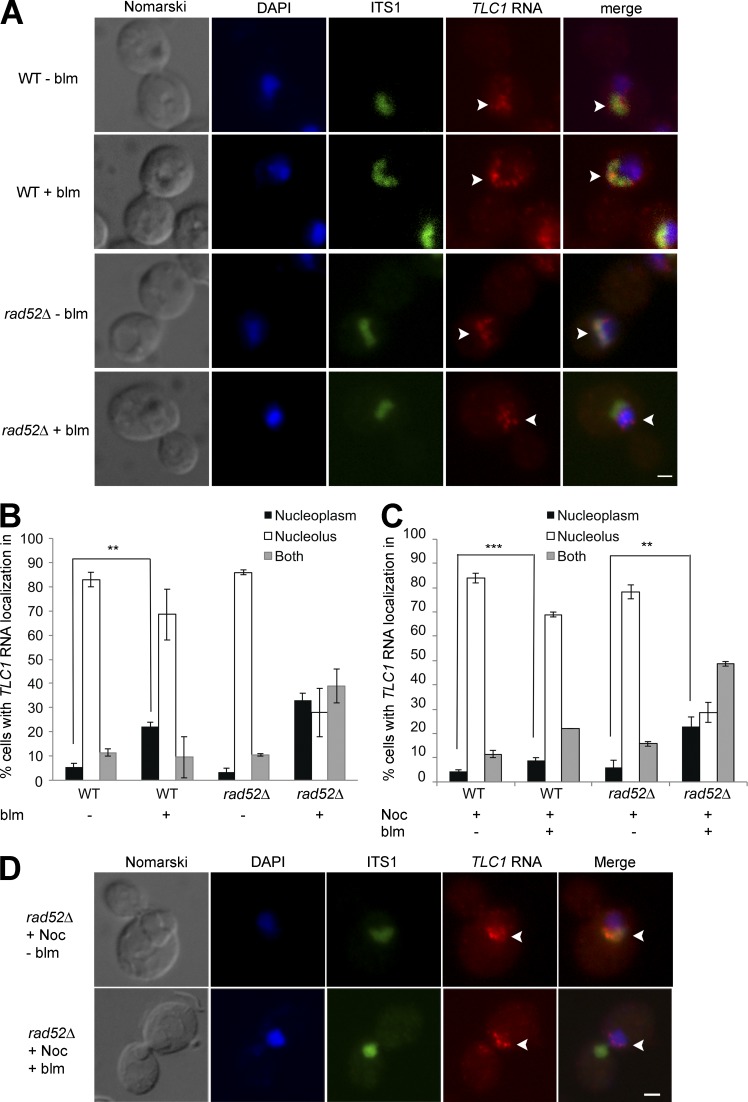
Figure 2.
TLC1RNA accumulates in the nucleoplasm in G2/M in rad52Δ cells after DNA damage. (A) FISH on TLC1 RNA in WT or rad52Δ cells treated or not with bleomycin (blm). Arrowheads indicate position of TLC1 RNA foci in the nucleus. Bar, 1 μm. (B) Quantification of TLC1 RNA distribution in the nucleus in WT or rad52Δ cells after treatment with bleomycin (blm); n = 200 cells. (C) TLC1 RNA can relocalize to the nucleoplasm from the nucleolus in rad52Δ cells treated with bleomycin. Quantification of TLC1 RNA distribution in the nucleus in WT or rad52Δ cells synchronized with nocodazole (Noc), followed by treatment with bleomycin (blm); n = 200–300 cells. (D) FISH on TLC1 RNA in rad52Δ cells synchronized with nocodazole (Noc) and treated or not with bleomycin (blm). Arrowheads indicate position of TLC1 RNA foci in cells. Bars, 1 µm. Error bars represent ±SD. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.005 (two-tailed t test).
To identify factors required for this intranuclear trafficking of TLC1 RNA, we focused on factors known to regulate telomere length. One of these factors is the Pif1 5′–3′ helicase, which removes telomerase from telomeres in late S/G2 and acts as a negative regulator of telomerase activity (Schulz and Zakian, 1994; Zhou et al., 2000). Quantification of TLC1 RNA localization during the cell cycle in a pif1Δ strain shows that deletion of PIF1 inhibits the nucleolar accumulation of TLC1 RNA in G2/M, as TLC1 RNA accumulated in the nucleoplasm in all the phases of the cell cycle (Figs. 1 C and S1 A). This result was validated using the pif1-m2 mutant, an allele with reduced nuclear activity of Pif1 (Schulz and Zakian, 1994). This mutant displays a phenotype midway between WT and pif1Δ strains, with TLC1 RNA present in both nucleoplasm and nucleolus in G2/M (Fig. 1 D and S1B). Altogether, these results suggest that Pif1 promotes the trafficking of TLC1 RNA from the nucleoplasm to the nucleolus in G2/M.
Regulation of TLC1 RNA nuclear trafficking by Rad52 after DNA damage
Given that TLC1 RNA molecules accumulate preferentially in the nucleolus during G2/M, we hypothesized that the nucleolar localization of TLC1 RNA could reduce the capacity of telomerase to interfere with HR to repair DSBs in G2/M (Diede and Gottschling, 1999). Indeed, in the yeast S. cerevisiae, HR is mostly excluded from the nucleolus, and DSBs in ribosomal DNA (rDNA) are repaired by HR in the nucleoplasm, suggesting that HR is exclusively nucleoplasmic (Lisby et al., 2003; Torres-Rosell et al., 2007). Furthermore, Pif1, which promotes the trafficking of TLC1 RNA to the nucleolus, inhibits de novo telomere addition by telomerase at DSBs (Schulz and Zakian, 1994; Phillips et al., 2015). To test this hypothesis, the distribution of TLC1 RNA molecules was determined by FISH after induction of DNA damage using bleomycin, a radiomimetic agent that preferentially generates DSBs (Chen and Stubbe, 2005). Yeast cells were exposed to 5 µg/ml bleomycin for 180 min, conditions that cause 90% of the cells to have at least one DSB per cell (Fig. S2 A). After treatment with bleomycin, FISH was performed to detect both TLC1 and ITS1 RNA. TLC1 RNA foci remained predominantly nucleolar in both bleomycin treated and untreated G2/M cells (Fig. 2 A). However, quantification of the phenotypes revealed a small but significant accumulation of G2/M cells with TLC1 RNA in the nucleoplasm in bleomycin-treated cells (Fig. 2 B), suggesting that DNA damage affect the nucleolar distribution of this RNA. To confirm the link between TLC1 RNA accumulation in the nucleolus and repair of DSB in the nucleoplasm, HR was inhibited by deletion of RAD52. Surprisingly, the percentage of G2/M cells with nucleolar TLC1 RNA foci decreased from 70% in WT cells to 30% in rad52Δ cells treated with bleomycin, and most cells accumulated TLC1 RNA foci predominantly in the nucleoplasm or in both compartments (Fig. 2, A and B).
To determine if the nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA in the presence of DSBs is caused by its retention in the nucleoplasm or by its relocalization from the nucleolus to nucleoplasm, yeast cells were synchronized in G2 with nocodazole (Fig. S2 B), followed by treatment with bleomycin. Although nocodazole-treated cells displayed TLC1 RNA foci in the nucleolus, treatment with bleomycin still resulted in the redistribution of TLC1 RNA foci toward the nucleoplasm in rad52Δ cells, suggesting a dynamic trafficking of this RNA between these two compartments (Fig. 2, C and D). Altogether, these results suggest that in cells containing DSBs, TLC1 RNA can relocalize from the nucleolus to the nucleoplasm and that its nucleolar retention depends on RAD52.
TLC1 RNA colocalizes with DSB sites in the nucleoplasm
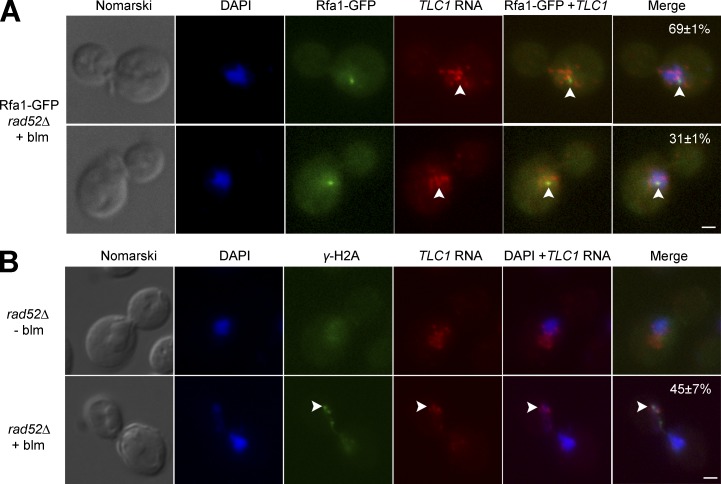
To understand the significance of the nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA in DNA damaged cells devoid of Rad52, the colocalization between TLC1 RNA and a cytological marker of DSBs was measured. Rfa1, the largest subunit of the heterotrimeric complex RPA, was used as a marker, because it is recruited to DSBs and binds ssDNA generated by resection (Alani et al., 1992; Krogh and Symington, 2004). For this reason, Rfa1 is frequently used as a specific cytological marker for DNA end processing in vivo (Gasior et al., 1998; Raderschall et al., 1999; Barlow et al., 2008). Rfa1 was fused to GFP and, similarly to ionizing radiation–induced DSBs, a single Rfa1-GFP focus was observed in cells treated with bleomycin, in both WT and rad52Δ cells (Fig. 3 A). To validate this assay, colocalization between TLC1 RNA and Rfa1-GFP foci in G2/M was measured in pif1-m2 cells treated with bleomycin. Because Pif1 plays a key role in removing telomerase from DSBs and inhibits de novo telomere addition (Myung et al., 2001), we expect an increased colocalization between TLC1 RNA and Rfa1-GFP foci in pif1-m2 compared with WT cells. Indeed, we observed a colocalization between a Rfa1-GFP focus and a TLC1 RNA focus in 29% of pif1-m2 cells treated with bleomycin, whereas such colocalization was observed in 16% of WT cells (Fig. S3 A). FISH was performed on Rfa1-GFP rad52Δ cells to detect endogenous TLC1 RNA after bleomycin treatment. In 31% of the cells, one of the TLC1 RNA foci colocalized with an Rfa1-GFP focus (Fig. 3 A and Fig. S3 B). This percentage is higher than in WT cells (Fig. S3 A) or compared to the colocalization of TLC1 RNA foci with a random nuclear focus (corresponding to the MDN1 transcription site), which colocalize only in 9% of the cells (Fig. S3 C).
Figure 3.
TLC1RNA partially colocalizes with DSB sites in rad52Δ cells. (A) FISH against TLC1 RNA in rad52Δ cells expressing Rfa1-GFP and treated with bleomycin (blm). Numbers in percentages represent the percentage of cells with the following phenotypes: no colocalization between a TLC1 RNA focus and Rfa1-GFP focus (top) or colocalization between a TLC1 RNA focus and Rfa1-GFP foci (bottom). Bar, 1 µm; n = 200 cells. (B) Dual FISH against TLC1 RNA and immunofluorescence on γ-H2A protein in rad52Δ cells after exposure or not to bleomycin (blm). Colocalization (indicated by arrowheads) was detected in 45 ± 7% of the cells. Bar, 1 µm; n = 200 cells.
It is possible that TLC1 RNA nucleoplasmic foci that are not colocalized with a Rfa1-GFP focus could be associated with other DNA damage sites (Fig. S3 D). To test this possibility, another cytological marker of DSB, γ-H2A, was combined with FISH on TLC1 RNA. In contrast to Rfa1-GFP, γ-H2A form several foci in mammalian and yeast cells after DNA damage (Rogakou et al., 1999; Mazumder et al., 2013). In yeast, γ-H2A accumulation is a direct readout of Mec1 activity at a DSB (Ira et al., 2004). Simultaneous FISH against TLC1 RNA and immunofluorescence (IF) with an antibody specific to γ-H2A was performed in cells treated or not with bleomycin. In these conditions, yeast cells exposed to 5 µg/ml bleomycin during 180 min contained between two and four γ-H2A foci per cell, whereas untreated cells did not contain any foci (Fig. 3 B). As observed with Rfa1-GFP, most TLC1 RNA foci were in the nucleoplasm in rad52Δ cells treated with bleomycin, but only one TLC1 RNA focus colocalized with one of the γ-H2A foci in 45% of the cells (Fig. 3 B). Altogether, these results show that during DNA damage and in the absence of Rad52, most TLC1 RNA molecules are excluded from the nucleolus and accumulate in the nucleoplasm in G2/M, and a fraction of these molecules accumulate at DSBs.
TLC1 RNA nucleoplasmic accumulation after DNA damage depends on Cdc13 and the MRX complex and is regulated by the DNA damage response pathway
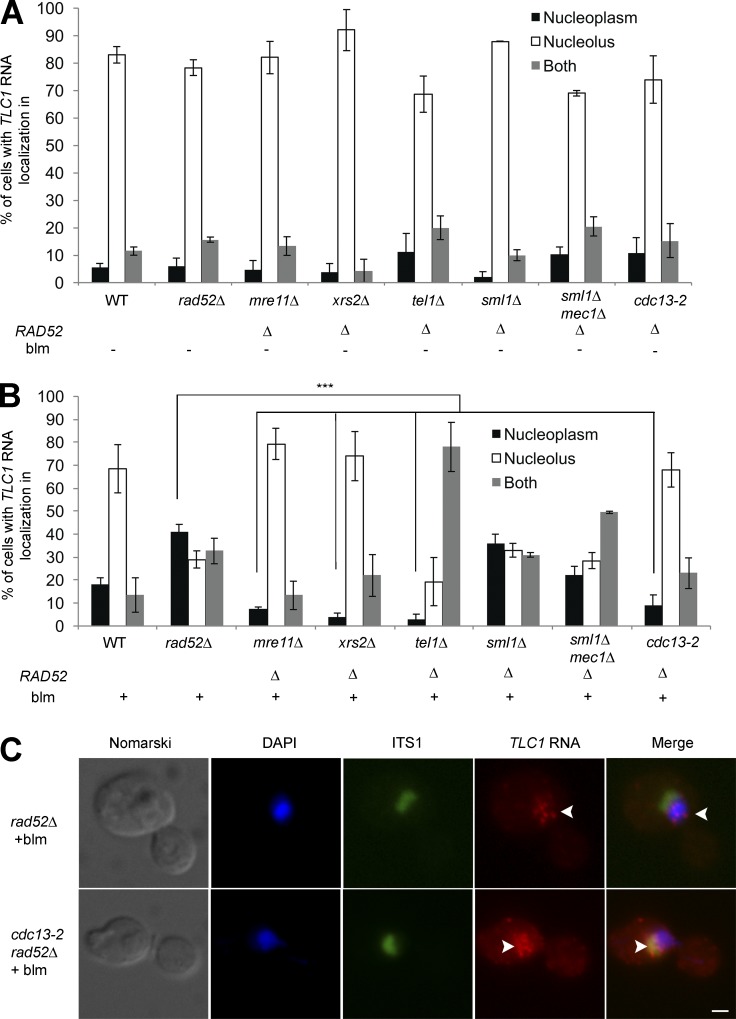
The observation that TLC1 RNA molecules colocalize with only a fraction of the DSBs raises questions concerning the link between TLC1 RNA trafficking and the DNA damage response. To confirm that TLC1 RNA accumulation in the nucleoplasm depends on the DNA damage response, factors upstream of Rad52, like the MRX complex (Mre11 and Xrs2), the ATM-like kinase Tel1 and the ATR-like kinase Mec1 were deleted in rad52Δ background cells to test their ability to suppress the nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA (Fig. 4 A). None of these deletions had any effect on the nucleolar distribution of TLC1 RNA in G2/M cells in the absence of DSBs. After induction of DSBs, deletion of MRE11 or XRS2 completely suppressed the nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA in rad52Δ cells (Fig. 4 B). This result is consistent with a function of MRX complex in DSBs processing and de novo telomere addition (Frank et al., 2006). However, deletion of TEL1 partially suppressed the nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA in rad52Δ cells, as this RNA accumulated in both nucleolus and nucleoplasm (Fig. 4 B). Given the role of Tel1 in DNA resection, it is possible that Tel1 might regulate TLC1 RNA nucleoplasmic accumulation by positively influencing the function of the MRX complex in the processing of DSBs, as it was shown to do at telomeres (Martina et al., 2012). On the other hand, deletion of MEC1 has no significant effect on TLC1 RNA trafficking (Fig. 4 B). Although Mec1 inhibits telomerase activity at DSBs by decreasing Cdc13 binding and by phosphorylation of the telomerase inhibitor Pif1 (Makovets and Blackburn, 2009; Zhang and Durocher, 2010), this activity is not required for TLC1 RNA trafficking, because this RNA still accumulated in the nucleolus. Altogether, these results are consistent with a model in which DSB processing and resection is required for TLC1 RNA relocalization from the nucleolus to nucleoplasm in the absence of RAD52.
Figure 4.
Genetic requirements for nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA after DNA damage in rad52Δ cells. (A) TLC1 RNA does not accumulate in the nucleoplasm in G2/M in the absence of DNA damage in rad52Δ, mre11Δ rad52Δ; xrs2Δ rad52Δ; tel1Δ rad52Δ; sml1Δ rad52Δ; sml1Δ mec1Δ rad52Δ and cdc13-2 rad52Δ cells. WT, rad52Δ, and sml1Δrad52Δ were used as control strains; n = 200–300 cells. (B) TLC1 RNA nucleoplasmic accumulation after induction of DNA damage requires Mre11 and Xrs2 of the MRX complex and Cdc13 and is regulated by Tel1. p-values are included in Table S2. Error bars represent ±SD; n = 150–300 cells. (C) FISH on TLC1 RNA in cdc13-2 rad52Δ cells treated or not with bleomycin. Arrowheads indicate the position of TLC1 RNA foci in cells. Bar, 1 µm. ***, P < 0.005 (two-tailed t test).
This model predicts that resected DSBs may retain telomerase in the nucleoplasm, and this retention should be mediated by a ssDNA-binding protein. Indeed, the single-strand telomeric binding protein Cdc13 was previously shown to be essential for the recruitment of telomerase at DNA breaks (Bianchi et al., 2004). This was revealed by using the cdc13-2 mutant, which disrupts the interaction between Cdc13 and the telomerase subunit Est1 (Nugent et al., 1996). We therefore tested the effect of the cdc13-2 mutation on the distribution of TLC1 RNA after DNA damage. In a WT RAD52 background, induction of DSBs in the cdc13-2 strain reduced the accumulation of TLC1 RNA in the nucleoplasm compared with a WT strain (Fig. S4 A). This effect is even more striking in a cdc13-2 rad52Δ strain, as TLC1 RNA did not accumulate in the nucleoplasm after exposure to bleomycin, showing that the cdc13-2 mutation completely suppressed the rad52Δ phenotype (Fig. 4, B and C). This result suggests that the Cdc13-Est1 interaction is essential for nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA after DNA damage.
Cdc13 clusters increase after DNA damage and accumulate at DSB sites
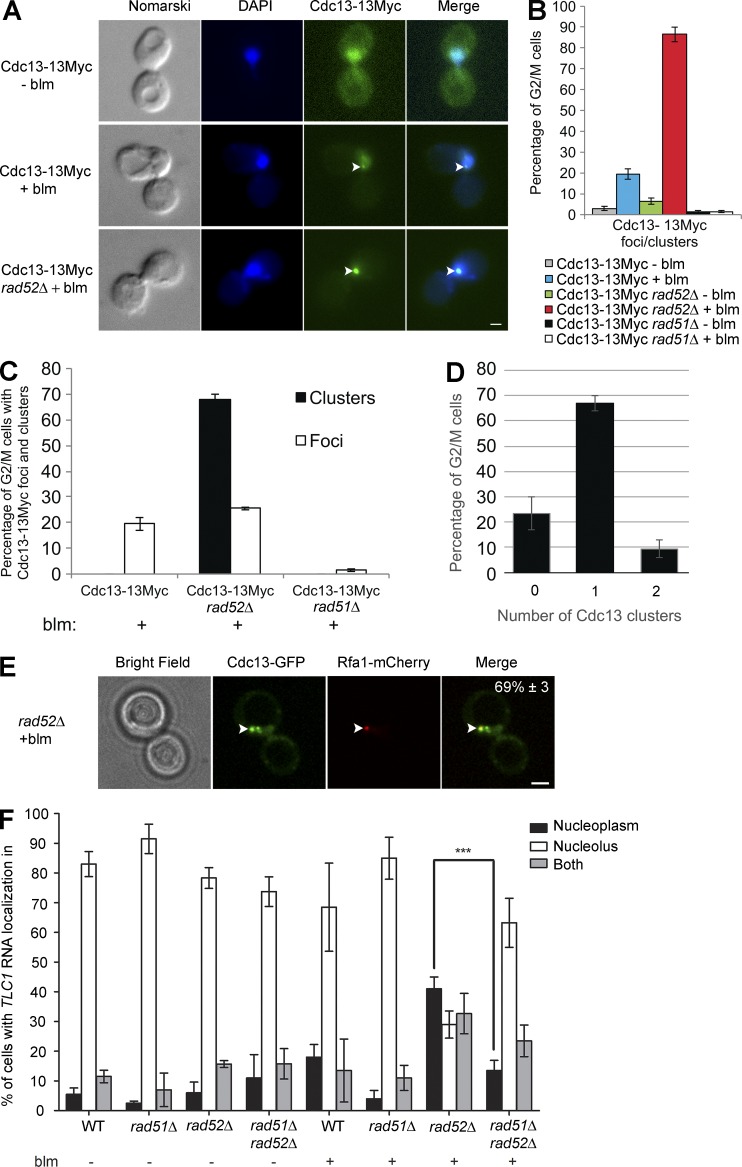
The abovementioned results show that in the absence of Rad52, Cdc13 plays a key role in the nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA after induction of DSBs. Recent work has shown that Cdc13 can be detected at a DSB by chromatin immunoprecipitation (Oza et al., 2009; Chung et al., 2010; McGee et al., 2010; Ribaud et al., 2012). We therefore examined whether TLC1 RNA nucleoplasmic accumulation is caused by the accumulation of Cdc13 at DSBs in WT and rad52Δ cells. Endogenous Cdc13 was tagged with 13 myc epitopes, and IF was performed to detect the distribution of myc-tagged Cdc13. In WT cells treated with bleomycin, Cdc13-13Myc accumulated as dim subnuclear foci in 20% of G2/M cells (Fig. 5, A and B). Surprisingly, deletion of RAD52 increased the number of cells with Cdc13 foci to more than 85% (Fig. 5 B). These results were confirmed using a Cdc13-GFP fusion protein in living yeast cells, which revealed the presence of a Cdc13 focus in over 50% of rad52Δ cells after bleomycin treatment (Fig. S4 B). The Cdc13 foci formed in rad52Δ cells were two- to threefold bigger and brighter than those observed in WT cells (Fig. 5 A and Fig. S4, C and D), likely reflecting an increased number of Cdc13 proteins associated with DSBs. To distinguish the larger Cdc13 foci observed in rad52Δ from the dimmer Cdc13 foci, we renamed the larger foci Cdc13 clusters. Notably, these clusters were only formed in rad52Δ cells in G2/M after DNA damage, with 65% of the cells containing one cluster and fewer cells containing two clusters (Fig. 5 D), suggesting that Rad52 inhibits Cdc13 accumulation at DSBs. However, we still detected Cdc13 foci in the same percentage of cells in both rad52Δ and WT cells (Fig. 5 C).
Figure 5.
Cdc13 accumulates at sites of DNA break in rad52Δ, but not in rad51Δ cells. (A) Cdc13 foci appear in WT and rad52Δ cells after DNA damage. Immunofluorescence (IF) analysis of Cdc13-myc was conducted in WT and rad52Δ cells, with or without bleomycin (blm) treatment. Arrowheads mark the position of Cdc13 foci. Bar, 1 µm. (B) Rad52 and Rad51 have opposite effect on Cdc13 foci formation. Quantification of Cdc13 foci/clusters formation in WT, rad52Δ, and rad51Δ strains, with or without bleomycin (blm) treatment; n = 200 cells. (C) Analysis of Cdc13 clusters and foci formation in WT, rad52Δ, and rad51Δ strains in DNA-damaged cells; n = 200 cells. (D) Quantification of the number of Cdc13 cluster per G2/M-damaged cells; n = 200 cells. (E) Colocalization of Cdc13-GFP cluster and Rfa1-mCherry focus in rad52Δ cell exposed to bleomycin. Arrowheads mark a colocalization event. Percentage of G2/M cells showing this phenotype is indicated in the last panel; n = 200 cells. (F) Quantification of TLC1 RNA distribution in the nucleus in WT, rad52Δ, rad51Δ, or rad51Δ rad52Δ cells after treatment with bleomycin; n = 200–344 cells. Error bars represent ±SD. ***, P < 0.005 (two-tailed t test).
To determine if Cdc13 accumulates at DSBs after bleomycin addition, the DSB marker Rfa1 was used to investigate the colocalization between Cdc13-GFP and Rfa1-mCherry in G2/M. Cdc13-GFP clusters colocalized with a Rfa1-mCherry focus in 69% of the cells (Fig. 5 E), indicating that Cdc13 accumulates at DSBs. To test if Cdc13 foci/clusters are also formed in the absence of another mediator of HR, such as Rad51, Cdc13 foci/cluster formation was measured in rad51Δ cells after bleomycin treatment. Indeed, a previous study had shown that Cdc13 recruitment to an irreparable HO-induced DSB is highly reduced in rad51Δ cells (Oza et al., 2009). Strikingly, both Cdc13 foci and clusters disappeared in rad51Δ cells (Fig. 5, B and C), whereas TLC1 RNA accumulated in the nucleolus in those cells (Fig. 5 F), reflecting that Rad51 positively influences Cdc13 accumulation and TLC1 RNA nucleoplasmic localization at DSBs. To determine the epistatic relationship between RAD51 and RAD52 in TLC1 RNA trafficking, TLC1 FISH was performed in a double-mutant rad51Δ rad52Δ strain. Interestingly, deletion of RAD51 suppresses the nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA observed in rad52Δ cells, suggesting that RAD51 is epistatic to RAD52 in this pathway (Fig. 5 F). Altogether, these results show that nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA observed in rad52Δ cells is linked, in part, to an increased accumulation of Cdc13 at DSBs. In the absence of Rad52, resected DSBs may be more accessible to Cdc13 binding, which may accumulate on the ssDNA and recruit telomerase.
Temporal analysis of Cdc13 foci formation and TLC1 RNA localization at DNA damage sites
Although the aforementioned data show that Cdc13 and TLC1 RNA can accumulate at DSBs after induction of DNA damage, it is not clear if their association with DSBs is an early or late event during DNA repair. Indeed, a late recruitment of Cdc13 and TLC1 RNA would probably suggest an indirect effect caused by the absence of DNA repair at DSBs and the accumulation of longer strands of ssDNA. To answer this question, we measured the kinetics of accumulation of Cdc13 and TLC1 RNA at DSBs in rad52Δ cells. Yeast cells were treated with bleomycin, and culture samples were taken at different time points. Yeast cells were fixed with formaldehyde and processed for IF and/or FISH. Immunofluorescence on Cdc13-myc showed that 50% of the cells already displayed a Cdc13 focus/cluster 30 min after induction of DNA damage (Fig. 6 A). The kinetics of Cdc13 foci/cluster formation was similar to the kinetics of accumulation of γ-H2A foci (Fig. 6 A), suggesting that Cdc13 accumulated rapidly at DSB sites in the absence of Rad52. A refined analysis of Cdc13 accumulation at DSBs was performed by separately quantifying cells with Cdc13 foci or clusters over time. This analysis revealed that the number of cells containing Cdc13 foci reached a peak at 30 min and stayed stable for the remainder of the treatment (Fig. 6 B). Surprisingly, Cdc13 clusters also appeared in over 30% of the cells after 30 min of bleomycin treatment (Fig. 6 B). However, the number of cells containing a Cdc13 cluster still increased over time. These results show that Cdc13’s association with DSBs is an early process after DNA damage in the absence of Rad52.
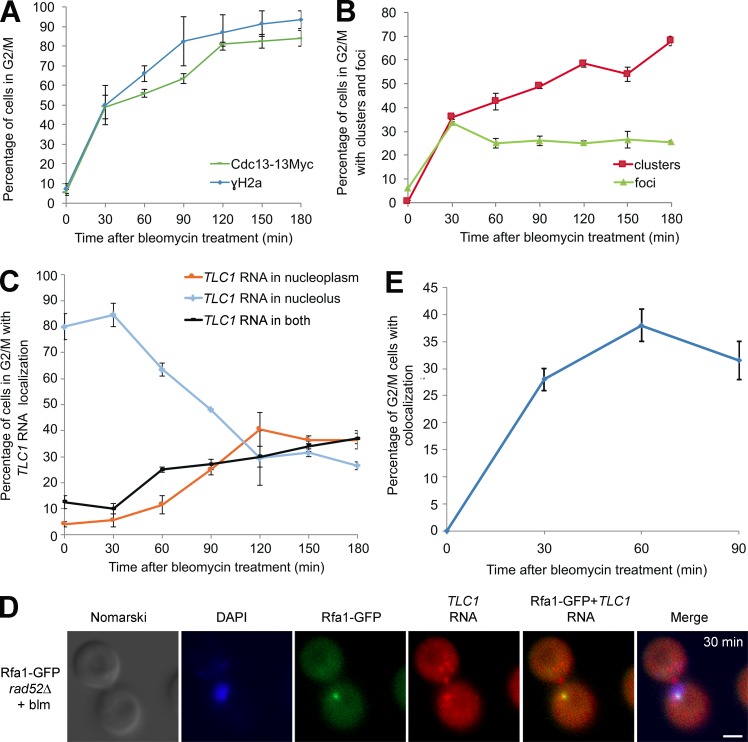
Figure 6.
Kinetics of accumulation of Cdc13 and TLC1 RNA at sites of DNA damage inrad52Δ cells. (A) Kinetics of γ-H2A and Cdc13 foci formation in G2/M cells after exposure to bleomycin. (B) Time course of Cdc13 foci and cluster formation in G2/M cells after exposure to bleomycin. (C) Kinetics of TLC1 RNA nucleoplasmic accumulation in G2/M cells after exposure to bleomycin. (D) Colocalization between TLC1 RNA focus and Rfa1-GFP focus in G2/M cells after 30 min of bleomycin exposure. Bar, 1 µm. (E) Kinetics of colocalization between a TLC1 RNA focus and a Rfa1-GFP focus in G2/M cells after exposure to bleomycin; n = 200 cells per time point. Error bars represent ±SD.
A similar kinetic analysis was performed on TLC1 RNA using FISH, in which the nucleoplasmic/nucleolar distribution of this RNA was quantified at different time points after induction of DNA damage. Unlike γ-H2A foci, which accumulated rapidly after DNA damage (Fig. 6 A), the nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA molecules started later, between 30 and 60 min after bleomycin treatment, and reached a plateau after 120 min (Fig. 6 C). We do not think that the difference in the kinetics of TLC1 RNA versus γ-H2A is a result of the lower sensitivity of the FISH assay versus IF, because single TLC1 RNA molecules are detected as single foci with this assay (Bajon et al., 2015). Interestingly, 30 min after induction of DNA damage, TLC1 RNA remained in the nucleolus even if 50% of the cells contain Cdc13 foci/clusters (Fig. 6, A and C), indicating that the association of Cdc13 with the DNA break sites is not the limiting step for the nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA.
These results show that nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA proceeds more slowly than the formation of Cdc13 foci/clusters. However, it is possible that a small number of TLC1 RNA molecules may associate rapidly with a DSB, whereas the majority of TLC1 RNA molecules still remain in the nucleolus. To test this possibility, colocalization of TLC1 RNA with Rfa1-GFP was measured in rad52Δ cells during a time-course treatment with bleomycin. Surprisingly, early colocalization of a single TLC1 RNA focus with the Rfa1-GFP focus was detected in 27% of the cells 30 min after initiation of DNA damage (Fig. 6, D and E). At this time point, most TLC1 RNA molecules remained outside of the DAPI-stained nucleoplasm (presumably in the nucleolus) in these cells. The colocalization between TLC1 RNA and Rfa1-GFP increased to nearly 40% of the cells after 60 min of bleomycin treatment and remained stable afterward (Fig. 6 E).
These results could be explained by a two-step process in the accumulation of TLC1 RNA in the nucleoplasm after DNA damage. One early step, which leads to the accumulation of a small number of TLC1 RNA molecules at a resected DSB (Fig. 6 E), and a late step, which corresponds to the global redistribution of bulk TLC1 RNA molecules from the nucleolus to the nucleoplasm, but not directly at DSBs (Fig. 6 C). This late redistribution may be triggered by the accumulation of unrepaired DSBs in the absence of RAD52. Once in the nucleoplasm, the TLC1 RNA molecules might be associated with Cdc13 at telomeres, which would explain why in cdc13-2 mutant, TLC1 RNA remains in the nucleolus even in the presence of DNA damage (Figs. 4 and S4). This raises questions regarding how unrepaired DSBs could trigger this relocalization of telomerase molecules.
The E3 SUMO ligase Siz1 regulates the nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA after DNA damage
The observation that TLC1 RNA molecules are excluded from the nucleolus and accumulate in the nucleoplasm in the presence of unrepaired DSBs suggests a specific regulation of this trafficking during DNA damage. To identify regulators of the intranuclear trafficking of TLC1 RNA, we focused on factors involved in sumoylation, a posttranslational modification that regulates DNA damage repair. Indeed, mutation or depletion of sumoylation enzymes in yeast and human cells notably results in defects in DNA repair, including recombination abnormalities and impaired DSB repair (Maeda et al., 2004; Branzei et al., 2006). Furthermore, sumoylation is known to regulate Rad52 and DSBs nuclear distribution in yeast (Torres-Rosell et al., 2007). In budding yeast, three mitotic SUMO E3 ligases have been identified, including two homologous Siz proteins (Siz1 and Siz2) and the Mms21 subunit of the essential Smc5/6 complex (Johnson and Gupta, 2001; Zhao and Blobel, 2005). Several factors involved in telomere maintenance are known to be sumoylated, including Cdc13, which is a substrate of both Siz1 and Siz2 (Hang et al., 2011). Interestingly, Cdc13 sumoylation increases after DNA damage, suggesting that Cdc13 activity may be regulated by SUMO during DNA damage (Hang et al., 2011).
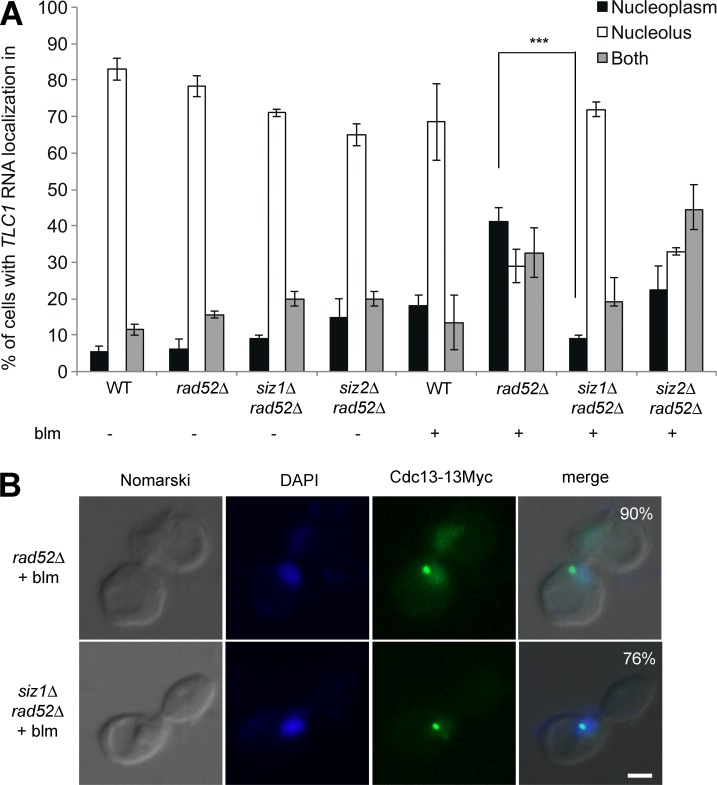
To determine if sumoylation regulates the spatial distribution of telomerase after DNA damage, TLC1 RNA localization was determined in a single mutant of two SUMO E3 ligases, siz1Δ and siz2Δ, in a rad52Δ background after treatment with bleomycin. In the absence of DNA damage, deletion of either SIZ1 or SIZ2 had no effect on the localization of TLC1 RNA to the nucleolus in G2/M (Fig. 7 A), suggesting that these SUMO E3 ligases do not regulate the cell cycle–dependent trafficking of TLC1 RNA. Interestingly, during bleomycin-induced DNA damage, the deletion of SIZ1, but not SIZ2, strongly decrease the nucleoplasmic accumulation of TLC1 RNA in a rad52Δ strain (Fig. 7 A). These results show that Siz1, but not Siz2, controls the spatial distribution of TLC1 RNA after DNA damage.
Figure 7.
The E3 SUMO ligase Siz1 is required for the accumulation of TLC1 RNA in the nucleoplasm of rad52Δ cells after DNA damage. (A) Nuclear distribution of TLC1 RNA in various single mutants of the E3 SUMO ligases (siz1Δ or siz2Δ) in rad52Δ genetic background with (+) or without (−) exposure to bleomycin (blm); n = 200–300 cells. Error bars represent ±SD. ***, P < 0.005 (two-tailed t test). (B) Cdc13 clusters are still formed in the siz1Δ rad52Δ strain after DNA damage. Immunofluorescence (IF) analysis of Cdc13-myc was conducted in rad52Δ and siz1Δ rad52Δ cells after bleomycin (blm) treatment. Bar, 1 µm; n = 200 cells.
One trivial explanation could be that Siz1 indirectly affects the trafficking of TLC1 RNA by modulating the processing of DSBs. To determine if Siz1 plays a role in the resection of DSBs, the kinetic of resection of a single HO cut site was measured in rad52Δ and siz1Δrad52Δ strains. No difference in the kinetic of DSB resection was observed in the absence of Siz1 (Fig. S5, A and B). Also, after DNA damage, we found that deletion of SIZ1 did not affect the formation of Rfa1-GFP foci, a marker of DSB resection (Fig. S5 C). To identify where Siz1 acts in the DNA repair pathway, serial dilutions of siz1Δ, siz2Δ, rad52Δ, and double-mutant siz1Δrad52Δ and siz2Δrad52Δ strains were spotted on plates containing different concentrations of bleomycin. Unlike SIZ2, deletion of SIZ1 increased the sensitivity of yeasts to bleomycin, although only at a higher concentration compared with a RAD52 deletion (Fig. S5 D). Interestingly, the siz1Δrad52Δ strain showed the same sensitivity to bleomycin as a rad52Δ strain, showing that RAD52 is epistatic to SIZ1. These results suggest that Siz1 acts downstream of Rad52 in the DNA repair pathway.
Because Siz1 is known to promote Cdc13 sumoylation after DNA damage (Hang et al., 2011), it may regulate Cdc13 clustering at DSBs and subsequent TLC1 RNA trafficking during DNA damage. To test this hypothesis, IF on Cdc13-myc was performed in siz1Δrad52Δ and rad52Δ strains after bleomycin treatment. Cdc13 clusters and foci still formed in the siz1Δ rad52Δ strain as in rad52Δ cells (Fig. 7 B). Altogether, these results show that Siz1 is not involved in DSBs processing or Cdc13 accumulation at resected DSB but acts downstream of this process.
Siz1 promotes de novo telomere addition in the absence of RAD52
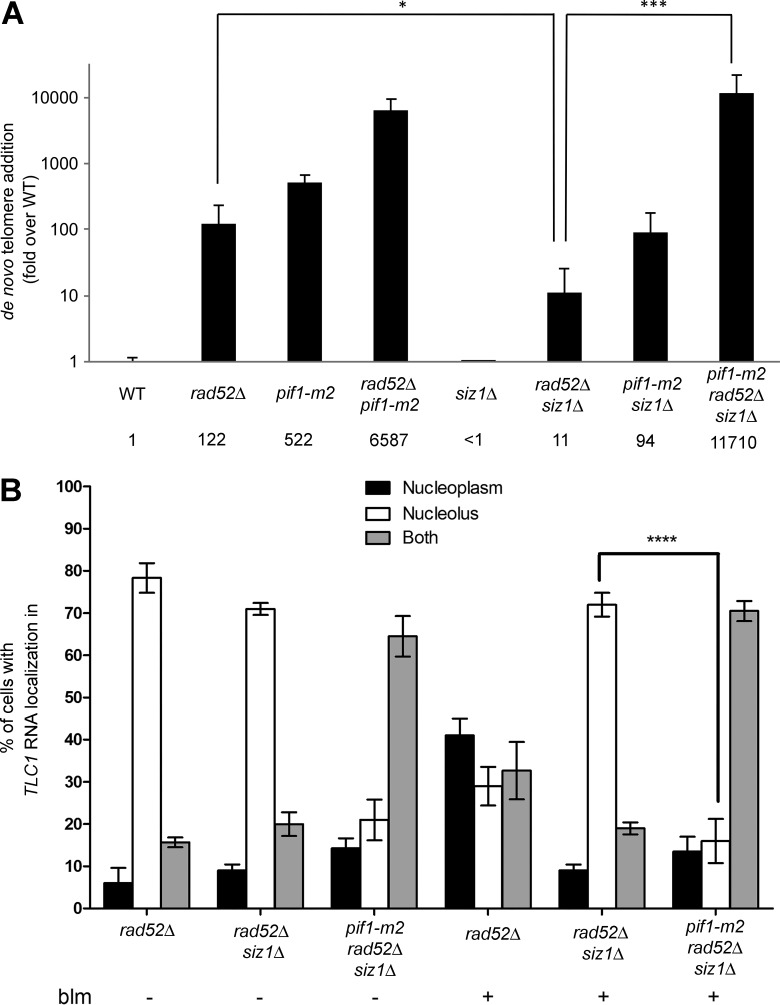
One key question is whether this cell cycle–dependent TLC1 RNA trafficking plays a role in de novo telomere addition at spontaneous DSBs. To answer this question, we used the GCR assay developed by the Kolodner laboratory (Chen and Kolodner, 1999). In this assay, two counterselectable markers (URA3 and CAN1) are inserted near the left telomere of chromosome V. Cells that undergo a GCR event (i.e., telomere addition, translocation) that leads to simultaneous loss of CAN1 and URA3 can be selected by growth on medium containing 5-FOA and canavanine. Afterward, the number of GCR events corresponding to telomere healing was quantified. The GCR assay was first performed in rad52Δ, pif1-m2, and pif1-m2 rad52Δ strains. As previously reported (Myung et al., 2001), deletion of RAD52 or the pif1-m2 mutation increase telomere healing rates (Fig. 8 A). Combining the pif1-m2 mutation with a rad52 deletion results in a 12-fold increase in de novo telomere addition compared with the pif1-m2 strain, as previously shown (Myung et al., 2001).
Figure 8.
Siz1 promotes de novo telomere addition in rad52Δ cells. (A) Quantification of de novo telomere addition events. Values are reported as fold over wild-type (WT). n = 9–34 cultures. Error bars represent ± 95% confidence interval. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.005 (Mann–Whitney t test). (B) The pif1-m2 mutant reduces the nucleolar accumulation of TLC1 RNA in rad52Δ siz1Δ cells. Nuclear distribution of TLC1 RNA in rad52Δ, siz1Δ rad52Δ, and pif1-m2 siz1Δ rad52Δ cells, with (+) or without (−) exposure to bleomycin (blm). Error bars represent ±SD; n = 200–300 cells. ****, P < 0.0001 (two-tailed t test).
Deletion of SIZ1 decreases the accumulation of TLC1 RNA in the nucleoplasm of rad52Δ cells after DNA damage (Fig. 6 A), which should reduce de novo telomere addition and GCR rates observed in a rad52Δ strain. In fact, an 11-fold reduction in telomere healing rates was observed in a siz1Δrad52Δ strain compared with the rad52Δ strain (Fig. 8 A). Because Pif1 is required to promote TLC1 RNA trafficking to the nucleolus, our model predicts that inhibition of Pif1 should suppress the nucleolar accumulation of TLC1 RNA observed in the siz1Δrad52Δ strain and increase GCR rates. Indeed, the pif1-m2 mutation partially suppresses the nucleolar accumulation of TLC1 in the rad52Δ siz1Δ mutant, as TLC1 RNA molecules accumulate in both nucleoplasm and nucleolus in the triple mutant pif1-m2 siz1Δ rad52Δ, with or without bleomycin treatment (Fig. 8 B). Deletion of SIZ1 in the pif1-m2 strain reduces GCR rates by sixfold, close to the twofold reduction previously reported for this double mutant (see Fig. 8 A). This could be because Pif1 is sumoylated during DNA damage (Hang et al., 2011), and the absence of Siz1 may affect the activity of Pif1 at sites of DNA damage. Strikingly, the triple mutant pif1-m2 siz1Δ rad52Δ restores the telomere healing rate to levels similar to the pif1-m2 rad52Δ strain (Fig. 8 A), which is consistent with our model that mutation in Pif1 bypasses the need for Siz1 activity for de novo telomere addition in rad52Δ cells.
Identification of telomere healing events in bleomycin treated cells
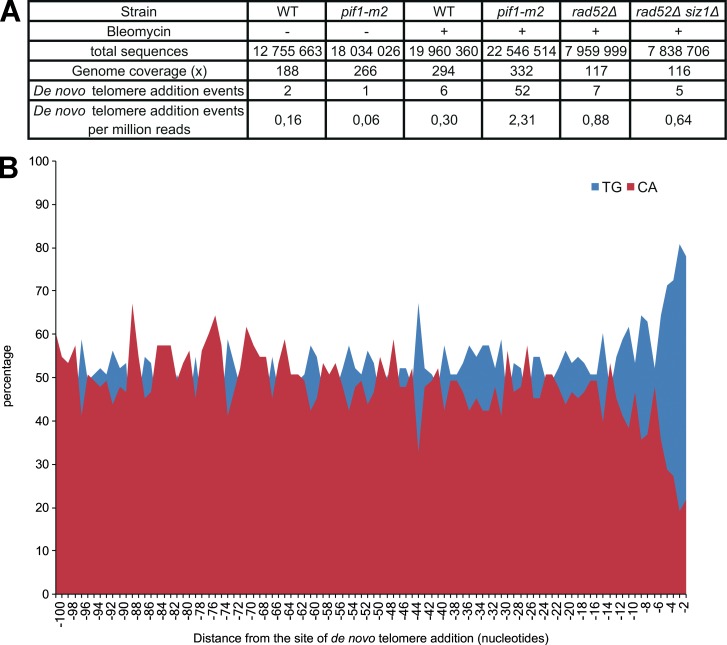
Although the GCR assay shows that Pif1, Rad52, and Siz1 regulate the frequency of telomere healing events, it remains unclear if de novo telomere addition really occurs in bleomycin-treated cells. To identify de novo telomere events in cells treated with bleomycin, WT, pif1-m2, rad52Δ, and rad52Δ siz1Δ cells were synchronized in G2/M with nocodazole prior treatment with bleomycin for 3 h. Genomic DNA was extracted and submitted to paired-end Illumina sequencing. Analysis of Illumina paired reads identified 73 reads containing de novo telomere events (Fig. 9 A and Table S3). 96% of these reads were identified in bleomycin-treated cells, and only three reads were identified from untreated cells, suggesting that these reads are not sequencing artifacts. Although this analysis most likely underestimates the occurrence of de novo telomere addition (see Materials and methods for details), more telomere healing events were identified per million reads in pif1-m2, rad52Δ, and rad52Δ siz1Δ cells treated with bleomycin compared with WT treated cells.
Figure 9.
Identification of telomere healing events in bleomycin-treated cells. (A) Analysis of reads containing de novo telomere events. (B) Percentage of T+G (blue) and C+A (red) nucleotides at each position within the 100 nt upstream of the site of de novo telomere addition.
Telomere healing events were observed on most chromosomes (Table S3). Surprisingly, 14% of the telomere healing events identified occurred in the rDNA locus on chromosome 12, which is close to the percentage of the yeast genome occupied by this locus (∼11%). Analysis of the sequences upstream de novo telomere addition events revealed the absence of nucleotide insertions or deletions, which is a feature of nonhomologous end joining and microhomology-mediated end joining repair (Sfeir and Symington, 2015). However, a TG-rich bias in the 10 nt upstream of the telomere addition sites was observed (Fig. 9 B), which was also previously reported for telomerase-dependent de novo telomere events (Putnam et al., 2004). Finally, the majority of these reads were found in the pif1-m2 strain, suggesting that these events are mediated by telomerase activity.
Discussion
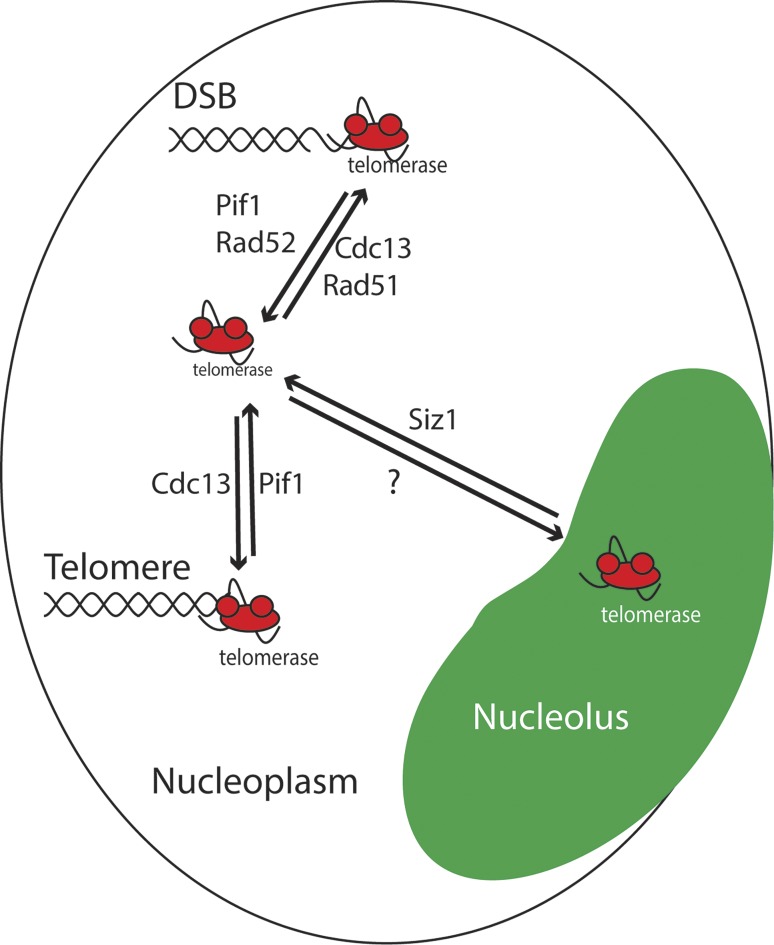
In this study, we used single-molecule imaging to study TLC1 RNA trafficking during the cell cycle and after induction of DNA damage. Our results demonstrate that TLC1 RNA, the limiting component of yeast telomerase, is engaged in an intranuclear trafficking during the cell cycle. In G1/S, TLC1 RNA molecules are present in the nucleoplasm, whereas in G2/M, they accumulate predominantly in the nucleolus. We also show that this trafficking depends on the helicase Pif1 and is linked to the presence of DNA damage. In addition to Pif1, the key recombination protein Rad52 strongly controls this trafficking in the presence of DNA damage, as it specifically suppresses the accumulation of TLC1 RNA molecules in the nucleoplasm and at DSBs generated by bleomycin by antagonizing the accumulation of Cdc13 at DNA breaks (Fig. 10).
Figure 10.
Model for telomerase trafficking in G2/M and at DNA damage sites. In the nucleoplasm, Pif1 activity removes telomerase from telomeres and promotes its accumulation in the nucleolus via an unknown mechanism. In the presence of DSBs, Pif1, and Rad52 inhibit the accumulation of telomerase and Cdc13, respectively, at break sites, leading to the accumulation of telomerase in the nucleolus and a reduction in de novo telomere addition. In the presence of DSBs, Siz1 is required for telomerase trafficking out of the nucleolus and for de novo telomere addition in rad52Δ cells.
However, the effect of a RAD52 deletion on the accumulation of Cdc13 at DSBs may not be simply caused by the accumulation of longer resected DNA in this mutant, because the deletion of RAD51, which also produces long ssDNA at DSBs (Sugawara et al., 1995; Zhu et al., 2008), completely abolishes the formation of Cdc13 foci. Interestingly, deletion of RAD51 suppresses the effect of a RAD52 deletion on TLC1 RNA trafficking. This result supports a previous observation that Rad51 is required for the recruitment of Cdc13 and Est2 to a nonrepairable DSB (Oza et al., 2009). Why Rad52 and Rad51 have opposite effects on the formation of Cdc13 foci is still unclear.
Using Illumina paired-end sequencing, we identified several reads containing de novo telomere addition events in the genome of yeasts treated with bleomycin. De novo telomere addition occurred downstream of TG-rich sequences less than 10 nt. A recent characterization of an endogenous hotspot of de novo telomere addition in yeast revealed a bipartite structure, with a TG-rich core sequence where telomere addition occurs, and an upstream proximal Stim sequence that binds Cdc13 and stimulates telomere addition (Obodo et al., 2016). Interestingly, de novo telomere addition is increased at this bipartite hotspot in the absence of Rad52. Hence, because of their short TG-rich core sequence, it is possible that several of the sites of de novo telomere addition identified in the DNA-sequencing study may contain this bipartite structure. Another surprising result is that 14% of the reads containing de novo telomeres were from the rDNA locus, suggesting the presence of telomerase activity in the nucleolus. Because DSBs in rDNA in yeast are processed in the nucleolus but repaired by HR in the nucleoplasm (Torres-Rosell et al., 2007), the unusual dynamics of these DSBs between the nucleolus and the nucleoplasm may explain in part their accessibility to telomerase activity in the nucleoplasm.
In addition, we demonstrate that the E3 SUMO ligase Siz1 regulates the spatial distribution of TLC1 RNA after DNA damage without affecting DSB processing or Cdc13 accumulation at DSBs. DNA damage is known to trigger a wave of sumoylation leading to simultaneous multisite modifications of several DNA repair proteins of the HR pathway in yeast (Psakhye and Jentsch, 2012). However, these sumoylation events depend on the Siz2 SUMO ligase and not on Siz1, suggesting that the effect of Siz1 on TLC1 RNA localization is independent of the main role of SUMO in the modulation of the HR pathway. Although the effect of a SIZ1 deletion on TLC1 RNA trafficking might be explained by the Siz1-dependent sumoylation of Cdc13 (Hang et al., 2011), this sumoylation event was shown to inhibit telomerase binding to Cdc13. Therefore, other targets of Siz1 may be involved in this process. Sumoylation by Siz1 is required for de novo telomere addition in the absence of Rad52 and, to a lesser extent, in a pif1-m2 strain. This requirement for Siz1 activity is completely suppressed in a double pif1-m2 rad52Δ mutation. These data support our model that by reducing TLC1 RNA trafficking to the nucleolus, the pif1-m2 mutation bypasses the spatial restriction on telomerase access to DNA breaks observed in the siz1Δ rad52Δ strain (Fig. 10).
In line with the observation that DNA repair is excluded from the nucleolus (Dion et al., 2013), our study reveals how the spatial segregation of telomerase and HR activities restricts telomerase access to DSBs. This process is not specific to budding yeast telomerase, because the catalytic subunit of human telomerase (hTERT) was also shown to accumulate in the nucleolus after ionizing radiation–induced DSBs (Wong et al., 2002), indicating that nucleolar localization of telomerase after DNA damage may be a conserved process during evolution.
Materials and methods
Constructs and strains
Table S1 lists strain genotypes. Yeast strains were generated by disrupting the RAD52, RAD51, SIZ1, SIZ2, MRE11, XRS2, TEL1, or MEC1 genes in W303 strain by a one-step PCR disruption method using KAN marker (Wach et al., 1994). The mec1Δ strains were kept viable by deletion of the SML1 gene (Zhao et al., 1998). In this strain, the KAN marker was removed by transforming cells with pSH47 expressed Cre recombinase. The cdc13-2 strain transformed with the plasmid pVL438 CDC13 (Ycp33 CEN, URA3, and CDC13; Chandra et al., 2001) was obtained from R. Wellinger’s laboratory (Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Canada). Deletion of RAD52 was followed by the elimination of the pVL438 CDC13 plasmid using 5-FOA. Strains carrying Rfa1-GFP, Rfa1-mCherry, Cdc13-GFP, and Cdc13-13Myc allele at the RFA1 and CDC13 chromosomal locus were generated by a PCR one-step tagging method using plasmids pFA6A-GFP-KANMX4, pFA6A-mCherry-Kan, or pFA6A-13Myc-KANMX4 (Knop et al., 1999). Verification of these strains was performed by PCR, microscopy, and/or Western blot. For Cdc13-GFP and Cdc13-13Myc strains, senescence experiments were conducted by repeatedly streaking strains. For all these strains, the RAD52 gene disruptions were obtained by using TRP1, KAN, or Hygro markers. RAD51 deletion was also obtained by using TRP1 marker.
Cell cycle–dependent localization of TLC1 RNA and induction of DSBs
Asynchronously growing WT yeast cells (W303) were grown in YEPD (yeast extract peptone-dextrose) until OD600 0.3 to 0.4, fixed with paraformaldehyde, and processed for FISH analysis to detect TLC1 RNA and ITS1 pre-rRNA. ITS1 FISH probe was provided by D. Zenklusen (Université de Montréal, Montréal, Quebec, Canada). The cell cycle stage of the cells was estimated by measuring the bud-to-mother size ratio (budding index) as G1 (cells without bud), S phase (cells with small to mid-size bud), and G2/M (cells with large bud or sharing the nucleus between mother and daughter). This method is highly reproducible for scoring G2/M cells, because nearly identical percentages of TLC1 RNA distribution were measured in nocodazole-treated cells and nontreated cells (see Fig. 2, B and C). For induction of DSBs, haploid WT and rad52Δ strains were grown in YEPD medium (at OD600 ∼0.2) and exposed to 5 µg/ml of bleomycin (BLE011.10; Bioshop) for 180 min. In these conditions, 90% of the cells have at least one DSB after 180 min (Fig. S2). The presence and number of DNA damage per cell after bleomycin treatment were quantified using the number of γ-H2A foci, which correlates with the number of DSBs per cell (Sedelnikova et al., 2002). For nocodazole treatment, WT and rad52Δ cells were grown in YEPD medium to OD600 ∼0.2 before addition of 15 µg/ml nocodazole for 90 min, and synchronization of cells in G2/M was monitored by microscopy. In these conditions, more than 90% of cells are in G2/M. 5 µg/ml bleomycin was then added, and cells were incubated for another 180 min.
FISH and IF
The yeast fixation protocol and fluorescent in situ hybridization to detect endogenous TLC1 RNA have been described previously (Pfingsten et al., 2012). Five Cy3-labeled 50-nt probes were used to detect the endogenous TLC1 RNA, and one Cy5-labeled 50-nt probe was used to detect the ITS1 pre-rRNA. For colocalization experiments with endogenous Rfa1-GFP, yeast was cultured at room temperature, and fixation was performed in 1× PBS, pH 7.4, to preserve GFP fluorescence. Dual FISH-IF or IF-only protocols were conducted as described previously (Gallardo and Chartrand, 2011). In brief, after the last wash of 1× SSC of the FISH protocol, spheroplasts were incubated in 1× PBS containing 0.1% BSA, 1× PBS containing 0.1% BSA and 0.1% NP40, and 1× PBS containing 0.1% BSA for 2 min each at room temperature. The primary antibodies used to detect γ-H2A (18255; Abcam) or myc epitope (9E10; Roche) were diluted to 1:5,000 and 1:400, respectively, in 1× PBS containing 0.1% BSA, 20 mM VRC, and 120 U/ml RNA Guard and incubated for 2 h at 37°C. Spheroplasts were washed with 1× PBS containing 0.1% BSA, 1× PBS containing 0.1% BSA and 0.1% NP-40, and 1× PBS containing 0.1% BSA for 2 min each at room temperature. The secondary antibody (Alexa Fluor 488 conjugate) was diluted to 1:1,000 in 1× PBS containing 0.1% BSA, 20 mM VRC, and 120 U/ml RNA Guard, and incubated 1h in the dark at room temperature. Finally, cells were washed in 1× PBS containing 0.1% BSA, 1× PBS containing 0.1% BSA and 0.1% NP-40, and 1× PBS 0.1% BSA for 1 min each at room temperature. The coverslips were incubated in 1× PBS containing DAPI before mounting on slides.
Image acquisition, deconvolution, and processing
All images were acquired using an Axio Imager 2 epifluorescence upright microscope (ZEISS) equipped with a 100× differential interference contrast (DIC) H (1.4 NA) objective and a Photometrics CoolSNAP fx CCD camera. Endogenous TLC1 RNA foci were detected using Cy3.0 filter, ITS1 probe was detected using Cy5.0 filter, and Rfa1-GFP or γ-H2A were detected using a FITC filter. Image acquisition times for DIC, DAPI, TLC1 RNA, and ITS1 pre-rRNA were 40, 20, 1,600, and 800 ms, respectively. Images were acquired and processed with ZEISS software or deconvolved by Autoquant X3 software using a theoretical PSF algorithm and analyzed using Metamorph software. 100 fields of yeast cells were acquired as Z stacks of 14 planes minimum, with 0.5 µm between planes in the Z axis. Inspection of all focal planes of each cell was performed to quantify colocalization between TLC1 RNA, ITS1 pre-rRNA (nucleolus) or DAPI (nucleoplasm), with reproducible results obtained with two or three different individuals. For each yeast strain, a total of 200 G2/M cells were randomly scored in two biologically independent experiments. The linescan application of Fiji or Metamorph software was also used to quantify TLC1 RNA, ITS1 RNA, and DAPI fluorescence distribution in the nucleus of yeast cells. Numbers are expressed as percentage of cells with TLC1 RNA located in the nucleoplasm or nucleolus or evenly distributed between both compartments. Simultaneous FISH on TLC1 and MDN1 RNA was performed to determine the percentage of colocalization of TLC1 RNA foci with a random nuclear focus, represented by the MDN1 transcription site. The MDN1 FISH probes were provided by D. Zenklusen.
Live-cell imaging
Cells expressing fusion protein Rfa1-GFP, Cdc13-GFP, or Cdc13-GFP and Rfa1-mCherry in rad52Δ genetic background were incubated overnight at 25°C in 2 ml SC-TRP and then diluted to OD600 ∼0.2 and grown for one cell cycle. Cdc13-GFP foci and colocalization between Cdc13-GFP and Rfa1-mCherry were induced by 5 µg/ml bleomycin for 3 h. Cells were collected by centrifugation at 2,000 g, mounted on standard glass slides, and covered with a coverslip appropriate to the optics of the microscope. All the images were acquired using an Axio Imager 2 epifluorescence upright microscope (ZEISS) equipped with a 100× DIC H (1.4 NA) objective and an Evolve fx EM-CCD camera or microscope AXIO OBSERVER Z1 confocal spinning disk (ZEISS) equipped with the same objective and camera. For each field of cells, 11 fluorescent images at each of the relevant wavelengths were obtained at 0.4-µm intervals along the Z axis. Inspection of all focal planes of each cell was performed to quantify colocalization. Image acquisition times for DIC, bright-field, GFP, and mCherry were 40, 40, 900, and 60 ms, respectively.
Quantitative analysis of Cdc13 foci and clusters
Determination of Cdc13 focus and cluster diameter and maximal fluorescence intensity was calculated as described previously (Gallardo et al., 2011).
DSB resection assay
Yeast was grown to early–mid log phase in YEP-raffinose medium at 30°C. HO endonuclease was induced by the addiction of 3% galactose. Samples were harvested before galactose addition and every 30 min after induction for 4 h. Genomic DNA was extracted and digested by PciI restriction enzyme. DNA fragments were separated on a 1% agarose gel and transferred on a neutral nylon membrane. Southern blot was performed with a probe generated by PCR amplification of a sequence close to the HO cut site. DNA loaded at each time point was normalized using a probe against the AGX1 gene. Intensities of bands on the Southern blot were quantified with Image Lab. Resection was measured as the ratio of the signal intensity for each time point relative to the signal intensity of the initial HO cleavage time point.
GCR assay and characterization of telomere healing events
All GCR rates were determined by fluctuation tests. Mutation rates were calculated using the median method (Putnam and Kolodner, 2010). Results shown are the mean of three to five experiments using five to seven cultures. After the GCR assay, DNA was extracted from 20 5-FOA+ Can+ colonies from each strain (but only eight for the WT strain). To identify the breaking point where the GCR took place, we used the approached used in (Motegi and Myung, 2007). In brief, 22 pairs of PCR primers were designed to cover the whole 12-kb region where the break could have happened to generate a 5-FOA+ Can+ colony. Each primer pair was designed to generate overlapping ∼600-bp amplicons. Starting from the centromere-proximal extremity, the first primer pair that did not give amplification is referred as the breaking point.
Each breaking point was further analyzed to characterize the presence of de novo telomere addition at the breaks. This analysis was performed as in (Motegi and Myung, 2007). In brief, each sample was amplified using the antisense PCR primer of the breaking point with a telomere primer (5′-CACCACACCCACACAC-3′). The antisense primer of the last working pair (flanking the breaking point) was also used with the telomere primer. Those two primer pairs served to identify de novo telomere addition. As controls, each sample was amplified using the breaking point primer pair and the last working primer pair. As a positive control, the telomere primer was used with an antisense primer that flanks the telomere 1L. Finally, one sample with a breaking point upstream of the breaking point analyzed and one downstream of it were added. Those were used as controls for the specificity of the primer pairs.
The results are displayed as a ratio of telomere healing events identified versus the number of clones characterized for each strain. Then, this ratio is applied on the spontaneous GCR rate calculated for the corresponding strain to establish a spontaneous telomere healing rate. This rate is than compared with the rate of the WT strain, which is set as 1.
Identification of telomere healing events by Illumina paired-end sequencing
Cultures were started from an OD600 of 0.2. When the OD600 reached 0.4, 15 µg/ml nocodazole was added to the culture. Cultures were incubated for 3 h until >80% of the cells were synchronized in G2/M. Synchronization was assessed by microscopy. If needed, 5 µg/ml bleomycin was added and cultures were incubated another 3 h before harvesting the cells. Genomic DNA was extracted, and 1 µg was sent for paired-end Illumina sequencing on an Illumina HiSeq2000. Each condition was done in duplicate. Genome coverage for each sample ranged from 25 to 210× (2,792,066 to 14,219,231 sequences).
Datasets were analyzed using a Galaxy (Afgan et al., 2016) modified version of a previously published workflow (Zampini et al., 2015). Sequences were filtered for a minimum length of 40 nt, an average quality of at least 20, and no more than 50 nt under a quality of 20. They were then aligned using the Burrows-Wheeler aligner against the sacCer3 reference genome (NCBI Assembly accession no. GCA_000146045.2) from which telomere sequences were removed. Read pairs for which both reads were successfully mapped do not contain de novo telomere additions and were discarded. The first 25 nt of the remaining pairs were aligned using Bowtie, and sequences which were mapped for either none or both of the paired end reads were discarded. Between 177,689 to 544,055 sequences remained for analysis in each dataset at this point. Read pairs were sorted according to the percentage of CA, CCA, and CCCA in the first 50 nt of the unmapped read. Unmapped reads with at least 24 nucleotides of telomeric repeats in their first 50 nt were then analyzed manually to identify telomere healing events. The remaining pairs were further filtered for at least 12 nt of telomeric repeats in the first 24 nt of the unmapped read and then analyzed in the same manner. Finally, to ensure that the events found were de novo telomere addition and not random addition of TG repeats, identified sequences were compared with the TLC1 RNA template.
Although this approach allows the detection of de novo telomere additions, it most likely underestimates their occurrence. First, Illumina sequencing biases against GC-rich and GC-poor regions may translate into fewer GC-rich telomere reads. Second, telomeres were removed from the reference genome in order for telomere-containing sequences to remain unmapped, but if the first 25 nt of a telomere sequence match an internal telomeric tract (as in the subtelomeric regions), the read was discarded after a successful alignment using Bowtie. Third, because a lot of sequences in the subtelomeric regions are shared between chromosomes ends, it is difficult to assign a sequence to a specific telomere. For this reason, subtelomeric sequences (10 kb from telomeres) were ignored in the analysis. Fourth, DNA fragments with identical sequences at both ends were ignored. These pseudopalindromes are artifacts created by the presence of long ssDNA (Star et al., 2014). One library from the rad52Δ strain was discarded because of the presence of a very high number of reads with pseudo-palindromes, possibly because rad52Δ cells have longer resected DNA at DSBs. Lastly, because telomere sequences shorter than 12 nt were not analyzed, short de novo telomere additions were ignored. Fragmentation of the DNA near a site of telomere addition during library preparation therefore means that some occurrences were missed.
Statistical analysis
A two-tailed Student’s t test or analysis of variance was used to calculate the statistical significance. A Mann–Whitney t test was used for the GCR assay. Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05 (*). Calculations were performed using GraphPad.
Online supplemental material
Fig. S1 presents TLC1 RNA localization in pif1Δ and pif1-m2 strains. Fig. S2 describes quantification of γ-H2A foci and cell cycle synchronization. Fig. S3 shows the analysis of TLC1 RNA colocalization with DSBs. Fig. S4 presents a quantitative analysis of Cdc13 foci. Fig. S5 shows that Siz1 is not involved in DSBs processing but acts downstream of Rad52 in DNA repair. Table S1 shows all yeast strains genotypes. Table S2 lists p-values of all the strains tested in Fig. 4 B. Table S3 lists all the de novo telomere addition identified by DNA sequencing.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank R. Wellinger, J. Cobb, R. Kolodner, D. Durocher, and L. Symington for yeast strains and D. Zenklusen (Université de Montréal) for the ITS1 and MDN1 FISH probes. We also thank R. Wellinger, L. Harrington, E. Querido, and M. Hendzel for critical reading of the manuscript.
This project was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP-89768). M. Lalonde is supported by a fellowship from the Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Santé. F. Gallardo was supported by a doctoral fellowship from the Terry Fox Foundation. G. Morin and H. Laprade were supported by a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada CDMC-CREATE fellowship. P. Chartrand holds a Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Santé Research Chair.
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author contributions: F. Ouenzar, M. Lalonde, and F. Gallardo performed FISH and IF experiments, analyzed microscopy data, and prepared strains. G. Morin helped to perform the FISH experiments shown in Fig 4. M. Lalonde prepared strains and performed GCR assays and analysis of Illumina sequencing. H. Laprade performed GCR assays and DNA resection. S. Tremblay-Belzile helped with bioinformatics analysis. F. Ouenzar, M. Lalonde, and P. Chartrand designed the experiments and wrote the paper.
Footnotes
Abbreviations used:
- DIC
- differential interference contrast
- DSB
- double-strand break
- GCR
- gross chromosomal rearrangement
- HR
- homologous recombination
- IF
- immunofluorescence
- NHEJ
- nonhomologous end joining
- rDNA
- ribosomal DNA
- ssDNA
- single-stranded DNA
- YEPD
- yeast extract peptone-dextrose
References
- Afgan E., Baker D., van den Beek M., Blankenberg D., Bouvier D., Čech M., Chilton J., Clements D., Coraor N., Eberhard C., et al. . 2016. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 44(W1):W3–W10. 10.1093/nar/gkw343 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alani E., Thresher R., Griffith J.D., and Kolodner R.D.. 1992. Characterization of DNA-binding and strand-exchange stimulation properties of y-RPA, a yeast single-strand-DNA-binding protein. J. Mol. Biol. 227:54–71. 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90681-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajon E., Laterreur N., and Wellinger R.J.. 2015. A single templating RNA in yeast telomerase. Cell Reports. 12:441–448. 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.06.045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow J.H., Lisby M., and Rothstein R.. 2008. Differential regulation of the cellular response to DNA double-strand breaks in G1. Mol. Cell. 30:73–85. 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.01.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi A., and Shore D.. 2008. How telomerase reaches its end: mechanism of telomerase regulation by the telomeric complex. Mol. Cell. 31:153–165. 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.06.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi A., Negrini S., and Shore D.. 2004. Delivery of yeast telomerase to a DNA break depends on the recruitment functions of Cdc13 and Est1. Mol. Cell. 16:139–146. 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.09.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branzei D., Sollier J., Liberi G., Zhao X., Maeda D., Seki M., Enomoto T., Ohta K., and Foiani M.. 2006. Ubc9- and mms21-mediated sumoylation counteracts recombinogenic events at damaged replication forks. Cell. 127:509–522. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra A., Hughes T.R., Nugent C.I., and Lundblad V.. 2001. Cdc13 both positively and negatively regulates telomere replication. Genes Dev. 15:404–414. 10.1101/gad.861001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., and Kolodner R.D.. 1999. Gross chromosomal rearrangements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae replication and recombination defective mutants. Nat. Genet. 23:81–85. 10.1038/12687 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., and Stubbe J.. 2005. Bleomycins: Towards better therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 5:102–112. 10.1038/nrc1547 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung W.H., Zhu Z., Papusha A., Malkova A., and Ira G.. 2010. Defective resection at DNA double-strand breaks leads to de novo telomere formation and enhances gene targeting. PLoS Genet. 6:e1000948 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000948 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counter C.M., Meyerson M., Eaton E.N., and Weinberg R.A.. 1997. The catalytic subunit of yeast telomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94:9202–9207. 10.1073/pnas.94.17.9202 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diede S.J., and Gottschling D.E.. 1999. Telomerase-mediated telomere addition in vivo requires DNA primase and DNA polymerases alpha and delta. Cell. 99:723–733. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81670-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dion V., Kalck V., Seeber A., Schleker T., and Gasser S.M.. 2013. Cohesin and the nucleolus constrain the mobility of spontaneous repair foci. EMBO Rep. 14:984–991. 10.1038/embor.2013.142 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank C.J., Hyde M., and Greider C.W.. 2006. Regulation of telomere elongation by the cyclin-dependent kinase CDK1. Mol. Cell. 24:423–432. 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.10.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo F., and Chartrand P.. 2011. Visualizing mRNAs in fixed and living yeast cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 714:203–219. 10.1007/978-1-61779-005-8_13 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo F., Olivier C., Dandjinou A.T., Wellinger R.J., and Chartrand P.. 2008. TLC1 RNA nucleo-cytoplasmic trafficking links telomerase biogenesis to its recruitment to telomeres. EMBO J. 27:748–757. 10.1038/emboj.2008.21 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo F., Laterreur N., Cusanelli E., Ouenzar F., Querido E., Wellinger R.J., and Chartrand P.. 2011. Live cell imaging of telomerase RNA dynamics reveals cell cycle-dependent clustering of telomerase at elongating telomeres. Mol. Cell. 44:819–827. 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.09.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasior S.L., Wong A.K., Kora Y., Shinohara A., and Bishop D.K.. 1998. Rad52 associates with RPA and functions with rad55 and rad57 to assemble meiotic recombination complexes. Genes Dev. 12:2208–2221. 10.1101/gad.12.14.2208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hang L.E., Liu X., Cheung I., Yang Y., and Zhao X.. 2011. SUMOylation regulates telomere length homeostasis by targeting Cdc13. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 18:920–926. 10.1038/nsmb.2100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ira G., Pellicioli A., Balijja A., Wang X., Fiorani S., Carotenuto W., Liberi G., Bressan D., Wan L., Hollingsworth N.M., et al. . 2004. DNA end resection, homologous recombination and DNA damage checkpoint activation require CDK1. Nature. 431:1011–1017. 10.1038/nature02964 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E.S., and Gupta A.A.. 2001. An E3-like factor that promotes SUMO conjugation to the yeast septins. Cell. 106:735–744. 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00491-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knop M., Siegers K., Pereira G., Zachariae W., Winsor B., Nasmyth K., and Schiebel E.. 1999. Epitope tagging of yeast genes using a PCR-based strategy: more tags and improved practical routines. Yeast. 15(10B):963–972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer K.M., and Haber J.E.. 1993. New telomeres in yeast are initiated with a highly selected subset of TG1-3 repeats. Genes Dev. 7(12a, 12A):2345–2356. 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2345 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh B.O., and Symington L.S.. 2004. Recombination proteins in yeast. Annu. Rev. Genet. 38:233–271. 10.1146/annurev.genet.38.072902.091500 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingner J., Hughes T.R., Shevchenko A., Mann M., Lundblad V., and Cech T.R.. 1997. Reverse transcriptase motifs in the catalytic subunit of telomerase. Science. 276:561–567. 10.1126/science.276.5312.561 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisby M., Mortensen U.H., and Rothstein R.. 2003. Colocalization of multiple DNA double-strand breaks at a single Rad52 repair centre. Nat. Cell Biol. 5:572–577. 10.1038/ncb997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydeard J.R., Lipkin-Moore Z., Jain S., Eapen V.V., and Haber J.E.. 2010. Sgs1 and exo1 redundantly inhibit break-induced replication and de novo telomere addition at broken chromosome ends. PLoS Genet. 6:e1000973 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000973 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda D., Seki M., Onoda F., Branzei D., Kawabe Y., and Enomoto T.. 2004. Ubc9 is required for damage-tolerance and damage-induced interchromosomal homologous recombination in S. cerevisiae. DNA Repair (Amst.). 3:335–341. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2003.11.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makovets S., and Blackburn E.H.. 2009. DNA damage signalling prevents deleterious telomere addition at DNA breaks. Nat. Cell Biol. 11:1383–1386. 10.1038/ncb1985 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangahas J.L., Alexander M.K., Sandell L.L., and Zakian V.A.. 2001. Repair of chromosome ends after telomere loss in Saccharomyces. Mol. Biol. Cell. 12:4078–4089. 10.1091/mbc.12.12.4078 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martina M., Clerici M., Baldo V., Bonetti D., Lucchini G., and Longhese M.P.. 2012. A balance between Tel1 and Rif2 activities regulates nucleolytic processing and elongation at telomeres. Mol. Cell. Biol. 32:1604–1617. 10.1128/MCB.06547-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder A., Tummler K., Bathe M., and Samson L.D.. 2013. Single-cell analysis of ribonucleotide reductase transcriptional and translational response to DNA damage. Mol. Cell. Biol. 33:635–642. 10.1128/MCB.01020-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee J.S., Phillips J.A., Chan A., Sabourin M., Paeschke K., and Zakian V.A.. 2010. Reduced Rif2 and lack of Mec1 target short telomeres for elongation rather than double-strand break repair. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 17:1438–1445. 10.1038/nsmb.1947 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J.K., and Haber J.E.. 1996. Cell cycle and genetic requirements of two pathways of nonhomologous end-joining repair of double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:2164–2173. 10.1128/MCB.16.5.2164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motegi A., and Myung K.. 2007. Measuring the rate of gross chromosomal rearrangements in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A practical approach to study genomic rearrangements observed in cancer. Methods. 41:168–176. 10.1016/j.ymeth.2006.07.025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozdy A.D., and Cech T.R.. 2006. Low abundance of telomerase in yeast: Implications for telomerase haploinsufficiency. RNA. 12:1721–1737. 10.1261/rna.134706 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myung K., Chen C., and Kolodner R.D.. 2001. Multiple pathways cooperate in the suppression of genome instability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 411:1073–1076. 10.1038/35082608 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent C.I., Hughes T.R., Lue N.F., and Lundblad V.. 1996. Cdc13p: a single-strand telomeric DNA-binding protein with a dual role in yeast telomere maintenance. Science. 274:249–252. 10.1126/science.274.5285.249 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obodo U.C., Epum E.A., Platts M.H., Seloff J., Dahlson N.A., Velkovsky S.M., Paul S.R., and Friedman K.L.. 2016. Endogenous hot spots of de novo telomere addition in the yeast genome contain proximal enhancers that bind Cdc13. Mol. Cell. Biol. 36:1750–1763. 10.1128/MCB.00095-16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oza P., Jaspersen S.L., Miele A., Dekker J., and Peterson C.L.. 2009. Mechanisms that regulate localization of a DNA double-strand break to the nuclear periphery. Genes Dev. 23:912–927. 10.1101/gad.1782209 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pâques F., and Haber J.E.. 1999. Multiple pathways of recombination induced by double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 63:349–404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennaneach V., Putnam C.D., and Kolodner R.D.. 2006. Chromosome healing by de novo telomere addition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Microbiol. 59:1357–1368. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05026.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennock E., Buckley K., and Lundblad V.. 2001. Cdc13 delivers separate complexes to the telomere for end protection and replication. Cell. 104:387–396. 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00226-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfingsten J.S., Goodrich K.J., Taabazuing C., Ouenzar F., Chartrand P., and Cech T.R.. 2012. Mutually exclusive binding of telomerase RNA and DNA by Ku alters telomerase recruitment model. Cell. 148:922–932. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J.A., Chan A., Paeschke K., and Zakian V.A.. 2015. The pif1 helicase, a negative regulator of telomerase, acts preferentially at long telomeres. PLoS Genet. 11:e1005186 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Psakhye I., and Jentsch S.. 2012. Protein group modification and synergy in the SUMO pathway as exemplified in DNA repair. Cell. 151:807–820. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.10.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam C.D., and Kolodner R.D.. 2010. Determination of gross chromosomal rearrangement rates. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2010:t5492 10.1101/pdb.prot5492 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam C.D., Pennaneach V., and Kolodner R.D.. 2004. Chromosome healing through terminal deletions generated by de novo telomere additions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 101:13262–13267. 10.1073/pnas.0405443101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raderschall E., Golub E.I., and Haaf T.. 1999. Nuclear foci of mammalian recombination proteins are located at single-stranded DNA regions formed after DNA damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 96:1921–1926. 10.1073/pnas.96.5.1921 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribaud V., Ribeyre C., Damay P., and Shore D.. 2012. DNA-end capping by the budding yeast transcription factor and subtelomeric binding protein Tbf1. EMBO J. 31:138–149. 10.1038/emboj.2011.349 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeyre C., and Shore D.. 2013. Regulation of telomere addition at DNA double-strand breaks. Chromosoma. 122:159–173. 10.1007/s00412-013-0404-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricchetti M., Dujon B., and Fairhead C.. 2003. Distance from the chromosome end determines the efficiency of double strand break repair in subtelomeres of haploid yeast. J. Mol. Biol. 328:847–862. 10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00315-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogakou E.P., Boon C., Redon C., and Bonner W.M.. 1999. Megabase chromatin domains involved in DNA double-strand breaks in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 146:905–916. 10.1083/jcb.146.5.905 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz V.P., and Zakian V.A.. 1994. The saccharomyces PIF1 DNA helicase inhibits telomere elongation and de novo telomere formation. Cell. 76:145–155. 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90179-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedelnikova O.A., Rogakou E.P., Panyutin I.G., and Bonner W.M.. 2002. Quantitative detection of (125)IdU-induced DNA double-strand breaks with gamma-H2AX antibody. Radiat. Res. 158:486–492. 10.1667/0033-7587(2002)158[0486:QDOIID]2.0.CO;2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sfeir A., and Symington L.S.. 2015. Microhomology-mediated end joining: A back-up survival mechanism or dedicated pathway? Trends Biochem. Sci. 40:701–714. 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.08.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M.S., and Gottschling D.E.. 1994. TLC1: template RNA component of Saccharomyces cerevisiae telomerase. Science. 266:404–409. 10.1126/science.7545955 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Star B., Nederbragt A.J., Hansen M.H.S., Skage M., Gilfillan G.D., Bradbury I.R., Pampoulie C., Stenseth N.C., Jakobsen K.S., and Jentoft S.. 2014. Palindromic sequence artifacts generated during next generation sequencing library preparation from historic and ancient DNA. PLoS One. 9:e89676 (published erratum appears in PLoS One. 2014. 9:e103170) 10.1371/journal.pone.0089676 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara N., Ivanov E.L., Fishman-Lobell J., Ray B.L., Wu X., and Haber J.E.. 1995. DNA structure-dependent requirements for yeast RAD genes in gene conversion. Nature. 373:84–86. 10.1038/373084a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata M., Sasaki M.S., Sonoda E., Morrison C., Hashimoto M., Utsumi H., Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Shinohara A., and Takeda S.. 1998. Homologous recombination and non-homologous end-joining pathways of DNA double-strand break repair have overlapping roles in the maintenance of chromosomal integrity in vertebrate cells. EMBO J. 17:5497–5508. 10.1093/emboj/17.18.5497 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira M.T., Förstemann K., Gasser S.M., and Lingner J.. 2002. Intracellular trafficking of yeast telomerase components. EMBO Rep. 3:652–659. 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf133 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Rosell J., Sunjevaric I., De Piccoli G., Sacher M., Eckert-Boulet N., Reid R., Jentsch S., Rothstein R., Aragón L., and Lisby M.. 2007. The Smc5-Smc6 complex and SUMO modification of Rad52 regulates recombinational repair at the ribosomal gene locus. Nat. Cell Biol. 9:923–931. 10.1038/ncb1619 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wach A., Brachat A., Pöhlmann R., and Philippsen P.. 1994. New heterologous modules for classical or PCR-based gene disruptions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 10:1793–1808. 10.1002/yea.320101310 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong J.M., Kusdra L., and Collins K.. 2002. Subnuclear shuttling of human telomerase induced by transformation and DNA damage. Nat. Cell Biol. 4:731–736. 10.1038/ncb846 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zampini É., Lepage É., Tremblay-Belzile S., Truche S., and Brisson N.. 2015. Organelle DNA rearrangement mapping reveals U-turn-like inversions as a major source of genomic instability in Arabidopsis and humans. Genome Res. 25:645–654. 10.1101/gr.188573.114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., and Durocher D.. 2010. De novo telomere formation is suppressed by the Mec1-dependent inhibition of Cdc13 accumulation at DNA breaks. Genes Dev. 24:502–515. 10.1101/gad.1869110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X., and Blobel G.. 2005. A SUMO ligase is part of a nuclear multiprotein complex that affects DNA repair and chromosomal organization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 102:4777–4782. (published erratum appears in Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005. 102:9086) 10.1073/pnas.0500537102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X., Muller E.G., and Rothstein R.. 1998. A suppressor of two essential checkpoint genes identifies a novel protein that negatively affects dNTP pools. Mol. Cell. 2:329–340. 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80277-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Monson E.K., Teng S.C., Schulz V.P., and Zakian V.A.. 2000. Pif1p helicase, a catalytic inhibitor of telomerase in yeast. Science. 289:771–774. 10.1126/science.289.5480.771 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z., Chung W.H., Shim E.Y., Lee S.E., and Ira G.. 2008. Sgs1 helicase and two nucleases Dna2 and Exo1 resect DNA double-strand break ends. Cell. 134:981–994. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.