Abstract
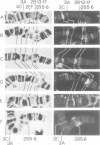
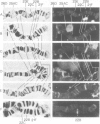
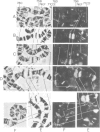
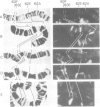
Salivary glands of third instar Drosophila melanogaster larvae were incubated in vitro in the presence of 5 x 10(-6) M 20-hydroxy-ecdysone. Steroid hormone was localized on the polytene chromosomes of the salivary gland by a combination of photoaffinity-labeling and indirect immunofluorescence microscopy. Steroid hormone binding to chromosomal loci and their puffing activity was correlated for the larval/prepupal puffing cycle characterized by puff stages 1-10. In general, there was a good correlation between the sequential and temporal puffing activity induced by 20-hydroxy-ecdysone and the binding of ecdysteroid hormone to these puffs. Ecdysteroid hormone was detected at intermolt, and at early and late puffs with two notable exceptions. Ecdysteroid was not detected at the two well-studied puffs at 23E and at 25AC, the former being an early puff, which is activated in the presence of 20-hydroxy-ecdysone, and the latter being an intermolt puff, which regresses more rapidly in the presence of hormone. Ecdysteroid hormone was present at puffs as long as the respective puff was active. Also, it apparently accumulated at late puff sites after induction. Since ecdysteroid binding to chromosomal loci is temporal as well as sequential during the larval/prepupal puffing cycle, additional factors besides steroid hormone are necessary for sequentially regulating puffing and concomitant gene activity during development from larvae to prepupae.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. I. Autosomal puffing patterns in a laboratory stock of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1967;21(4):398–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00336950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. VI. Induction by ecdysone in salivary glands of D. melanogaster cultured in vitro. Chromosoma. 1972;38(3):255–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00290925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Puffing patterns in Drosophila melanogaster and related species. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1972;4:101–151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-37164-9_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Richards G. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. III. Consequences of ecdysone withdrawal. Dev Biol. 1976 Dec;54(2):241–255. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90302-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Dependence upon ecdysone concentration. Dev Biol. 1973 Nov;35(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. II. The effects of inhibitors of protein synthesis. Dev Biol. 1974 Jul;39(1):141–157. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(74)80016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER H. J. [The puffs of salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophilia melanogaster. Part 1. Observations on the behavior of a typical puff in the normal strain and in two mutants, giant and lethal giant larvae]. Chromosoma. 1959;10:654–678. doi: 10.1007/BF00396591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belyaeva E. S., Vlassova I. E., Biyasheva Z. M., Kakpakov V. T., Richards G., Zhimulev I. F. Cytogenetic analysis of the 2B3-4-2B11 region of the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. II. Changes in 20-OH ecdysone puffing caused by genetic defects of puff 2B5. Chromosoma. 1981;84(2):207–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00399132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronemeyer H., Hameister H., Pongs O. Photoinduced bonding of endogenous ecdysterone to salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus tentans. Chromosoma. 1981;82(4):543–559. doi: 10.1007/BF00295012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenman S. G. Radio-ligand binding assay of specific estrogens using a soluble uterine macromolecule. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Jan;28(1):127–130. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Chromosome puff activity and protein synthesis in larval salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4550–4554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepesant J. A., Kejzlarova-Lepesant J., Garen A. Ecdysone-inducible functions of larval fat bodies in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5570–5574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M., Hämmerling G. J., Rajewsky K. Analysis of the repertoire of anti-NP antibodies in C57BL/6 mice by cell fusion. I. Characterization of antibody families in the primary and hyperimmune response. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Jun;8(6):393–400. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaltmann K., Pongs O. A simple procedure for blotting of proteins to study antibody specificity and antigen structure. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980;361(2):207–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaltmann K., Pongs O. Identification and characterization of the ecdysterone receptor in Drosophila melanogaster by photoaffinity labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker V. K., Ashburner M. The control of ecdysterone-regulated puffs in Drosophila salivary glands. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]