Abstract
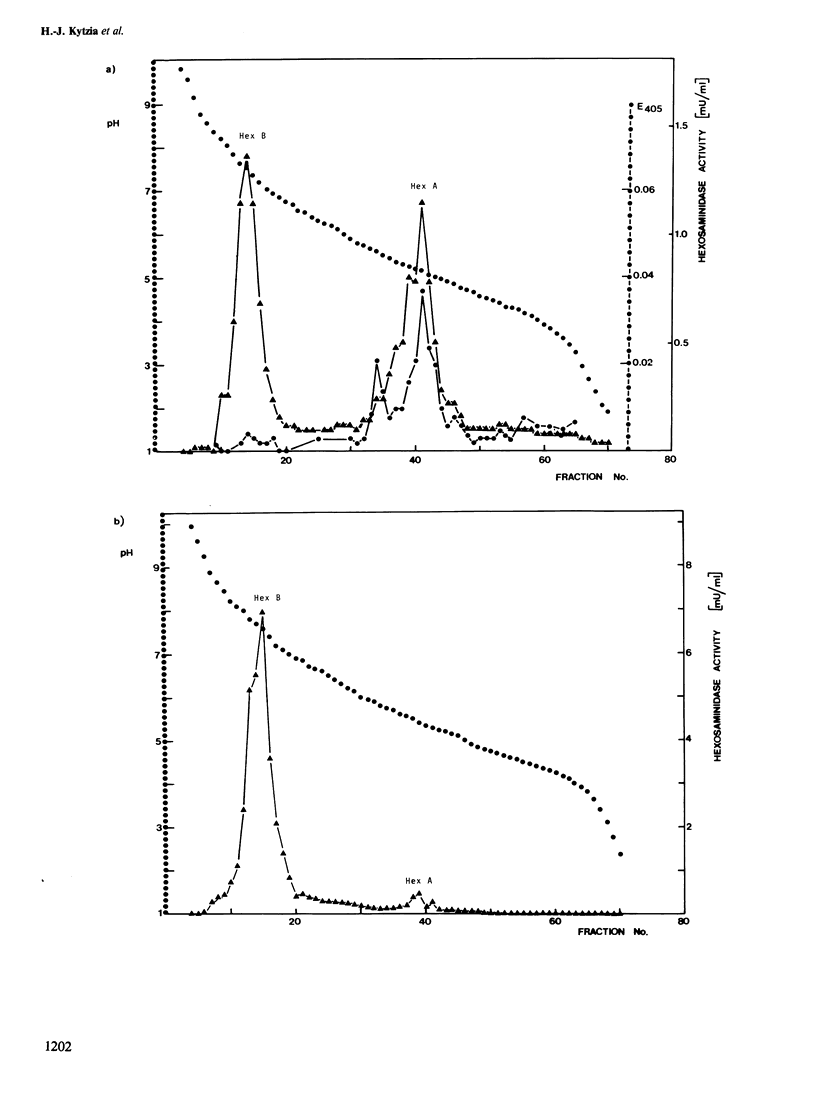
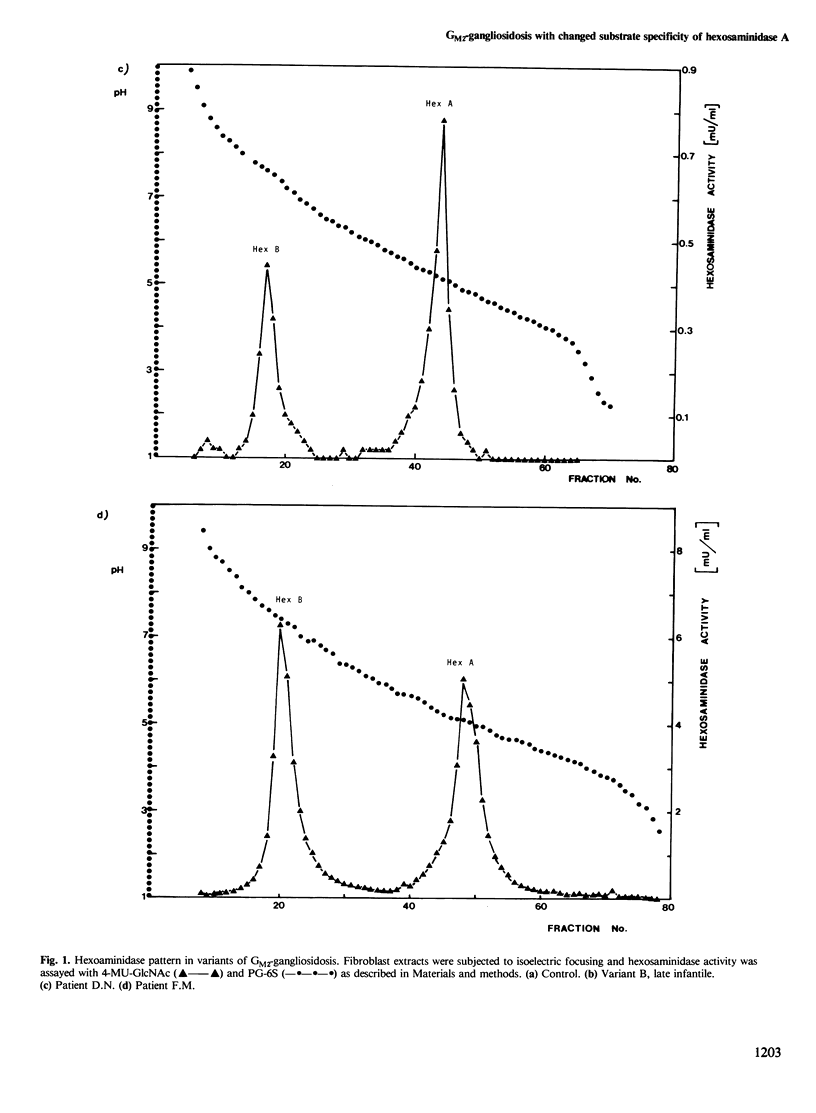
The levels of hexosaminidase A activity in cultivated fibroblasts of two patients with GM2-gangliosidosis were close to the normal range with 4-methylumbelliferyl-beta-D-2-acetamido-2-deoxyglucopyranoside and 4-methylumbelliferyl-beta-D-2-acetamido-2-deoxygalactopyranoside as substrates, and the enzymes were normal in most parameters analyzed. However, the enzymes of both patients were almost completely inactive against two specific substrates for hexosaminidase A, rho-nitrophenyl-6-sulfo-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranoside, and ganglioside GM2 in the presence of GM2-activator. Fibroblast extracts of both patients showed normal hexosaminidase B and GM2-activator activity, the latter was strongly decreased in two cases with variant AB. It is suggested that human hexosaminidase A may contain two different active sites which might be inactivated separately by different mutations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bearpark T. M., Stirling J. L. A difference in the specificities of human liver N-acetyl-beta-hexosaminidases A and B detected by their activities towards glycosaminoglycan oligosaccharides. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):997–1000. doi: 10.1042/bj1730997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bearpark T., Stirling J. L. Clearance of human N-acetyl-beta-hexosaminidases from rat circulation. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):435–439. doi: 10.1042/bj1680435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann E., Burg J., Stephan G., Sandhoff K. Complexing of glycolipids and their transfer between membranes by the activator protein for degradation of lysosomal ganglioside GM2. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):455–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann E., Sandhoff K. AB variant of infantile GM2 gangliosidosis: deficiency of a factor necessary for stimulation of hexosaminidase A-catalyzed degradation of ganglioside GM2 and glycolipid GA2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3979–3983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann E., Sandhoff K. Purification and characterization of an activator protein for the degradation of glycolipids GM2 and GA2 by hexosaminidase A. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Dec;360(12):1837–1849. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1979.360.2.1837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E., Yamanaka T., Rapin I., Adachi M., Suzuki K., Suzuki K. The AB-variant of GM2-gangliosidosis. Clinical, biochemical, and pathological studies of two patients. Acta Neuropathol. 1980;52(3):189–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00705807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Neufeld E. F. Biosynthesis of lysosomal enzymes in fibroblasts. Synthesis as precursors of higher molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4937–4945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., von Figura K., Conzelmann E., Nehrkorn H., Sandhoff K. Lysosomal enzyme precursors in human fibroblasts. Activation of cathepsin D precursor in vitro and activity of beta-hexosaminidase A precursor towards ganglioside GM2. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jul;125(2):317–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechtman P., Gordon B. A., Ng Ying Kin N. M. Deficiency of the hexosaminidase A activator protein in a case of GM2 gangliosidosis; variant AB. Pediatr Res. 1982 Mar;16(3):217–222. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198203000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirabayashi Y., Li Y. T., Li S. C. The protein activator specific for the enzymic hydrolysis of GM2 ganglioside in normal human brain and brains of three types of GM2 gangliosidosis. J Neurochem. 1983 Jan;40(1):168–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb12667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara K., Sobue M., Uemura D., Tsuji M., Nakanishi Y. N-Acetylgalactosamine 4,6-bissulfate in rat urine. I. Isolation, identification and chemical synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 21;437(2):416–430. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresse H., Fuchs W., Glössl J., Holtfrerich D., Gilberg W. Liberation of N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate by human beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase A. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12926–12932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresse H., Paschke E., von Figura K., Gilberg W., Fuchs W. Sanfilippo disease type D: deficiency of N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase required for heparan sulfate degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6822–6826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. C., Hirabayashi Y., Li Y. T. A new variant of type-AB GM2-gangliosidosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jul 30;101(2):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saifer A., Perle G. Automated determination of serum hexosaminidase A by pH inactivation for detection of Tay-Sachs disease heterozygotes. Clin Chem. 1974 May;20(5):538–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K., Christomanou H. Biochemistry and genetics of gangliosidoses. Hum Genet. 1979;50(2):107–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00390234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K., Harzer K., Wässle W., Jatzkewitz H. Enzyme alterations and lipid storage in three variants of Tay-Sachs disease. J Neurochem. 1971 Dec;18(12):2469–2489. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K. Variation of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase-pattern in Tay-Sachs disease. FEBS Lett. 1969 Aug;4(4):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



