Abstract
Despite the increasing use of rare earth elements (REEs) and oxides (REOs) in various technologies, the information on their ecotoxicological hazard is scarce. Here, the effects of La3+, Ce3+, Pr3+, Nd3+, Gd3+, CeO2, and eight doped REOs to marine bacteria Vibrio fischeri and freshwater protozoa Tetrahymena thermophila were studied in parallel with REO dopant metals (Co2+, Fe3+, Mn2+, Ni2+, Sr2+). The highest concentrations of REOs tested were 100 mg/L with protozoa in deionized water and 500 mg/L with bacteria in 2% NaCl. Although (i) most REOs produced reactive oxygen species; (ii) all studied soluble REEs were toxic to bacteria (half-effective concentration, EC50 3.5–21 mg metal/L; minimal bactericidal concentration, MBC 6.3–63 mg/L) and to protozoa (EC50 28–42 mg/L); and (iii) also some dopant metals (Ni2+, Fe3+) proved toxic (EC50 ≤ 3 mg/L), no toxicity of REOs to protozoa (EC50 > 100 mg/L) and bacteria (EC50 > 500 mg/L; MBC > 500 mg/L) was observed except for La2NiO4 (MBC 25 mg/L). According to kinetics of V. fischeri bioluminescence, the toxicity of REEs was triggered by disturbing cellular membrane integrity. Fortunately, as REEs and REOs are currently produced in moderate amounts and form in the environment insoluble salts and/or oxides, they apparently present no harm to aquatic bacteria and protozoa.
Keywords: lanthanides, nanoparticles, doped metal oxides, speciation, hazard evaluation, bioluminescence, cellular membrane integrity, viability, ciliates, Microtox™
1. Introduction
Chemically uniform group of metals, lanthanides (La–Lu), form together with yttrium (Y) and scandium (Sc) the group of REEs. REEs, in particular REOs, are increasingly used in many fields, e.g., catalysis, electronics, wind power generators, glass polishing and ceramics, metallurgical additives and alloys, high strength magnets, fuel cells, gas separation membranes, and fuel additives [1,2,3]. Probably the most rapid increase of REEs production is expected for neodymium (Nd) and dysprosium (Dy), as they are used in magnets of wind turbines and electric/hybrid cars [4,5]. In addition to use in industry, there is a long-term practice of the application of REEs-based micro-fertilizers, and REEs may also be introduced to environment during the production and application of phosphorous fertilizers [6,7,8,9]. Some REEs, such as gadolinium (Gd), are also used in health-related applications: in particular, Gd chelates are used as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging [10] and may reach the environment via waste streams. Indeed, increase of REEs concentrations (especially gadolinium) in water bodies due to the anthropogenic activities over the past two decades has been reported [11,12]. In general, REEs are considered of average supply risk, low environmental implications and low-to-medium vulnerability to supply restrictions, and currently China is the leading producer and trader of REEs [3,13]. However, mining operators must now mitigate respective environmental impacts; thus, assessment of the toxicological hazard of the REEs for aquatic biota is needed [14]. Recently, it was reported that in REE-contaminated areas, phytotoxicity may be a concern [15]. It has been shown than lanthanum (La) accumulates in different organisms and thus may pose a hazard to species belonging to higher levels of the food chain [16]. In addition, people may receive elevated doses of REE via food [17,18]. Unfortunately, information on the environmental hazard for REEs other than cerium (Ce) and lanthanum (La) is limited and available data vary [1,16,19,20]. Even for La, very little information on toxicity to microorganisms has been published [16].
Concerning REOs, there is already a substantial amount of ecotoxicological data on CeO2 but not for other types of REOs [21,22]. Although CeO2 is used in a variety of applications, e.g., as a fuel additive [23], there is still no consensus on its hazard to living organisms [24].
Thus, analogously to REEs, information on toxicity of REOs to aquatic biota is very limited. It is important to note that REOs can be also produced as composites. For example, the physicochemical properties of metal oxides can be tuned via doping [25], i.e., introducing metals into the crystal structure of the oxides at the level of their synthesis often allows to widen the fields of applications of these oxides. The wide variety of composite oxides makes the evaluation of their case-by-case potential effects even more complicated and justifies the introduction of bioassays that allow for the evaluation of their toxic properties relatively cost-efficiently and rapidly.
Gonzalez et al. [1] in their recent review have emphasized the major challenges and research needs in ecotoxicology of lanthanides: (i) the chemical speciation of lanthanides in ecotoxicological test media must be taken into account as due to the formation of insoluble chemical species in majority of ecotoxicological test media, a remarkable underestimation of the lanthanides’ toxicity is a realistic scenario; (ii) mechanistic studies are needed to reveal possible existence of common mechanisms or modes of action across the lanthanide series.
The aim of the current paper was to address currently existing data gaps on ecotoxicity of REEs and REOs by providing toxicity data for five REEs (lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, and gadolinium) and nine (doped) REOs for two unicellular aquatic organisms (Gram-negative bacteria Vibrio fischeri and particle-feeding protozoa Tetrahymena thermophila). We also addressed the challenges/research needs pointed out by Gonzalez et al. [1] by (i) conducting the toxicity testing and experiments in media (deionized water for protozoa and 2% NaCl for Vibrio fischeri) that do not support formation of insoluble complexes (phosphates, carbonates and hydroxides of REEs), thus providing comparable toxicity data for different REEs and (doped) REOs; and (ii) studying whether the disturbance of biological membrane integrity is the main biological event in triggering toxic effects of REEs and REOs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Rare Earth Oxide (REO) Particles
The (doped) REOs studied in this work are listed and described in Table 1. The oxides were synthesized using spray pyrolysis technique [26]. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method was used for analysis of specific surface area (SSA) and for calculation of primary particle size of studied REO particles. Both techniques are described in detail in Joonas et al. [27].
Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of the (doped) rare earth oxide particles measured in 100 mg/L suspensions in deionized water (modified from Joonas et al. [27]).
| Compound | Specific Surface Area (SSA), m2/g a | Primary Size, nm (BET) a | Hydro-Dynamic Size (nm) in DI (DLS) b | ζ-Potential (mV) in DI b | pH in DI c | pH in 2% NaCl c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce0.9Gd0.1O2 | 31.1 | 27 | 280 | −16.6 | 6.3 | 6.3 |
| LaFeO3 | 72 | 126 | 177 | 16.2 | 6.5 | 6.4 |
| Gd0.97CoO3 | 34 | 230 | 166 | 18.8 | 6.3 | 6.3 |
| LaCoO3 | 14 | 590 | 285 | −17.5 | 6.7 | 6.4 |
| (La0.5Sr0.5)0.99MnO3 | 7 | 137 | 194 | −1.8 | 7.3 | 6.9 |
| CeO2 | 22 | 38 | 172 | 8.5 | 6.5 | 6.5 |
| Ce0.8Pr0.2O2 | 361 | 23 | 147 | 16.6 | 6.3 | 6.3 |
| (La0.6Sr0.4)0.95CoO3 | 15 | 65 | 160 | 22.7 | 7.4 | 9.5 |
| La2NiO4 | 3 | 284 | 266 | −6.6 | 8.6 | 8.6 |
a the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method was used for analysis of the specific surface area (SSA) and for calculation of the primary particle size; b after centrifugation at 160× g for 10 min to remove large agglomerates DI- deionized water; a,b data taken from Joonas et al. [27]; c measured in the suspension of 1000 mg/L.
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of REO Particle Suspensions
REO powder (~20 mg) was weighed and mixed with deionized (DI) water (18.2 MΩ, pH 5.6 ± 0.1, Milli-Q, Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) to obtain a stock suspension of 1 g/L. The stock suspension was sonicated for 3 min (40 W, probe sonicator, Branson Ultrasonics Corporation, Danbury, CT, USA) and vortexed before use. Hydrodynamic size and ζ-potential of REO particles (100 mg/L) were measured in DI water using Malvern Zetasizer Nano-ZS (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK). The solubility of the only REO (La2NiO4), that proved toxic in our assays (see Section 3.3), was analyzed in two test media used in the toxicity assays of the current study: deionized water and 2% NaCl. For that, La2NiO4 stock suspension (1000 mg/L) was diluted with DI water or 2% NaCl to obtain concentration of 25 mg/L and let settle at room temperature for 24 h. La and Ni concentrations in the La2NiO4 were quantified with the total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (TRXF; Picofox S2, Bruker Nano GmbH, Berlin, Germany). For this, 1 mL of suspension was pipetted into 1.5 mL Eppendorf tube and the particles were pelleted by centrifugation at 20,000× g for 30 min. After centrifugation, 50 μL of the supernatant was carefully removed, mixed with gallium (Ga) internal standard (Fluka) in the ratio of 1:1 and 5 μL of this mixture was pipetted onto a quartz carrier disc. The concentration of metals was quantified with the Spectra software (version 7.2.5.0, Bruker Nano GmbH, Berlin, Germany).
2.3. Soluble Metal Salts Analyzed for Toxicity
The soluble metal salts tested in protozoan and bacterial toxicity tests were as follows: Ni(NO3)2·6H2O (Merck KGaA, Nottingham, UK, purity ≤ 100%), Co(NO3)2·6H2O (VWR, 98%), Gd(NO3)3·6H2O (Sigma Aldrich, Oslo, Norway, 99.9%), Sr(NO3)2 (Honeywell, Morristown, NJ, USA, 100%), Mn(NO3)2·6H2O (American Elements, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 100%), La(NO3)3·6H2O (Treibacher Industrie AG, Althofen, Austria, ≥95–100%), Ce(NO3)3·6H2O (Treibacher Industrie AG, ≥95–100%), Fe(NO3)3·9H2O (Sigma Aldrich, 99.99%), Pr(NO3)3·6H2O (Sigma Aldrich, 99.9%) Nd(NO3)3·6H2O (Sigma Aldrich, 99.9%). pH values of the stock solutions (1000 mg/L) were in the range of 4.5–5.6 (in DI water) and 5.2–6.6 (in 2% NaCl), except for Fe(NO3)3 that was more acidic (pH 2.1 in DI water and 2.3 in 2% NaCl).
2.4. Quantification of Reactive Oxygen Species
For further characterization, the abiotic reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation potential i.e., ability to generate ROS in DI water without the test organisms present, was determined for REO powders in the dark as described previously [28]. The REO particles were incubated at concentrations 1, 10 and 100 mg/L in triplicates on 96-well black polypropylene microplate for 24 h with two different dyes: (i) 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein-diacetate (DCFH-DA, Life Technologies, Paisley, UK) that can detect wide variety of ROS, Mn3O4 NPs [28] (provided by University of Bremen, Bremen, Germany) were used as a positive control; and (ii) 3′-(p-hydroxyphenyl) fluorescein (HPF, Life Technologies) that is used to detect hydroxyl radicals, known •OH producing Fenton reaction (triggered by mixing 100 µmol/L FeSO4·7H2O (Reachim, analytical grade) with 1.47 mmol/L H2O2 (Sigma-Aldrich) was used as a positive control.
2.5. Vibrio fischeri Kinetic Bioluminescence Inhibition Test (a Flash-Assay) in 2% NaCl and in PBS (Phosphate-Buffered Saline) Containing 2% NaCl
A kinetic acute bioluminescence inhibition assay (exposure time 30 min) with bacteria Vibrio fischeri was performed at room temperature (~20 °C) in 96-well microplates following the Flash-assay protocol [29]. Briefly, 100 μL of bacterial suspension was added to 100 μL of tested compound in the microplate well by automatic dispensing. Bacterial luminescence was continuously recorded during the first 30 s after dispensing (no additional mixing of the sample). After 30-min incubation, luminescence was recorded again. The Microplate Luminometer Orion II (Berthold Detection Systems, Pforzheim, Germany) controlled by the Simplicity version 4.2 Software was used. Reconstituted V. fischeri reagent (Aboatox, Turku, Finland) was used and all the chemicals and their two-fold dilutions were prepared in 2% NaCl. Each test was performed in 5–7 replicates. In each measurement series both negative (2% NaCl) and positive (3,5-dichlorophenol, 3,5-DCP) controls were included. Inhibition of bacterial luminescence (INH%) by the chemical was calculated as follows:
| (1) |
| (2) |
KF (correction factor) denotes for the natural loss of luminescence of the control (i.e., bacterial suspension in 2% NaCl). IC0 and IT0 are the maximum values of luminescence during first 5 s after dispensing test bacteria to the control and test sample, respectively. IC30 and IT30 are the respective luminescence values after 30 min. EC50 is the nominal concentration of a compound reducing the bacterial bioluminescence by 50%. EC50 values were calculated from dose-effect data using REGTOX software (version EV7.0.5, Eric Vindimian, Paris, France) for Microsoft Excel™ (version 2010, Microsoft Corporation) [30].
For the evaluation of the speciation on bioavailability of REEs, we performed the Vibrio fischeri Flash assay in the medium containing phosphate, i.e., instead of 2% NaCl, PBS+NaCl was used throughout. Otherwise the assay was performed as described in the beginning of this Section. For that, PBS+NaCl medium was prepared: NaCl 19 g, KCl 0.2 g, Na2HPO4 1.42 g, and KH2PO4 0.24 g per litre DI water, pH = 7.4 (Cold Spring Harbor Protocols). Lyophilized bacteria were reconstituted as always in special diluent containing per litre: 20 g NaCl, 2.035 g MgCl2·6H2O and 0.3 g KCl. All toxicants were diluted in PBS+NaCl medium.
2.6. Vibrio fischeri Viability Assay (a ‘Spot Test’)
Vibrio fischeri viability assay (a ‘Spot test’) was performed as described in detail in Suppi et al. [31]. The assay evaluates the ability of the toxicant-exposed bacteria to form colonies on toxicant-free nutrient agar after 24-h exposure to the tested chemicals in 2% NaCl. Briefly, 100 μL of the V. fischeri suspension was added to 100 μL of varying concentrations of tested chemicals in 2% NaCl. Exponential (2-fold) dilution series of the REOs suspensions in the range of 1.5–500 mg compound/L and soluble metal salts in the range of 0.1–500 mg metal/L (depending on the toxicity of the compound; nominal concentrations) were tested. Incubation of bacteria with toxicants was performed in 96-well microplates (non-tissue culture treated, Greiner Bio-One) at 20–23 °C for 24 h without shaking, in the dark. After 24 h of exposure to the toxicants (or 2% NaCl), 3 μL of the cell suspension from each microplate well was pipetted as a ‘spot’ onto an agarized BH (Beneckea-Harvey) growth medium containing (per Litre): yeast extract 3 g, tryptone 5 g, glycerol (99%) 2 mL, NaCl 30 g Na2HPO4·12H2O 9.45 g, KH2PO4 1 g, (NH4)2HPO4 0.5 g, MgSO4·7H2O 0.3 g, agar 15 g). The inoculated agar plates were incubated for 72 h at 22–23 °C. Minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) of the tested chemicals was determined as the lowest tested nominal concentration of a chemical which completely inhibited the ability of bacteria to form visible colonies after plating onto toxicant-free agar-plates. Each experiment was repeated at least three times.
2.7. Tetrahymena thermophila Viability Assay
Protozoan viability assay was conducted with Tetrahymena thermophila (strain BIII) using ATP concentration of the cell suspension for quantification of the viable biomass. For more details, see Jemec et al. [32]. Briefly, the cells were cultured in SSP medium supplemented with antibiotics penicillin G and streptomycin sulphate, and fungicide amphotericin B. The cells were harvested at logarithmic growth phase by centrifugation at 300× g for 5 min at 4 °C, washed in DI water and the culture density for viability assays was adjusted to 106 cells/mL (OD600 nm = 2). To assess the effect of REEs and (doped) REOs towards protozoa, 100 µL of T. thermophila cells in DI water were exposed to 100 µL of REE or (doped) REO formulations in DI water at different concentrations (final cell density 5 × 105 cells/mL) on 96-well polystyrene plate for 24 h at 25 °C in the dark. Pure DI water with the same final density of T. thermophila culture served as a negative control. The pH of the samples varied in the range of 5–7 after 24-h exposure. All the concentrations were tested in at least triplicate; non-toxic (doped) REO particles (see Section 3.3.) were tested at least on two and REEs and dopants on at least three separate days. After the experiment, the cells were visualized with light microscope Olympus CX41 equipped with DP71 camera (Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The viability was quantified by extracting ATP and measuring its content in the samples by applying luciferin-luciferase method described earlier [33].
2.8. Data Analysis
V. fischeri 30-min EC50 (the nominal concentration where bioluminescence inhibition was 50% compared to untreated control) and T. thermophila 24-h EC50 (the nominal concentration where based on ATP concentration the viability had decreased 50% compared to untreated control) with their respective 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated from the dose-response curves by applying the log-normal model of REGTOX software for Microsoft Excel™ [30]. For abiotic ROS generation, the differences between untreated and treated samples were assessed in R Statistical Software (version 3.2.3, R Foundation) using ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc test. All calculated results were considered statistically significant when 95% CI did not overlap or statistical test resulted in p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Studied Rare Earth Oxide (REO) Particles
According to the primary size of the REO particles, four of the studied preparations could be considered nanoparticles (NPs) as their average particle size was <100 nm (Table 1). The hydrodynamic size and the ζ-potential of particles were characterized in two media: deionized water (DI) that was used as a test medium for protozoan viability assay and 2% NaCl that was a test medium for marine bacteria Vibrio fischeri. The hydrodynamic size of the REO particles in deionized water ranged from 147 to 285 nm (Table 1). As described in Joonas et al. [27], zeta potential of particles was measured after removal of large REO agglomerates by centrifugation, to obtain a reliable value and was ranging from −16.6 to +22.7 mV in DI water. It was not possible to measure hydrodynamic size and ζ-potential of particles in 2% NaCl as particles heavily agglomerated and settled. The pH values of the REO suspensions in DI and 2% NaCl were mostly neutral except for La2NiO4 and (La0.6Sr0.4)0.95CoO3 which were alkaline, pH from 8.6 to 9.5 (Table 1).
3.2. Analysis of Potential of REO Particles to Generate Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Abiotic Conditions
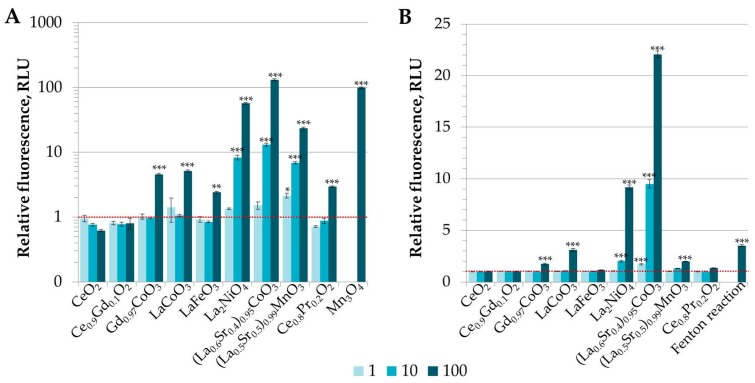
Besides dissolution, another mechanism of action suggested for metal-containing particles, especially nanoparticles, is production of reactive oxygen species [21,34,35,36]. Indeed, most of the elements studied in this work (all lanthanides, Fe, Mn, Co, and Ni) are transition metals that due to their various oxidation states are considered to have oxidative capacity [36]. Thus, the ability of (doped) REO particles was studied in abiotic conditions, i.e., only in DI water with no test organisms present. After 24-h incubation, most of the doped REOs generated ROS as can be seen in Figure 1. The ROS production potency of REOs evaluated by the fluorescence of DCFH decreased in the order (La0.6Sr0.4)0.95CoO3 > La2NiO4 > (La0.5Sr0.5)0.99MnO3 > LaCoO3 > Gd0.97CoO3 > Ce0.8Pr0.2O2 > LaFeO3, while Ce0.9Gd0.1O2 and CeO2 did not increase the fluorescence of DCFH compared to the control (Figure 1A). Five doped REO particles could also produce •OH radicals and the order according to potency was similar: (La0.6Sr0.4)0.95CoO3 > La2NiO4 > LaCoO3 > (La0.5Sr0.5)0.99MnO3 > Gd0.97CoO3 (Figure 1B). These results indicate that dopants seem to have the dominant role in determining the oxidative potential of REO particles as all REOs containing cobalt, nickel or manganese as a dopant were capable of producing •OH radicals. In addition, the results were in accordance with study performed by Aruoja et al. [28] who showed that in abiotic conditions, Co3O4 and Mn3O4 in nanoform were capable of producing ROS (•OH radicals) even without photoactivation. Furthermore, although iron is a known triggerer of hydroxyl radical producing a Fenton reaction [37], LaFeO3 particles were least potent among ROS generating REOs and did not induce •OH radicals; similarly, Fe3O4 did not induce ROS in abiotic conditions in the study by Aruoja et al. [28]. Nickel is also a known producer of ROS in cells; however, the levels are usually lower compared to Fe and Co [38]. Although REEs did not seem to enhance ROS potency of REO particles in abiotic conditions at the same level as dopants, they still might have a role in organisms as Pagano et al. [39] showed that chlorides of some REEs like yttrium (Y), Ce and samarium (Sm) were capable of inducing excess ROS formation in sea urchin early embryos while others (La and Nd) produced ROS at similar levels to control. Similar to our results indicating that Ce-containing REO particles do not induce ROS (Figure 1), Ce NPs with a primary diameter of 3–5 nm and agglomerate size of 15–25 nm were shown to reduce ROS levels in A2780 ovarian cancer cells in vitro [40].
Figure 1.
Abiotic generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by the rare earth oxide (REO) particles in deionized water measured after 24-h incubation with fluorescent dyes DCFH-DA (A) and HPF (B). Mn3O4 (A) and Fenton reaction (B) were included as positive controls. Concentrations are shown in the insets and are nominal, in mg compound/L. Dotted line indicates background fluorescence = 1.0. The asterisk (*) marks significant difference (p < 0.05); (**) highly significant difference (p < 0.01), and (***) very highly significant difference (p < 0.001) from the control.
3.3. Toxicity Evaluation of REEs and (Doped) REOs
3.3.1. Toxicity to Bacteria Vibrio fischeri
Vibrio fischeri are naturally luminescent Gram-negative marine bacteria that also are known under the name of Photobacterium phosphoreum NRRL-B-11177 and Aliivibrio fischeri [41]. V. fischeri rapidly responds to bioavailable toxicants with decrease in its natural bioluminescence in the time-scale of seconds-to-minutes, depending on the toxicant and its concentration, due to the disturbance of the integrity of cellular membrane, which functionality is essential for the central energy metabolism of the bacteria [42]. Therefore, the reduction of light output is a reflection of inhibition in bacterial metabolic activity and is proportional to the toxicity of the chemical or test sample [43]. The first bioluminescence inhibition assay using V. fischeri was commercialized already in 1979 as a Microtox™ (AZUR Environmental, Carlsbad, CA, USA) test and it is still probably the most widely used ecotoxicological test worldwide due to its low cost, rapidness, and great comparability as according to the literature, a lot of toxicity data for various chemicals have been obtained by applying this assay [41,44,45]. We have previously shown that as the suspensions of (nano) particles are often turbid due to insolubility and agglomeration of particles, a kinetic Flash Assay format of the V. fischeri bioluminescence inhibition assay [46] and not the format of conventional Microtox™ assay is better suited for toxicity evaluation of turbid suspensions of nanoparticles. The luminescence inhibition by toxicants is a sub-lethal response but it correlates well with the lethal endpoints for bacterium such as inability to grow on nutrient agar after exposure to the toxic concentration of the chemical [28]—a test format that was employed also in the current study for the evaluation of the minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) of studied chemicals to V. fischeri. In addition, other test formats employing V. fischeri have been used for toxicity evaluation, such as inhibition of V. fischeri growth by toxicants in complex medium [47]. The average (from 2–5 experiments) toxicity values of REEs and (doped) REOs for V. fischeri obtained in this study are presented in Table 2. Altogether, data obtained with two different test formats are presented: 30-min luminescence inhibition assay (30-min EC50) and evaluation of the ability of bacteria to form colonies on agar media after 24-h incubation with toxicant (24-h MBC) (Table 2).
Table 2.
Toxicity of (doped) rare earth oxide particles and soluble metal salts to protozoa Tetrahymena thermophila and bacteria Vibrio fischeri. The rare earth elements (REEs) in REOs are indicated in bold letters. The average EC50 a values with their 95% confidence intervals (in the brackets) are presented. N indicates the number of repetitive experiments performed to obtain the average value. For MBC b values, the representative value is presented (i.e., the value obtained in majority of experiments).
| Compound | Toxicity Endpoint | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 24-h Decrease of Viability, % | 30-min Inhibition of Luminescence, % | Ability to Yield Colonies on Agar Plates after 24-h Exposure to Chemical | |
| Protozoa T. thermophila | Bacteria V. fischeri | Bacteria V. fischeri | |
| (Doped) rare earth oxides | EC50 a, mg compound/L | MBC b, mg compound/L | |
| Ce0.9Gd0.1O2 | >100; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 |
| LaFeO3 | >100; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 |
| Gd0.97CoO3 | >100; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 |
| LaCoO3 | >100; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 |
| (La0.5Sr0.5)0.99MnO3 | >100; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 |
| CeO2 | >100; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 |
| Ce0.8Pr0.2O2 | >100; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 |
| (La0.6Sr0.4)0.95CoO3 | >100; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 |
| La2NiO4 | >100; N = 2 | >500; N = 2 | 25; N = 4 |
| Rare earth elements | EC50, mg metal/L | MBC, mg metal/L | |
| Ce(NO3)3·6H2O | 41.7 (38.3–46.5); N = 3 | 6.70 (5. 81–8.48); N = 5 | 12.5; N = 3 |
| Gd(NO3)3·6H2O | 28.4 (27.3–30.6); N = 3 | 3.53 (3.38–3.76); N = 5 | 6.25; N = 3 |
| La(NO3)3·6H2O | 41.9 (38.0–47.2); N = 3 | 20.93 (17.07–25.94), N = 5 | 62.5; N = 4 |
| Nd(NO3)3·6H2O | 29.8 (29.5–31.2); N = 2 | 6.87 (6.66–8.57); N = 3 | 15.6; N = 4 |
| Pr(NO3)3·6H2O | 30.8 (26.6–35.8); N = 2 | 12.17 (11.08–14.82); N = 3 | 12.5; N = 4 |
| Dopant metals | EC50, mg metal/L | MBC, mg metal/L | |
| Fe(NO3)3·9H2O | 4.9 (4.4–5.3); N = 3 | 0.44 (0.40–0.46); N = 6 | 1.25; N = 4 |
| Co(NO3)2·6H2O | >100; N = 4 | 462 (404–564); N = 5 | 62.5; N = 5 |
| Mn(NO3)2·6H2O | 82.0 (76.9–90.4); N = 4 | >500; N = 5 | >500; N = 3 |
| Ni(NO3)2·6H2O | 2.7 (2.6–2.9); N = 3 | >500; N = 5 | 1.25; N = 5 |
| Sr(NO3)2 | >100; N = 2 | >500; N = 5 | >500; N = 3 |
a EC50—half-effective concentration; b MBC—minimal bactericidal concentration.
The EC50 values obtained from 30-min inhibition of luminescence toxicity test (Table 2) were slightly lower than previously reported for Ce and Gd analyzed in the V. fischeri assay (EC50 > 6.4 mg/L) [19]. This fact may be explained by different lanthanides compound tested (nitrates in the current study and chlorides in the work of González et al. [19]).
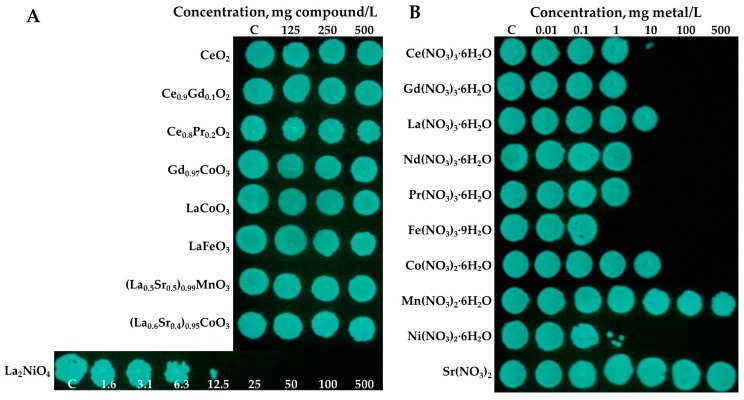
All the studied (doped) REOs were not toxic to V. fischeri in the bioluminescence inhibition assay even at the highest tested concentration, i.e., 30-min EC50 >500 mg/L (Table 2; Figure 2), showing that REOs are benign according to this test. Analogously, no toxic effects for CeO2 for V. fischeri was observed by Velzeboer et al. [48]: 15-min EC50 >100 mg/L. However, in the ‘Spot test’ after 24-h incubation La2NiO4 was bactericidal to V. fischeri already at 25 mg/L (Figure 2A; Table 2). Other REOs were not inhibitory in this assay (Figure 2A; Table 2). For the comparison, CuO and ZnO nanoparticles that are considered intrinsically biocidal [49] were toxic to V. fischeri in the same type of assays already in the concentration range of 1–10 mg/L [28].
Figure 2.
Bactericidal action of studied (doped) rare earth oxides (A) and salts of respective rare earth elements and dopants (B) to Vibrio fischeri. Bactericidal properties were evaluated by determining the colony-forming ability of the bacteria after exposure to suspensions of the particles in 2% NaCl for 24 h at room temperature, 22–23 °C. After exposure, 3 μL of bacterial suspension was transferred onto toxicant-free agarized nutrient medium and plates were incubated for 72 h at 22–23 °C. The concentrations are in mg compound/L (REO) or mg metal/L (REE salts), and nominal. Blue-green spots are bioluminescent bacterial colonies photographed in the dark. Minimal bactericidal concentration, MBC, is the lowest tested concentration that inhibited the bacterial ability to grow (form a colony on nutrient agar). MBC of La2NiO4 = 25 mg/L. For other REOs MBC > 500 mg/L. See also Table 2.
Although REOs were benign to Vibrio fischeri, all studied REEs in their soluble form were toxic to bacteria (30-min EC50 3.5–20.9 mg metal/L; 24-h MBC, 6.3–62.5 mg metal/L) (Figure 2B, Table 2). The respective dose-response curves are presented in Figure 3A. For the comparison, the toxicity of Cu and Zn ions to V. fischeri was 2.7 mg Zn/L and 0.42 Cu/L (30-min EC50 values; bioluminescence inhibition assay) [28].
Figure 3.
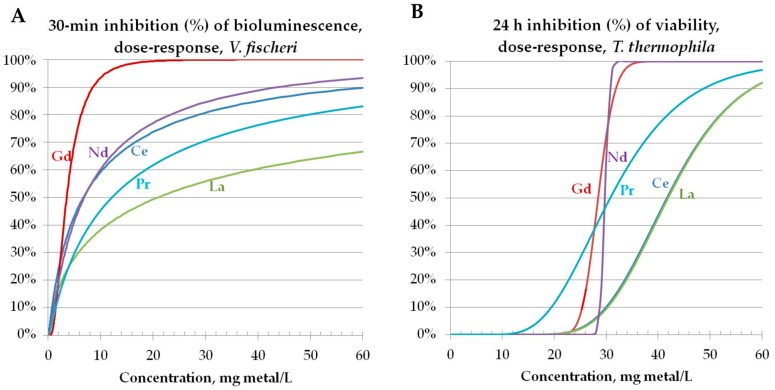
Toxicity of REEs to Vibrio fischeri (A) and Tetrahymena thermophila (B). Dose-response curves based on 30-min inhibition of bacterial luminescence (A) or cellular viability after 24-h exposure evaluated by ATP content of protozoan suspensions (B) are presented. The dose-response curves are constructed by combining the results from 2–5 different independent experiments (altogether 6–10 parallels). See also Table 2 and Figure 6.
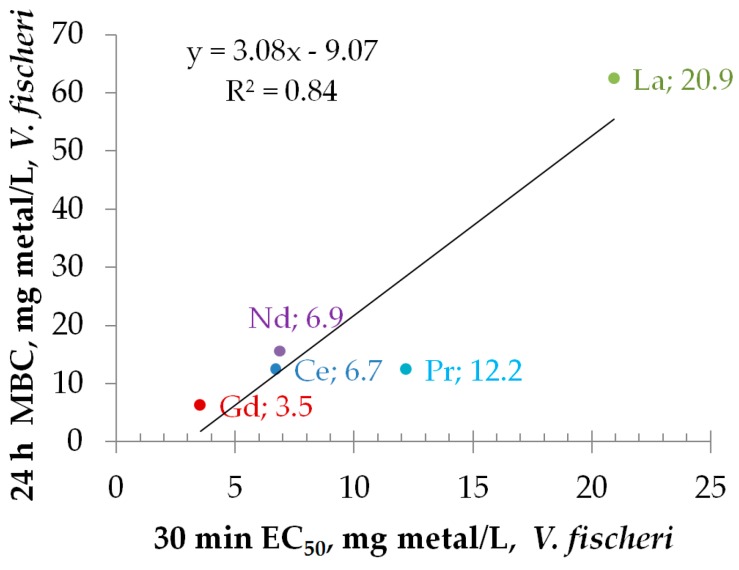
In Figure 4, toxicity of soluble salts of Gd, Nd, Ce, Pr, and La in two different V. fischeri assay formats was compared. 30-min inhibition of luminescence is a sub-acute toxicity endpoint and evaluation of MBC is based on the toxic endpoint, i.e., the inability of the cells to grow following the exposure to toxic concentration of the chemical. Despite the endpoints are different, the 30-min EC50 and 24-h MBC values for lanthanides correlated reasonably well (R2 = 0.84) although the MBC values were on average 2-fold higher (Table 2; Figure 4).
Figure 4.
30-min EC50 versus 24-h MBC (Vibrio fischeri), mg metal/L. EC50 values were calculated from dose-response curves of 30-min inhibition of bioluminescence. 24-h minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) is the lowest tested concentration to which bacteria were exposed for 24 h that prevented bacteria from growing (form colonies) after re-inoculation on nutrient agar. Tested metals are indicated as data labels accompanied by the respective 30-min EC50 values. See also Table 2.
In addition to REEs that are mostly the constituent metals of the studied REOs, also the soluble salts of the dopant metals (Co2+, Fe3+, Mn2+, Ni2+, Sr2+) were evaluated for their toxicity as these metals may be solubilized from the oxides and cause toxic effects [27]. In general, Co2+, Mn2+ and Sr2+ were not toxic (EC50 > 100 mg/L) or of relatively low toxicity in our assays; contrarily, Ni2+ was highly toxic in both tests where contact time with test organisms was 24 h (EC50 or MBC < 3 mg/L). Only Fe3+ proved very toxic in all three test formats (EC50 < 5 mg/L) but this effect cannot be attributed to acidic environment (although the stock solution was acidic; see Section 2.3) as in all tests the pH values at EC50 concentrations exceeded 5 (that did not affect the viability of selected microorganisms) (Table 2).
Our data on toxicity of iron and nickel are in accordance with the data from the literature. According to Storz and Imlay [50], the concentration of iron in the cells should be kept at low level as high concentrations of iron are toxic, mostly due to generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Sorokina et al. [51] have reported 30-min EC50 values for recombinant luminescent E. coli bacteria as 8.5 mg Fe2+/L and 1.3 mg Fe3+/L, i.e., quite similar to our data for V. fischeri (0.44 mg Fe3+/L) (Table 2). Concerning toxicity of nickel, its toxic effect to microorganisms is considered to occur (i) due to binding of Ni to catalytic residues of enzymes and also inhibiting enzymes allosterically; (ii) replacing the essential metals from metalloproteins; and (iii) causing indirectly oxidative stress although Ni is considerably weak generator of oxidative damage when compared to iron or copper [52].
3.3.2. Toxicity to Protozoa Tetrahymena thermophila
Tetrahymena thermophila is a freshwater ciliated protozoan that, as a protist, is a predator of bacteria and prey for metazooplankton in aquatic food webs [53]. Like prokaryotic V. fischeri, Tetrahymena is also a unicellular model organism used in toxicology for decades [54]; but differently from V. fischeri, eukaryotic T. thermophila is capable of internalizing nano- and microscale particles by phagocytosis [55]. The latter ability makes it also suitable for the current study. Interestingly, T. thermophila is capable of surviving in DI water for at least as long as a week [56] due to its contractile-vacuole system, which maintains constant osmotic pressure in the cell [55]. This ability has been exploited in some recent studies [32,57] where T. thermophila was exposed to silver that forms easily insoluble chemical species in various test media as lanthanides do. Thus, to avoid lanthanide interactions with media components, the toxicity tests with T. thermophila were performed in DI water.
Although many of the studied REOs were capable of producing abiotic ROS (Section 3.2, Figure 1), analogously to V. fischeri, the REOs were not toxic to protozoa T. thermophila (24-h EC50 > 100 mg/L) (Table 2). The latter was not surprising as ROS-generating Ag nanoparticles proved to be toxic towards T. thermophila only by dissolving; this suggests that T. thermophila has efficient mechanisms to cope with oxidative stress [57]. For the comparison, CuO and ZnO nanoparticles were toxic to T. thermophila in the same type of assay in the concentration range of 1–10 mg/L [28]. Analogously to bacterial assays, all studied five REEs in their soluble form were toxic to protozoa (24-h EC50 from 28–42 mg/L) (Table 2; Figure 3B) being less toxic than Cu and Zn ions (24-h EC50 7 mg Zn/L and 0.7 mg Cu/L [28]).
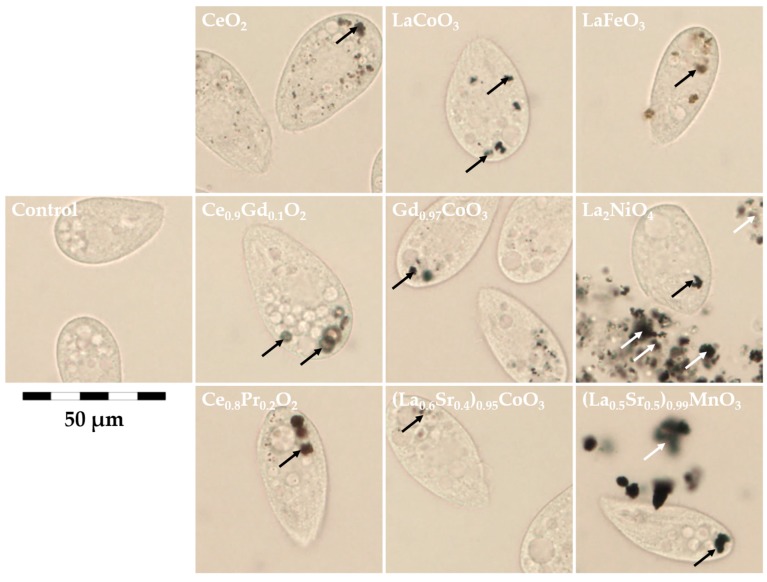
Despite T. thermophila was resistant to REO particles at concentrations up to 100 mg/L, visualization with microscope revealed that some of the food vacuoles were still filled with agglomerates of the REO particles after 24-h exposure (Figure 5). Previous studies with various particles have indicated that as soon as T. thermophila comes to contact with the particles, its food vacuoles start to fill up and after digestion, the pellets of agglomerated particles are excreted to the environment [28,33,58,59,60]. Alarmingly, compared to other freshwater invertebrates, T. thermophila has higher tolerance to heavy metals [21,49]; thus, although T. thermophila removes possibly toxic particles from the environment, the particles might still pose harm to more sensitive higher trophic levels that feed on protozoa during the REO particles are still inside the protozoan.
Figure 5.
Viable protozoa T. thermophila exposed to 100 mg/L of various REOs for 24 h. Black arrows indicate food vacuoles filled with agglomerated REO particles, white arrows indicate particle-agglomerates released to the environment.
3.3.3. Toxicity to Algae Raphidocelis subcapitata (Data Taken from the Literature): Comparison of Toxicity Pattern of REEs and REOs to Three Aquatic Species (Bacteria, Protozoa, Algae)
The toxicity of the same set of REEs and REOs as in the current study was evaluated for the algae Raphidocelis subcapitata in the 72-h growth inhibition assay by Joonas et al. [27]. Differently from the toxic effects of REE to bacteria V. fischeri that somewhat varied (Table 2), the REEs were of comparable toxicity to algae (72-h EC50 values 1.2–1.4 mg metal/L) and were highly inhibitory to algal growth. The toxicity of REEs to protozoa was about 20–30 fold lower than to algae and toxicity to bacteria was about 10–20 fold lower than to algae, depending on bacterial toxicity endpoint. Out of the 5 REEs studied, Gd was the most toxic and La the least toxic lanthanide to bacteria V. fischeri and protozoa T. thermophila, supporting the proposed hypothesis that heavier lanthanides are more toxic than the lighter ones [61]. The very high toxicity of lanthanides toward algae (EC50 ~ 1 mg/L;) observed by Joonas et al. [27] was explained by authors by indirect effect of REEs via nutrient removal from the algal growth medium as a result of formation of insoluble REE’s phosphates. In the ‘Spot test’ in DI-water performed in parallel with the same algae, the 24-h MBC values of soluble salts of La, Ce, Pr, and Gd were much higher, 10 mg/L [27].
As described above, studied REOs were not toxic in protozoan viability assay and bacterial assays, except for La2NiO4 that was bactericidal to V. fischeri at 25 mg/L (Table 2; Figure 2A). Analogously, Joonas et al. [27] did not observe toxic effects for algae for the studied REOs in the ‘Spot test’ (MBC ≥ 100 mg/L) except La2NiO4 that was biocidal to algae at 10 mg/L and the authors proved that the toxic effect of La2NiO4 was due to dissolved Ni. Due to the toxicity of La2NiO4 in the 24-h growth inhibition assay for V. fischeri (24-h MBC = 25 mg/L; Table 2), we quantified the solubilized fraction of Ni and La in the suspension of 25 mg/L of La2NiO4. The concentration of soluble La in DI-incubated La2NiO4 was 0.081 mg/L and soluble Ni 0.56 mg/L. The respective concentrations in 2% NaCl incubated La2NiO4 were 0.087 mg La/L and 0.48 mg Ni/L. As the level of solubilized Ni (0.56 mg/L) was close to the 24-h MBC value (1.25 mg Ni/L), the solubilized Ni was assumingly the reason for the toxic effect of La2NiO4 (Table 2) as formerly proposed also by Joonas et al. [27].
One has to mention that in the algal growth inhibition assay also other REOs were adversely acting in lower concentrations compared to protozoan or bacterial assays (72-h EC50 values for algae were from 2.1 for (La0.6Sr0.4)0.95CoO3 to 98 mg/L for Ce0.9Gd0.1O2), but that effect was caused by entrapping algae into the agglomerates of the particles and restricting their growth [27].
Thus, it seems that the joint “opinion” of algae, protozoa and bacteria was that the REOs were not toxic to investigated aquatic species unless doped with toxic metals (such as Ni), the shedding of which may lead to toxic effects.
3.4. Effect of REEs on the Kinetics of Vibrio fischeri Bioluminescence
As shown in Table 2, all tested soluble REEs but not REOs proved toxic in the bioassays used in the current study. Most of the chemicals are toxic starting from a certain concentration due to the basal toxicity, i.e., affecting structures and functions common to all types of cells/organisms [62]. When we consider prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells (bacteria versus protozoa, for example), such a common structure is cell membrane. Moreover, in case of unicellular organisms the cell wall/membrane also separates the organism from the abiotic environment. As bacteria are unicellular organisms, they are protected from external, often hostile environment by strong cell wall [63]. Based on their cell envelope structure, the bacteria are classified into two broad groups: Gram-negative and Gram-positive. Vibrio fischeri is a Gram-negative bacterium. The biggest difference between Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria is concerning the peptidoglycan layer in the cell wall. The peptidoglycan of Gram-positive bacteria is 30 nm and in the Gram-negative bacteria just 2–3 nm thick but covered by another membrane—an outer membrane that is composed of phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides facing to the external environment [64].
As described above, the bioluminescence of bacteria V. fischeri is correlated with its metabolic activity and energetic metabolism—the process taking place inside the cell on cellular membrane. Indeed, the half-effective concentrations of chemicals that led to the inhibition of luminescence of Photobacterium phosphoreum (EC50) correlated reasonably well with octanol/water partition coefficients of the chemicals, acute L(E)C50 data from the ecotoxicological assays, in vitro toxicity data for animal cell lines and even with in vivo data for rats and mice [65].
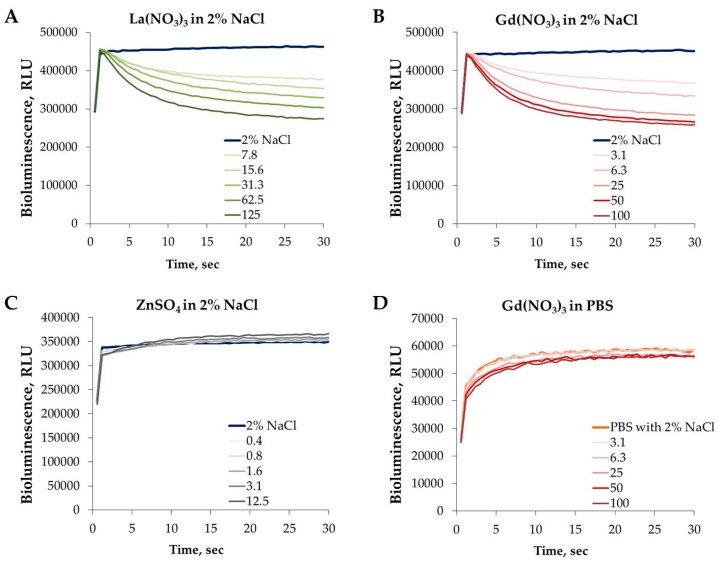
In addition, the time-scale and pattern of the kinetics of bacterial luminescence to the certain chemical allows comparison of the toxic action of different chemicals in respect of disturbance of the cellular membrane integrity [66]. As REEs have a very high affinity to phosphates, we hypothesized that the kinetics of the luminescence of Vibrio fischeri could be a very good mechanistic toxicity endpoint reflecting the early changes in the bacterial membrane (loss of integrity) due to exposure to REEs. The changes in bioluminescence of V. fischeri can be followed starting from the first seconds of the contact of bacteria with chemicals (Figure 6A,B). Although Figure 6 shows only the effects of Gd3+ and La3+, all five studied lanthanides were characterized by the rapidly acting (within 1st seconds of exposure; Figure 6A,B) inhibitory effect on bacterial bioluminescence (data not shown). For the comparison, exposure of bacteria to Zn (Figure 6C) did not induce analogous rapid changes in luminescence even at >10 mg Zn2+/L concentrations although the 30-min EC50 values for Zn and Gd are comparable (27 and 35 mg/L). The rapid decrease in bacterial bioluminescence upon exposure to REEs is probably due to the interactions between REEs and bacterial outer membrane. Indeed, according to Evans [61], the physiological properties of the lanthanides can be explained on the basis of their attachment to the outside of the cell membrane, with resulting disturbances in the cellular transport of metal ions. The strong attachment of positively charged lanthanide ions onto bacteria is also supported by negative ζ-potential of the V. fischeri cells (−21.8 mV; data not shown). Takahashi et al. [67] showed that phosphate and carboxylate groups are responsible for the adsorption of REEs on bacterial cell surface (Gram-negative E. coli and Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis were studied). The same conclusion was reached by Markai et al. [68] studying interaction of Eu with B. subtilis and by Texier et al. [69] for binding of Eu on Gram-negative bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Martinez et al. [70] in their studies with B. subtilis showed that light REE (La, Ce, Pr, Nd) had lower binding affinity than heavy REE (e.g., Tm, Yb, Lu). Ngwenya et al. [71] studied in more detail the lanthanide sorption sites on the Gram-negative bacterial surface using X-ray absorption spectroscopic measurements and EXAFS (Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure analysis) and suggested that the phosphate sites located on N-acetylglucosamine phosphate (a structural component of Lipid A in lipopolysaccharides, LPS, in the bacterial outer membrane) are assumingly the binding site of REEs. Interestingly, a positively charged deca-peptide antibiotic Colistin (polymyxin E) has somewhat similar mechanism of action by binding to the lipid A moiety and disrupting the integrity of the bacterial outer membrane resulting in cell death [72]. Importantly, Colistin is commercialized for the use in both human and veterinary medicine as the last line to combat infections caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria such as Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella pneumoniae [73].
Figure 6.
Kinetics of the Vibrio fischeri bioluminescence inhibition by La3+(A), Gd3+ (B,D), and Zn2+ (C) in 2% NaCl (A–C) and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 2% NaCl (D). Bacteria were exposed to different dilutions of soluble salts of Gd3+ and La3+ (rare earth elements), and Zn2+ and luminescence was followed during first 30 s of the contact with chemicals. Tested nominal concentrations (mg metal/L) are shown in the inset.
3.5. Toxicity of REEs to Aquatic Organisms Depends on Speciation
One important factor affecting bioavailability of REEs is speciation: due to the formation of insoluble chemical species in majority of ecotoxicological test media the toxicity of lanthanides may be underestimated [1], and it is difficult to compare the toxicity data for different species obtained using different test media. On the other hand, when the speciation is reflecting the situation in the environment, the data are very relevant and informative for the environmental risk assessment.
We studied the effect of test media on the toxicity of REEs to V. fischeri by analyzing the effect of gadolinium on bioluminescence kinetics during 1st seconds of the exposure to gadolinium. As lanthanides have very high affinity to phosphates (they form insoluble phosphates) we tested the toxic effect of Gd nitrate in 2% NaCl (Figure 6B) and in phosphate buffered saline containing 2% NaCl (Figure 6D). It is evident that addition of phosphate converts gadolinium not toxic to V. fischeri by converting the ionic form of gadolinium to insoluble Gd phosphate.
Thus, although the soluble salts of lanthanides are all toxic, in the environmental settings they are rarely in the bioavailable (soluble) form as they form insoluble hydroxides, carbonates, phosphates, fluorides, and oxalates. Sulphates of lanthanides are sparingly soluble. For biology, the most important fact is that lanthanide phosphates and carbonates are insoluble under physiological conditions, i.e., pH 7.4 characteristic to body fluids [61]. However, at lower pHs the mobility of lanthanides (La, Gd, Ce were analyzed at pH 7.5, 5.5 and 3.5) in the soil increased [74]. Weltje et al. [75] studied the speciation and toxicity of trivalent lutetium (Lu3+) to Vibrio fischeri and showed that only free Lu3+ ions were toxic to V. fischeri. Also, within pH range 4.50–6.50 free Lu3+ was dominating species but in higher pH the free Lu3+ concentration rapidly decreased and at pH 7.5 free Lu3+ was reduced by about 80%.
Acidification in the vicinity of bacterial outer membrane where the excretion of the bacterial acidic metabolic by-products such as acetate [76] may locally acidify the environment is quite a realistic scenario. Phagocytosed REO particles may also exert toxicity due to modifications taking place in the acidic intracellular environment: lipid membrane dephosphorylation by shed metal ions from REO in acidic conditions of macrophage lysosomes has been suggested as the acute toxicity mechanism in TPH-1 cells (a human monocytic cell line) in vitro [77].
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Given the increased use of REEs and REOs worldwide, we studied the toxicity of a series of rare earth elements and oxides to marine bacteria Vibrio fischeri and freshwater protozoa Tetrahymena thermophila, to provide the necessary data for the ecotoxicological hazard evaluation of these compounds.
The results of the current study showed that lanthanide-based REOs did not pose a hazard to bacteria and protozoa, but use of toxic metals (such as Ni) as dopants in REOs may significantly decrease their environmental safety. We also showed that toxicity of REEs depends on speciation that leads to the variation of the toxicity values obtained from different assays performed in different test media.
Although soluble REEs were toxic to bacteria, we agree with Gonzalez et al. [19] who evaluated the toxicity of Ce, Gd, and Lu using a battery of aquatic species (algae, daphnids, rotifers, luminescent bacteria, hydra), that presence of lanthanides in the environment assumingly will not pose remarkable environmental risk except at some hotspots or for peak concentrations. We also provided an additional experimental proof on mechanism of toxic action of lanthanides (La3+, Ce3+, Pr3+, Nd3+, Gd3+) by disturbing the integrity of biological membrane.
We feel that the data obtained are important in the context of safety evaluation of REEs and REOs and are also informative for researchers working on e.g., new UV-visible wavelength semiconductor photocatalysts for pollutant removal in water as well as for evaluation of role of microbes in biogeochemical cycles.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Estonian Research Council grant IUT23-5 and COST Action TD1407 (NOTICE).
Author Contributions
Anne Kahru and Irina Blinova conceived and designed the experiments; Imbi Kurvet, Katre Juganson, and Heiki Vija performed the experiments; all authors, including Mariliis Sihtmäe and Guttorm Syvertsen-Wiig, analyzed the data and contributed to the writing of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Gonzalez V., Vignati D.A.L., Leyval C., Giamberini L. Environmental fate and ecotoxicity of lanthanides: Are they a uniform group beyond chemistry? Environ. Int. 2014;71:148–157. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2014.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Campbell G.A. Rare earth metals: A strategic concern. Miner. Econ. 2014;27:21–31. doi: 10.1007/s13563-014-0043-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Haque N., Hughes A., Lim S., Vernon C. Rare earth elements: Overview of mining, mineralogy, uses, sustainability and environmental impact. Resources. 2014;3:614. doi: 10.3390/resources3040614. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alonso E., Sherman A.M., Wallington T.J., Everson M.P., Field F.R., Roth R., Kirchain R.E. Evaluating rare earth element availability: A case with revolutionary demand from clean technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012;46:3406–3414. doi: 10.1021/es203518d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Guyonnet D., Planchon M., Rollat A., Escalon V., Tuduri J., Charles N., Vaxelaire S., Dubois D., Fargier H. Material flow analysis applied to rare earth elements in Europe. J. Clean. Prod. 2015;107:215–228. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.04.123. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tyler G. Rare earth elements in soil and plant systems—A review. Plant Soil. 2004;267:191–206. doi: 10.1007/s11104-005-4888-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Volokh A.A., Gorbunov A.V., Gundorina S.F., Revich B.A., Frontasyeva M.V., Pal C.S. Phosphorus-fertilizer production as a source of rare-earth elements pollution of the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 1990;95:141–148. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(90)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pang X., Li D.C., Peng A. Application of rare-earth elements in the agriculture of China and its environmental behavior in soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2002;9:143–148. doi: 10.1007/BF02987462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Liu X.S., Wang J.C., Yang J., Fan Y.B., Wu Y.P., Zhang H. Application of rare earth phosphate fertilizer in western area of China. J. Rare Earths. 2006;24:423–426. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Telgmann L., Sperling M., Karst U. Determination of gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents in biological and environmental samples: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2013;764:1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2012.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hatje V., Bruland K.W., Flegal A.R. Increases in anthropogenic gadolinium anomalies and rare earth element concentrations in San Francisco bay over a 20 year record. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016;50:4159–4168. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b04322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kulaksiz S., Bau M. Anthropogenic dissolved and colloid/nanoparticle-bound samarium, lanthanum and gadolinium in the Rhine river and the impending destruction of the natural rare earth element distribution in rivers. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013;362:43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2012.11.033. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Graedel T.E., Harper E.M., Nassar N.T., Nuss P., Reck B.K. Criticality of metals and metalloids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015;112:4257–4262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1500415112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Leguay S., Campbell P.G.C., Fortin C. Determination of the free-ion concentration of rare earth elements by an ion-exchange technique: Implementation, evaluation and limits. Environ. Chem. 2016;13:478–488. doi: 10.1071/EN15136. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Carpenter D., Boutin C., Allison J.E., Parsons J.L., Ellis D.M. Uptake and effects of six rare earth elements (REEs) on selected native and crop species growing in contaminated soils. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0129936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Herrmann H., Nolde J., Berger S., Heise S. Aquatic ecotoxicity of lanthanum—A review and an attempt to derive water and sediment quality criteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016;124:213–238. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.09.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Xu X.K., Zhu W.Z., Wang Z.J., Witkamp G.J. Distributions of rare earths and heavy metals in field-grown maize after application of rare earth-containing fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2002;293:97–105. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(01)01150-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhang S.Z., Shan X.Q. Speciation of rare earth elements in soil and accumulation by wheat with rare earth fertilizer application. Environ. Pollut. 2001;112:395–405. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gonzalez V., Vignati D.A.L., Pons M.N., Montarges-Pelletier E., Bojic C., Giamberini L. Lanthanide ecotoxicity: First attempt to measure environmental risk for aquatic organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2015;199:139–147. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Babula P., Adam V., Opatrilova R., Zehnalek J., Havel L., Kizek R. Uncommon heavy metals, metalloids and their plant toxicity: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2008;6:189–213. doi: 10.1007/s10311-008-0159-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Juganson K., Ivask A., Blinova I., Mortimer M., Kahru A. NanoE-Tox: New and in-depth database concerning ecotoxicity of nanomaterials. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015;6:1788–1804. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.6.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Taylor N.S., Merrifield R., Williams T.D., Chipman J.K., Lead J.R., Viant M.R. Molecular toxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles to the freshwater alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is associated with supra-environmental exposure concentrations. Nanotoxicology. 2016;10:32–41. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2014.1002868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Montini T., Melchionna M., Monai M., Fornasiero P. Fundamentals and catalytic applications of CeO2-based materials. Chem. Rev. 2016;116:5987–6041. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dahle J.T., Arai Y. Environmental geochemistry of cerium: Applications and toxicology of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2015;12:1253–1278. doi: 10.3390/ijerph120201253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pokhrel S., Nel A.E., Madler L. Custom-designed nanomaterial libraries for testing metal oxide toxicity. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013;46:632–641. doi: 10.1021/ar300032q. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Messing G.L., Zhang S.C., Jayanthi G.V. Ceramic powder synthesis by spray-pyrolysis. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1993;76:2707–2726. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1993.tb04007.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Joonas E., Aruoja V., Olli K., Syvertsen-Wiig G., Vija H., Kahru A. Potency of (doped) rare earth oxide particles and their constituent metals to inhibit algal growth and induce direct toxic effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017;593–594:478–486. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Aruoja V., Pokhrel S., Sihtmäe M., Mortimer M., Maedler L., Kahru A. Toxicity of 12 metal-based nanoparticles to algae, bacteria and protozoa. Environ. Sci. Nano. 2015;2:630–644. doi: 10.1039/C5EN00057B. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.ISO 21338:2010—Water quality—Kinetic Determination of the Inhibitory Effects of Sediment, Other Solids and Coloured Samples on the Light Emission of Vibrio fischeri (Kinetic Luminescent Bacteria Test) International Organization for Standardization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Vindimian E. MSExcel Macro REGTOX EV7.0.5.xls. [(accessed on 5 July 2011)];2005 Available online: http://www.normalesup.org/~vindimian/en_download.html.
- 31.Suppi S., Kasemets K., Ivask A., Künnis-Beres K., Sihtmäe M., Kurvet I., Aruoja V., Kahru A. A novel method for comparison of biocidal properties of nanomaterials to bacteria, yeasts and algae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015;286:75–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.12.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jemec A., Kahru A., Potthoff A., Drobne D., Heinlaan M., Boehme S., Geppert M., Novak S., Schirmer K., Rekulapally R., et al. An interlaboratory comparison of nanosilver characterisation and hazard identification: Harmonising techniques for high quality data. Environ. Int. 2016;87:20–32. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2015.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mortimer M., Kasemets K., Kahru A. Toxicity of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles to ciliated protozoa Tetrahymena thermophila. Toxicology. 2010;269:182–189. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2009.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kahru A., Dubourguier H.-C., Blinova I., Ivask A., Kasemets K. Biotests and biosensors for ecotoxicology of metal oxide nanoparticles: A mini review. Sensors. 2008;8:5153–5170. doi: 10.3390/s8085153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ivask A., Juganson K., Bondarenko O., Mortimer M., Aruoja V., Kasemets K., Blinova I., Heinlaan M., Slaveykova V., Kahru A. Mechanisms of toxic action of Ag, ZnO and CuO nanoparticles to selected ecotoxicological test organisms and mammalian cells in vitro: A comparative review. Nanotoxicology. 2014;8:57–71. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2013.855831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tao F., Gonzalez-Flecha B., Kobzik L. Reactive oxygen species in pulmonary inflammation by ambient particulates. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003;35:327–340. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(03)00280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Arbab A.S., Bashaw L.A., Miller B.R., Jordan E.K., Lewis B.K., Kalish H., Frank J.A. Characterization of biophysical and metabolic properties of cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and transfection agent for cellular MR imaging. Radiology. 2003;229:838–846. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2293021215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kasprzak K.S., Sunderman F.W., Salnikow K. Nickel carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2003;533:67–97. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2003.08.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pagano G., Guida M., Siciliano A., Oral R., Kocbas F., Palumbo A., Castellano I., Migliaccio O., Thomas P.J., Trifuoggi M. Comparative toxicities of selected rare earth elements: Sea urchin embryogenesis and fertilization damage with redox and cytogenetic effects. Environ. Res. 2016;147:453–460. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2016.02.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Giri S., Karakoti A., Graham R.P., Maguire J.L., Reilly C.M., Seal S., Rattan R., Shridhar V. Nanoceria: A rare-earth nanoparticle as a novel anti-angiogenic therapeutic agent in ovarian cancer. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e54578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kurvet I., Ivask A., Bondarenko O., Sihtmäe M., Kahru A. LuxCDABE-transformed constitutively bioluminescent Escherichia coli for toxicity screening: Comparison with naturally luminous Vibrio fischeri. Sensors. 2011;11:7865–7878. doi: 10.3390/s110807865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hastings J.W., Makemson J., Dunlap P.V. How are growth and luminescence regulated independently in light organ symbionts. Symbiosis. 1987;4:3–24. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bulich A.A. A practical and reliable method for monitoring the toxicity of aquatic samples. Process Biochem. 1982;17:45–47. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kaiser K.L.E., Devillers J. Ecotoxicity of Chemicals to Photobacterium phosphoreum. Handbook of Ecotoxicological Data. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers; Yverdon, Switzerland: 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Parvez S., Venkataraman C., Mukherji S. A review on advantages of implementing luminescence inhibition test (Vibrio fischeri) for acute toxicity prediction of chemicals. Environ. Int. 2006;32:265–268. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2005.08.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lappalainen J., Juvonen R., Vaajasaari K., Karp M. A new flash method for measuring the toxicity of solid and colored samples. Chemosphere. 1999;38:1069–1083. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00352-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gellert G. Sensitivity and significance of luminescent bacteria in chronic toxicity testing based on growth and bioluminescence. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2000;45:87–91. doi: 10.1006/eesa.1999.1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Velzeboer I., Hendriks A.J., Ragas A.M.J., Van de Meent D. Aquatic ecotoxicity tests of some nanomaterials. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008;27:1942–1947. doi: 10.1897/07-509.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bondarenko O., Juganson K., Ivask A., Kasemets K., Mortimer M., Kahru A. Toxicity of Ag, CuO and ZnO nanoparticles to selected environmentally relevant test organisms and mammalian cells in vitro: A critical review. Arch. Toxicol. 2013;87:1181–1200. doi: 10.1007/s00204-013-1079-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Storz G., Imlay J.A. Oxidative stress. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1999;2:188–194. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5274(99)80033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sorokina E.V., Yudina T.P., Bubnov I.A., Danilov V.S. Assessment of iron toxicity using a luminescent bacterial test with an Escherichia coli recombinant strain. Microbiology. 2013;82:439–444. doi: 10.1134/S0026261713040115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Macomber L., Hausinger R.P. Mechanisms of nickel toxicity in microorganisms. Metallomics. 2011;3:1153–1162. doi: 10.1039/c1mt00063b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sherr E.B., Sherr B.F. Significance of predation by protists in aquatic microbial food webs. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2002;81:293–308. doi: 10.1023/A:1020591307260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sauvant M.P., Pepin D., Piccinni E. Tetrahymena pyriformis: A tool for toxicological studies. A review. Chemosphere. 1999;38:1631–1669. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Frankel J. Cell biology of Tetrahymena thermophila. In: Asai D.J., Forney J.D., editors. Tetrahymena thermophila, Methods in Cell Biology. Volume 62. Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: 2000. pp. 27–125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Koppelhus U., Hellunglarsen P., Leick V. Physiological-parameters affecting the chemosensory response of Tetrahymena. Biol. Bull. 1994;187:1–7. doi: 10.2307/1542159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Juganson K., Mortimer M., Ivask A., Pucciarelli S., Miceli C., Orupõld K., Kahru A. Mechanisms of toxic action of silver nanoparticles in the protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila: From gene expression to phenotypic events. Environ. Pollut. 2017;225:481–489. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Juganson K., Mortimer M., Ivask A., Kasemets K., Kahru A. Extracellular conversion of silver ions into silver nanoparticles by protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts. 2013;15:244–250. doi: 10.1039/C2EM30731F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Mortimer M., Kahru A., Slaveykova V.I. Uptake, localization and clearance of quantum dots in ciliated protozoa Tetrahymena thermophila. Environ. Pollut. 2014;190:58–64. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2014.03.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Mortimer M., Petersen E.J., Buchholz B.A., Orias E., Holden P.A. Bioaccumulation of multiwall carbon nanotubes in Tetrahymena thermophila by direct feeding or trophic transfer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016;50:8876–8885. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b01916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Evans C.H. Biochemistry of the Lanthanides. Springer Science+Business Media; New York, NY, USA: 1990. pp. p. 22, p. 221 and p. 341. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Ekwall B. Correlation between cyto-toxicity in vitro and LD50-values. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1983;52:80–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1983.tb02685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Silhavy T.J., Kahne D., Walker S. The bacterial cell envelope. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010;2:a000414. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Rai M.K., Deshmukh S.D., Ingle A.P., Gade A.K. Silver nanoparticles: The powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012;112:841–852. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kahru A. Ecotoxicological tests in non-ecotoxicological research: Contribution to 3Rs. Use of luminescent photobacteria for evaluating the toxicity of 47 MEIC reference chemicals. ALTEX. 2006;23:302–308. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Mortimer M., Kasemets K., Heinlaan M., Kurvet I., Kahru A. High throughput kinetic Vibrio fischeri bioluminescence inhibition assay for study of toxic effects of nanoparticles. Toxicol. In Vitro. 2008;22:1412–1417. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2008.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Takahashi Y., Chatellier X., Hattori K.H., Kato K., Fortin D. Adsorption of rare earth elements onto bacterial cell walls and its implication for REE sorption onto natural microbial mats. Chem. Geol. 2005;219:53–67. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.02.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Markai S., Andres Y., Montavon G., Grambow B. Study of the interaction between europium (III) and Bacillus subtilis: Fixation sites, biosorption modeling and reversibility. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003;262:351–361. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9797(03)00096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Texier A.C., Andres Y., Illemassene M., Le Cloirec P. Characterization of lanthanide ions binding sites in the cell wall of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000;34:610–615. doi: 10.1021/es990668h. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Martinez R.E., Pourret O., Takahashi Y. Modeling of rare earth element sorption to the gram positive Bacillus subtilis bacteria surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014;413:106–111. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2013.09.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Ngwenya B.T., Mosselmans J.F.W., Magennis M., Atkinson K.D., Tourney J., Olive V., Ellam R.M. Macroscopic and spectroscopic analysis of lanthanide adsorption to bacterial cells. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 2009;73:3134–3147. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.03.018. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Dijkmans A.C., Wilms E.B., Kamerling I.M.C., Birkhoff W., Ortiz-Zacarias N.V., van Nieuwkoop C., Verbrugh H.A., Touw D.J. Colistin: Revival of an old polymyxin antibiotic. Ther. Drug Monit. 2015;37:419–427. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Rhouma M., Beaudry F., Theriault W., Letellier A. Colistin in pig production: Chemistry, mechanism of antibacterial action, microbial resistance emergence, and one health perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2016;7:1789. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Cao X.D., Chen Y., Wang X.R., Deng X.H. Effects of redox potential and pH value on the release of rare earth elements from soil. Chemosphere. 2001;44:655–661. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00492-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Weltje L., Verhoof L., Verweij W., Hamers T. Lutetium speciation and toxicity in a microbial bioassay: Testing the free-ion model for lanthanides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004;38:6597–6604. doi: 10.1021/es049916m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Luli G.W., Strohl W.R. Comparison of growth, acetate production, and acetate inhibition of Escherichia-coli strains in batch and fed-batch fermentations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990;56:1004–1011. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1004-1011.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Li R.B., Ji Z.X., Chang C.H., Dunphy D.R., Cai X.M., Meng H., Zhang H.Y., Sun B.B., Wang X., Dong J.Y., et al. Surface interactions with compartmentalized cellular phosphates explain rare earth oxide nanoparticle hazard and provide opportunities for safer design. ACS Nano. 2014;8:1771–1783. doi: 10.1021/nn406166n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]