Abstract
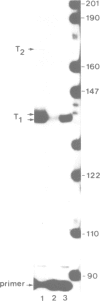
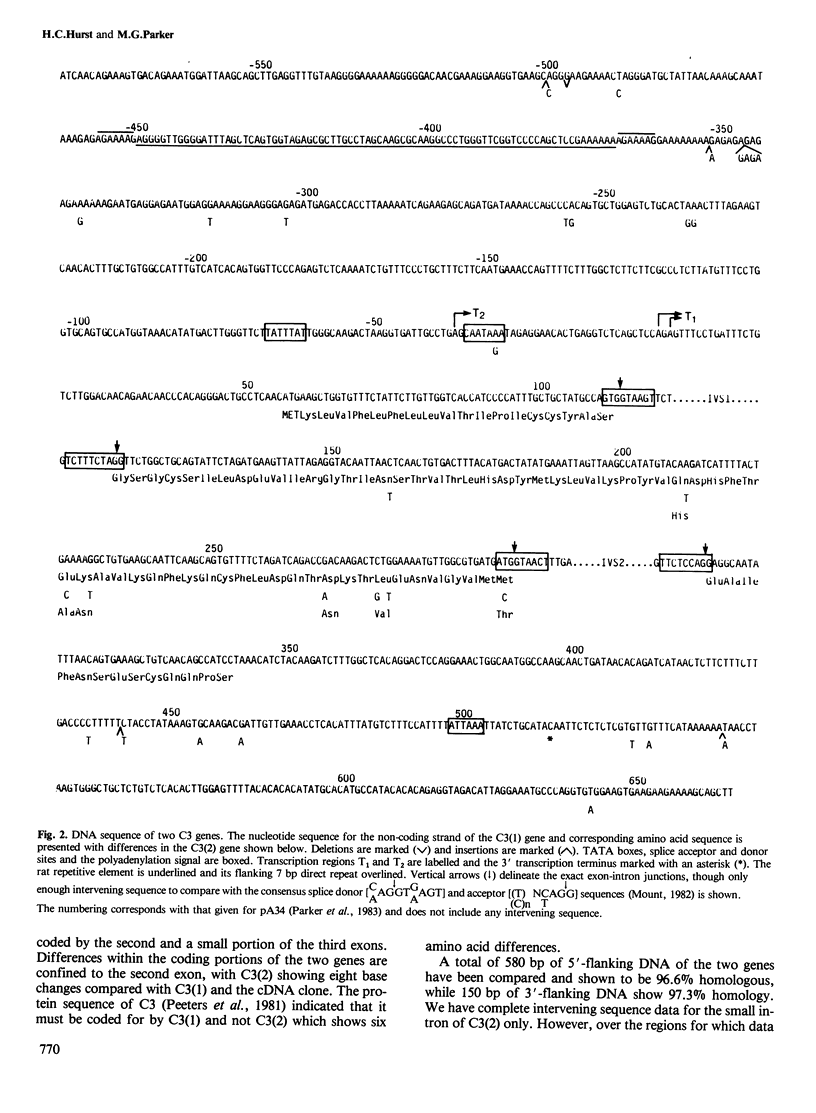
In the rat there are two non-allelic genes C3(1) and C3(2) for the C3 polypeptide of prostatic steroid binding protein. We have cloned and sequenced both genes and show that only C3(1) is responsible for the production of authentic C3. Although there is a marked difference in their transcriptional activity, the two genes share extensive DNA sequence homology there being only one base difference from nucleotide - 235 to within the first intron. Transcript mapping has shown that there are two distinct C3 transcripts which share a unique 3' terminus but have 5' termini 38 bases apart each preceded by a 'TATA' box homology. Interestingly, an identical repetitive element is present just upstream of both genes. Both families of transcripts, which are produced in a ratio of 18:1, are coordinately regulated by testosterone.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barta A., Richards R. I., Baxter J. D., Shine J. Primary structure and evolution of rat growth hormone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4867–4871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L., Clayton J., Friedland P., Kedes L. H. SEQ: a nucleotide sequence analysis and recombination system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):279–294. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Regulation of gene expression: possible role of repetitive sequences. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1052–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.451548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G., McGhee J. Methylation and gene control. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):602–603. doi: 10.1038/296602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Ansorge W. Improvements of DNA sequencing gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J., Gannon F. Current models of steroid hormone action: a critique. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:425–450. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Bovey R., Young R. A. Tissue-specific expression of mouse-alpha-amylase genes: nucleotide sequence of isoenzyme mRNAs from pancreas and salivary gland. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyns W., De Moor P. Prostatic binding protein. A steriod-binding protein secreted by rat prostate. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):221–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyns W., Peeters B., Mous J., Rombauts W., De Moor P. Purification and characterisation of prostatic binding protein and its subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):181–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins S. J., Gehring U. Molecular mechanisms of steroid hormone action. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;28:313–397. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60650-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung A., Sippel A. E., Grez M., Schütz G. Exons encode functional and structural units of chicken lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemischka I., Sharp P. A. The sequences of an expressed rat alpha-tubulin gene and a pseudogene with an inserted repetitive element. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):330–335. doi: 10.1038/300330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maat J., van Beveren C. P., van Ormondt H. The nucleotide sequence of adenovirus type 5 early region E1: the region between map positions 8.0 (HindIII site) and 11.8 (SmaI site). Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. Functional relationships between transcriptional control signals of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvihill E. R., LePennec J. P., Chambon P. Chicken oviduct progesterone receptor: location of specific regions of high-affinity binding in cloned DNA fragments of hormone-responsive genes. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):621–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. J., Parker M. G. Androgen-regulated expression of a cloned rat prostatic c3 gene transfected into mouse mammary tumor cells. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):495–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90469-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. J., Parker M. G. Effect of androgen on the transcription of rat prostatic binding protein genes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Aug;27(3):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. G., Mainwaring W. I. Effects of androgens on the complexity of poly(A) RNA from rat prostate. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. G., Scrace G. T., Mainwaring W. I. Testosterone regulates the synthesis of major proteins in rat ventral prostate. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 15;170(1):115–121. doi: 10.1042/bj1700115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. G., White R., Hurst H., Needham M., Tilly R. Prostatic steroid-binding protein. Isolation and characterization of C3 genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M., Needham M., White R., Hurst H., Page M. Prostatic steroid binding protein: organisation of C1 and C2 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5121–5132. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters B., Rombauts W., Mous J., Heyns W. Structural studies on rat prostatic binding protein. The primary structure of its glycosylated component C3. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):115–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Friedman J. DNA methylation and its possible biological roles. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;25:33–52. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60482-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier P. H., Cortese R. A fast and simple method for sequencing DNA cloned in the single-stranded bacteriophage M13. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Milner R. J., Bloom F. E., Lerner R. A. Common 82-nucleotide sequence unique to brain RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4942–4946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]