Abstract
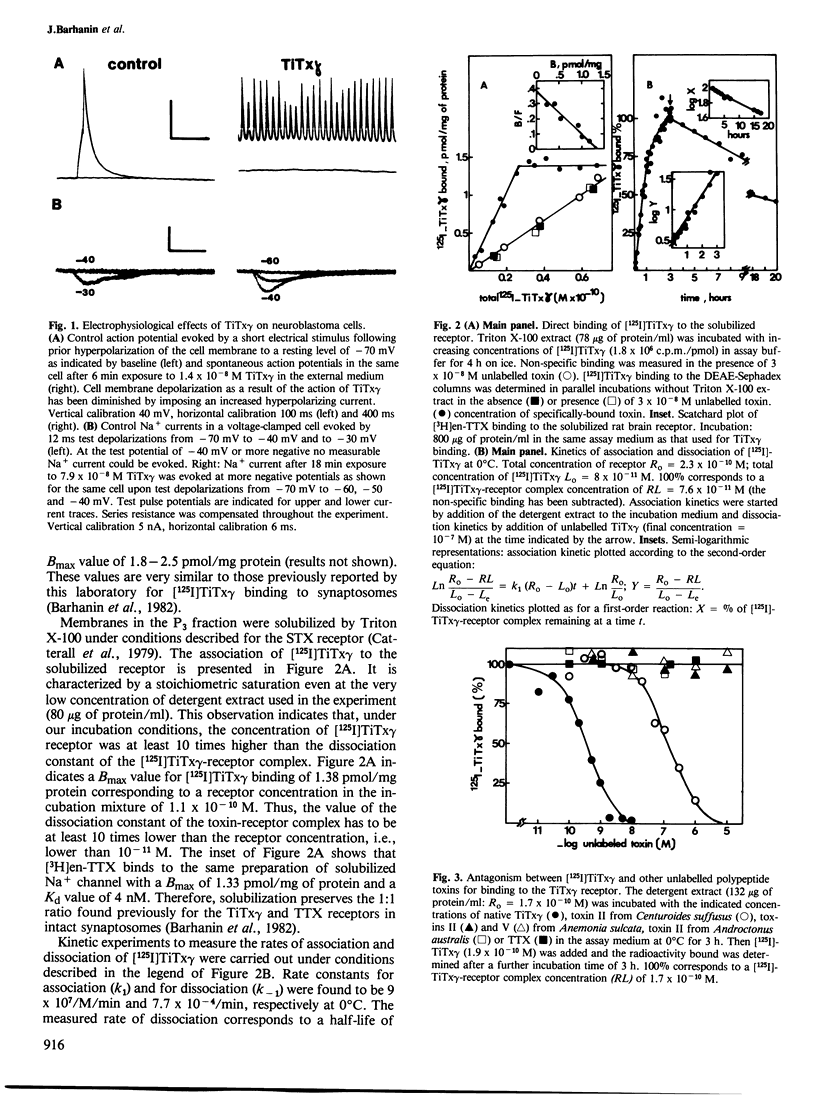
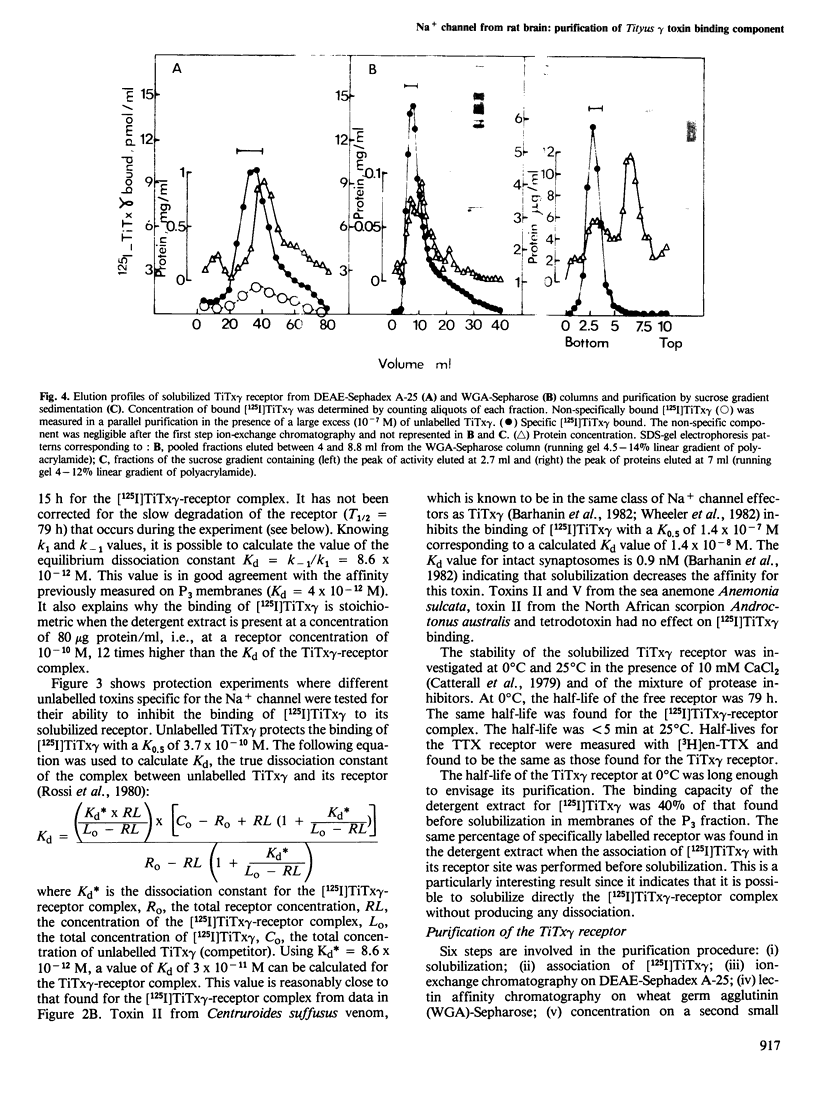
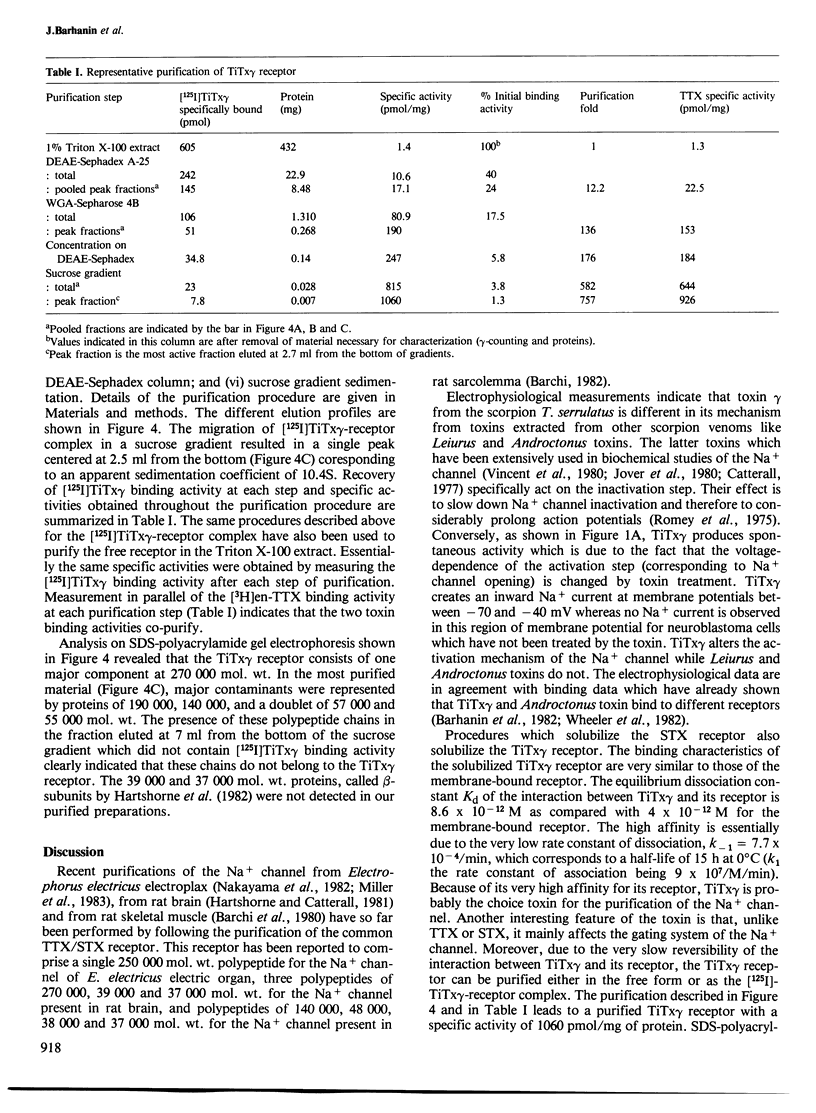
Electrophysiological studies with neuroblastoma cells have shown that toxin gamma from the venom of the scorpion Tityus serrulatus is a new toxin specific for the gating system of the Na+ channel. The procedure which solubilizes the tetrodotoxin receptor from rat brain also solubilizes the Tityus gamma toxin receptor. Binding experiments on the solubilized receptor with a radioiodinated derivative of Tityus gamma toxin have shown: (i) that the TiTx gamma-receptor complex is very stable with a dissociation constant of 8.6 X 10(-12) M and a very slow dissociation (T 1/2 = 15 h); (ii) that the toxin recognizes a class of sites with a 1:1 stoichiometry with those for tetrodotoxin (Bmax = 1.3 pmol/mg protein). The radioiodinated Tityus gamma-receptor complex has been substantially purified by ion-exchange chromatography, lectin affinity chromatography and sucrose gradient sedimentation. A ratio of one Tityus gamma toxin binding site per tetrodotoxin binding site was found throughout the purification. The purified material exhibited a sedimentation coefficient of 10.4S and had an apparent mol. wt. of 270 000 on SDS-gel electrophoresis. No other polypeptide chains were demonstrated to be associated with this large protein in the Tityus gamma receptor. The main conclusion is that the tetrodotoxin binding site associated with the selectivity filter of the Na+ channel and the Tityus gamma toxin binding site associated with the gating component are probably carried by the same polypeptide chain.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Charge movement associated with the opening and closing of the activation gates of the Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):533–552. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L. Biochemical studies of the excitable membrane sodium channel. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1982;23:69–101. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60622-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L., Cohen S. A., Murphy L. E. Purification from rat sarcolemma of the saxitoxin-binding component of the excitable membrane sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1306–1310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barhanin J., Giglio J. R., Léopold P., Schmid A., Sampaio S. V., Lazdunski M. Tityus serrulatus venom contains two classes of toxins. Tityus gamma toxin is a new tool with a very high affinity for studying the Na+ channel. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12553–12558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Membrane potential-dependent binding of scorpion toxin to the action potential Na+ ionophore. Studies with a toxin derivative prepared by lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8660–8668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Morrow C. S., Hartshorne R. P. Neurotoxin binding to receptor sites associated with voltage-sensitive sodium channels in intact, lysed, and detergent-solubilized brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11379–11387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicheportiche R., Balerna M., Lombet A., Romey G., Lazdunski M. Synthesis of new, highly radioactive tetrodotoxin derivatives and their binding properties to the sodium channel. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;104(2):617–625. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin S. M. Active transport of sodium and potassium ions by the sodium and potassium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase from renal medulla. Reconstitution of the purified enzyme into a well defined in vitro transport system. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5630–5642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. Purification of the saxitoxin receptor of the sodium channel from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Messner D. J., Coppersmith J. C., Catterall W. A. The saxitoxin receptor of the sodium channel from rat brain. Evidence for two nonidentical beta subunits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13888–13891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugues M., Romey G., Duval D., Vincent J. P., Lazdunski M. Apamin as a selective blocker of the calcium-dependent potassium channel in neuroblastoma cells: voltage-clamp and biochemical characterization of the toxin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1308–1312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques Y., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Molecular properties of the action potential Na+ ionophore in neuroblastoma cells. Interactions with neurotoxins. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7383–7392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jover E., Martin-Moutot N., Couraud F., Rochat H. Binding of scorpion toxins to rat brain synaptosomal fraction. Effects of membrane potential, ions, and other neurotoxins. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):463–467. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson S. R., Curatalo C. J., Reed J., Raftery M. A. A rapid and precise assay for tetrodotoxin binding to detergent extracts of excitable tissues. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;99(1):72–84. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R. Principal glycopeptide of the tetrodotoxin/saxitoxin binding protein from Electrophorus electricus: isolation and partial chemical and physical characterization. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):462–470. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama H., Withy R. M., Raftery M. A. Use of a monoclonal antibody to purify the tetrodotoxin binding component from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7575–7579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi B., Vuilleumier P., Gache C., Balerna M., Lazdunski M. Affinity labeling of the digitalis receptor with p-nitrophenyltriazene-ouabain, a highly specific alkylating agent. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9936–9941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio S. V., Laure C. J., Giglio J. R. Isolation and characterization of toxic proteins from the venom of the Brazilian scorpion Tityus serrulatus. Toxicon. 1983;21(2):265–277. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(83)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Balerna M., Barhanin J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Binding of sea anemone toxin to receptor sites associated with gating system of sodium channel in synaptic nerve endings in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1646–1650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler K. P., Barhanin J., Lazdunski M. Specific binding of toxin II from Centruroides suffusus suffusus to the sodium channel in electroplaque membranes. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5628–5634. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




