Abstract
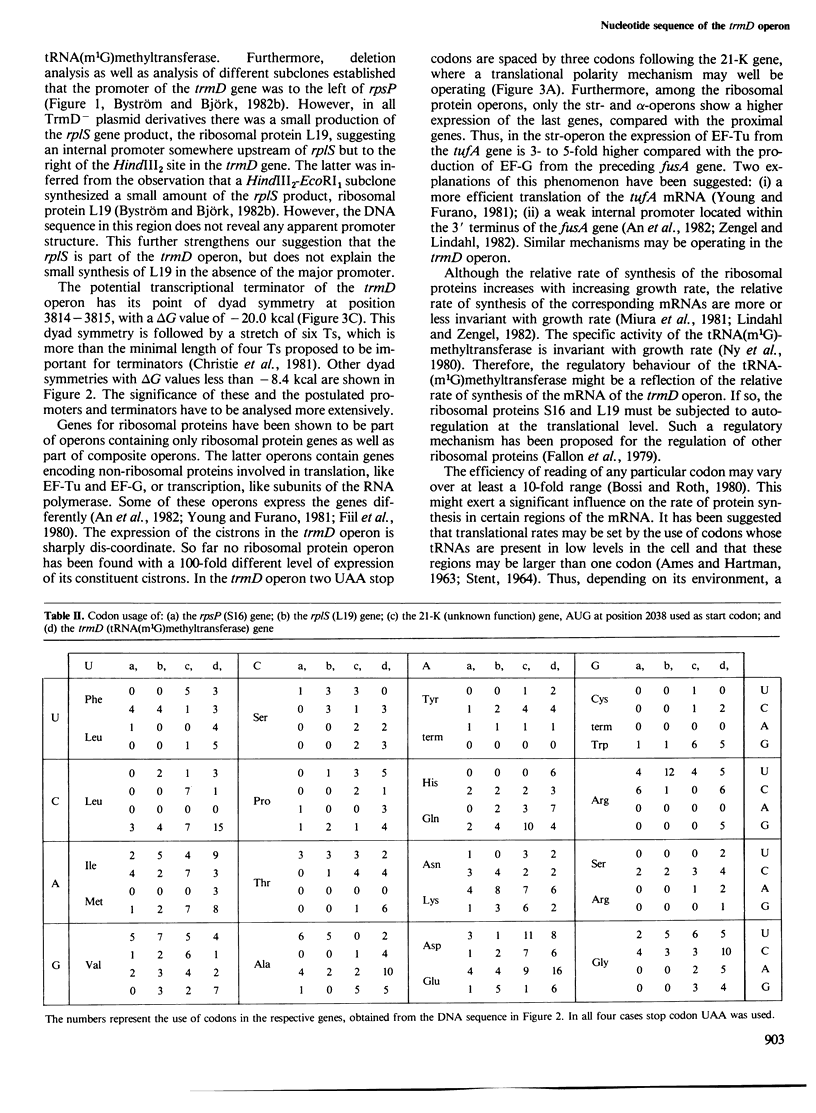
The nucleotide sequence of a 4.6-kb SalI-EcoRI DNA fragment including the trmD operon, located at min 56 on the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome, has been determined. The trmD operon encodes four polypeptides: ribosomal protein S16 (rpsP), 21-K polypeptide (unknown function), tRNA-(m1G)methyltransferase (trmD) and ribosomal protein L19 (rplS), in that order. In addition, the 4.6-kb DNA fragment encodes a 48-K and a 16-K polypeptide of unknown functions which are not part of the trmD operon. The mol. wt. of tRNA(m1G)methyltransferase determined from the DNA sequence is 28 424. The probable locations of promoter and terminator of the trmD operon are suggested. The translational start of the trmD gene was deduced from the known NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of the purified enzyme. The intercistronic regions in the operon vary from 9 to 40 nucleotides, supporting the earlier conclusion that the four genes are co-transcribed, starting at the major promoter in front of the rpsP gene. Since it is known that ribosomal proteins are present at 8000 molecules/genome and the tRNA-(m1G)methyltransferase at only approximately 80 molecules/genome in a glucose minimal culture, some powerful regulatory device must exist in this operon to maintain this non-coordinate expression. The codon usage of the two ribosomal protein genes is similar to that of other ribosomal protein genes, i.e., high preference for the most abundant tRNA isoaccepting species. The trmD gene has a codon usage typical for a protein made in low amount in accordance with the low number of tRNA-(m1G)methyltransferase molecules found in the cell.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An G., Lee J. S., Friesen J. D. Evidence for an internal promoter preceding tufA in the str operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):548–553. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.548-553.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Ruth J. R. The influence of codon context on genetic code translation. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):123–127. doi: 10.1038/286123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Arfsten U. Primary structure of protein L19 from the large subunit of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):508–516. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byström A. S., Björk G. R. Chromosomal location and cloning of the gene (trmD) responsible for the synthesis of tRNA (m1G) methyltransferase in Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(3):440–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00330046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byström A. S., Björk G. R. The structural gene (trmD) for the tRNA(m1G)methyltransferase is part of a four polypeptide operon in Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(3):447–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00330047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Farnham P. J., Platt T. Synthetic sites for transcription termination and a functional comparison with tryptophan operon termination sites in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4180–4184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. P., Bremer H. Macromolecular composition during steady-state growth of Escherichia coli B-r. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):270–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.270-281.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon A. M., Jinks C. S., Strycharz G. D., Nomura M. Regulation of ribosomal protein synthesis in Escherichia coli by selective mRNA inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3411–3415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H., Fiers W. Preferential codon usage in prokaryotic genes: the optimal codon-anticodon interaction energy and the selective codon usage in efficiently expressed genes. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harr R., Hagblom P., Gustafsson P. Two-dimensional graphic analysis of DNA sequence homologies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):365–374. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjalmarsson K. J., Byström A. S., Björk G. R. Purification and characterization of transfer RNA (guanine-1)methyltransferase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1343–1351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isono K. Genes encoding ribosomal proteins S16 and L19 form a gene cluster at 56.4 min in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 24;165(3):265–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00332525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Zengel J. M. Expression of ribosomal genes in bacteria. Adv Genet. 1982;21:53–121. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura A., Krueger J. H., Itoh S., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. Growth-rate-dependent regulation of ribosome synthesis in E. coli: expression of the lacZ and galK genes fused to ribosomal promoters. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):773–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neihardt F. C., Parker J., McKeever W. G. Function and regulation of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:215–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierlich D. P. Regulation of bacterial growth, RNA, and protein synthesis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:393–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.002141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Björk G. R. Growth rate-dependent regulation of transfer ribonucleic acid (5-methyluridine) methyltransferase in Escherichia coli B/r. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):67–73. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.67-73.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Thomale J., Hjalmarsson K., Nass G., Björk G. R. Non-coordinate regulation of enzymes involved in transfer RNA metabolism in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 30;607(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S., Bloch P. L., Reeh S., Neidhardt F. C. Patterns of protein synthesis in E. coli: a catalog of the amount of 140 individual proteins at different growth rates. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Arfsten A. E., Reusser F., Nomura M. DNA sequences of promoter regions for the str and spc ribosomal protein operons in E. coli. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):215–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENT G. S. THE OPERON: ON ITS THIRD ANNIVERSARY. MODULATION OF TRANSFER RNA SPECIES CAN PROVIDE A WORKABLE MODEL OF AN OPERATOR-LESS OPERON. Science. 1964 May 15;144(3620):816–820. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3620.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A strategy of DNA sequencing employing computer programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2601–2610. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Rombauts W., Wittmann-Liebold B. The complete amino acid sequence of protein S16 from Escherichia coli. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Aug;358(8):989–1002. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1977.358.2.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. S., Furano A. V. Regulation of the synthesis of E. coli elongation factor Tu. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. M., Lindahl L. A secondary promoter for elongation factor Tu synthesis in the str ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):487–492. doi: 10.1007/BF00334145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



