Abstract
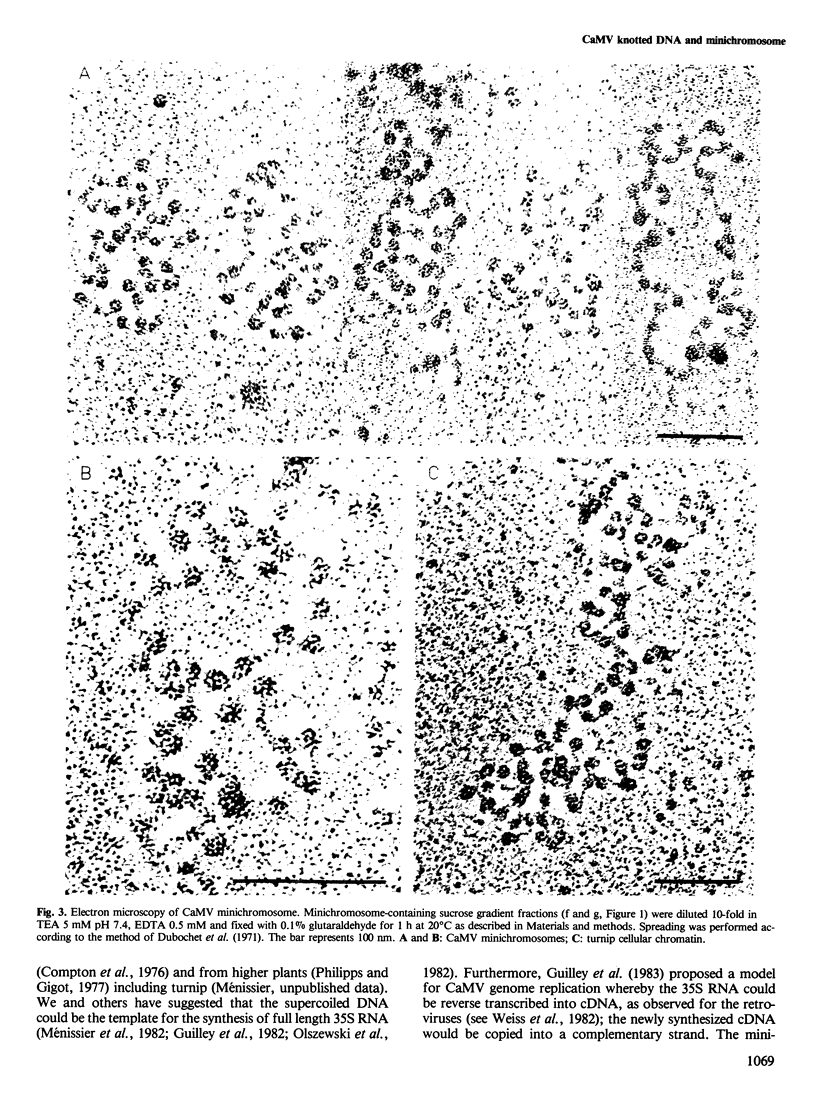
Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) DNA exists under different topological forms in infected plants. First, the population of encapsidated CaMV DNA molecules appears heterogeneous when analysed by gel electrophoresis. The electron microscopic study reported here reveals that CaMV virion DNA contains simple and multiple topological knots. Second, a supercoiled DNA form never found in virions exists as a chromatin-like nucleoprotein complex with nucleosome subunits in the nuclei of infected leaves. The compaction ratio of the minichromosomes is compatible with the nucleosomal structure, the number of nucleosomes (41.0 +/- 2.5) is in keeping with the length of the viral genome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellard M., Oudet P., Germond J. E., Chambon P. Subunit structure of simian-virus-40 minichromosome. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):543–553. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. L., Bellard M., Chambon P. Biochemical evidence of variability in the DNA repeat length in the chromatin of higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4382–4386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey S. N., Lomonossoff G. P., Hull R. Characterisation of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA sequences which encode major polyadenylated transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6735–6747. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremisi C., Pignatti P. F., Croissant O., Yaniv M. Chromatin-like structures in polyoma virus and simian virus 10 lytic cycle. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.204-211.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet J., Ducommun M., Zollinger M., Kellenberger E. A new preparation method for dark-field electron microscopy of biomacromolecules. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Apr;35(1):147–167. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franck A., Guilley H., Jonard G., Richards K., Hirth L. Nucleotide sequence of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigot C., Philipps G., Nicolaieff A., Hirth L. Some properties of tobacco protoplast chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2315–2329. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. Chromatin structure: deduced from a minichromosome. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1202–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilley H., Dudley R. K., Jonard G., Balàzs E., Richards K. E. Transcription of Cauliflower mosaic virus DNA: detection of promoter sequences, and characterization of transcripts. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):763–773. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Hohn B., Lesot A., Lebeurier G. Restriction map of native and cloned cauliflower mosaic virus DNA. Gene. 1980 Oct;11(1-2):21–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90083-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Richards K., Geneviève-Lebeurier Cauliflower mosaic virus on its way to becoming a useful plant vector. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;96:194–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Aloni Y. Isolation and characterization of various forms of simian virus 40 DNA-protein complexes. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Davis J. L., Calendar R. Novel topologically knotted DNA from bacteriophage P4 capsids: studies with DNA topoisomerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3979–3989. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Liu C. C., Alberts B. M. Type II DNA topoisomerases: enzymes that can unknot a topologically knotted DNA molecule via a reversible double-strand break. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):697–707. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olszewski N., Hagen G., Guilfoyle T. J. A transcriptionally active, covalently closed minichromosome of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA isolated from infected turnip leaves. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):395–402. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90156-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipps G., Gigot C. DNA associated with nucleosomes in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Oct;4(10):3617–3626. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.10.3617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volovitch M., Drugeon C., Yot P. Studies on the single-stranded discontinuities of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2913–2925. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong C., Muller S., Lebeurier G., Hirth L. Identification by immunoprecipitation of cauliflower mosaic virus in vitro major translation product with a specific serum against viroplasm protein. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):971–976. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]