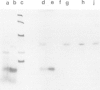
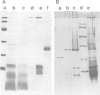
Abstract
Human interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) purified to electrophoretic homogeneity by a cation exchange h.p.l.c., was used for the development of monoclonal antibodies. Following immunization, spleen lymphocytes of two mice showing the highest binding and neutralizing titers were isolated, fused with NSO mouse myeloma cells and cloned. The screening of hybridomas was based on precipitation of the immune complexes with a second antibody and recovery of the biological activity of IFN-gamma from the precipitate. Twenty nine independent hybridomas secreting antibodies specific to IFN-gamma were obtained. Twelve out of these 29 hybridomas produced antibodies that neutralized the antiviral activity of pure as well as crude IFN-gamma. Moreover, IFN-gamma obtained by various induction procedures was neutralized as well, indicating that these various IFN-gamma subtypes are immunologically cross-reactive. Immune precipitation of partially purified 125I-labelled IFN-gamma by several monoclonal antibodies revealed two protein bands of 26,000 and 21,000 daltons. Immunoaffinity chromatography of IFN-gamma gave a 50-fold purification to a specific activity > or = 4 x 10(7) units/mg. Two of the monoclonal antibodies were found suitable for a sensitive and rapid double antibody solid-phase radioimmunoassay, allowing the detection of IFN-gamma at concentrations of at least 4 ng/ml (150 units/ml) within 8 h.
Full text
PDF
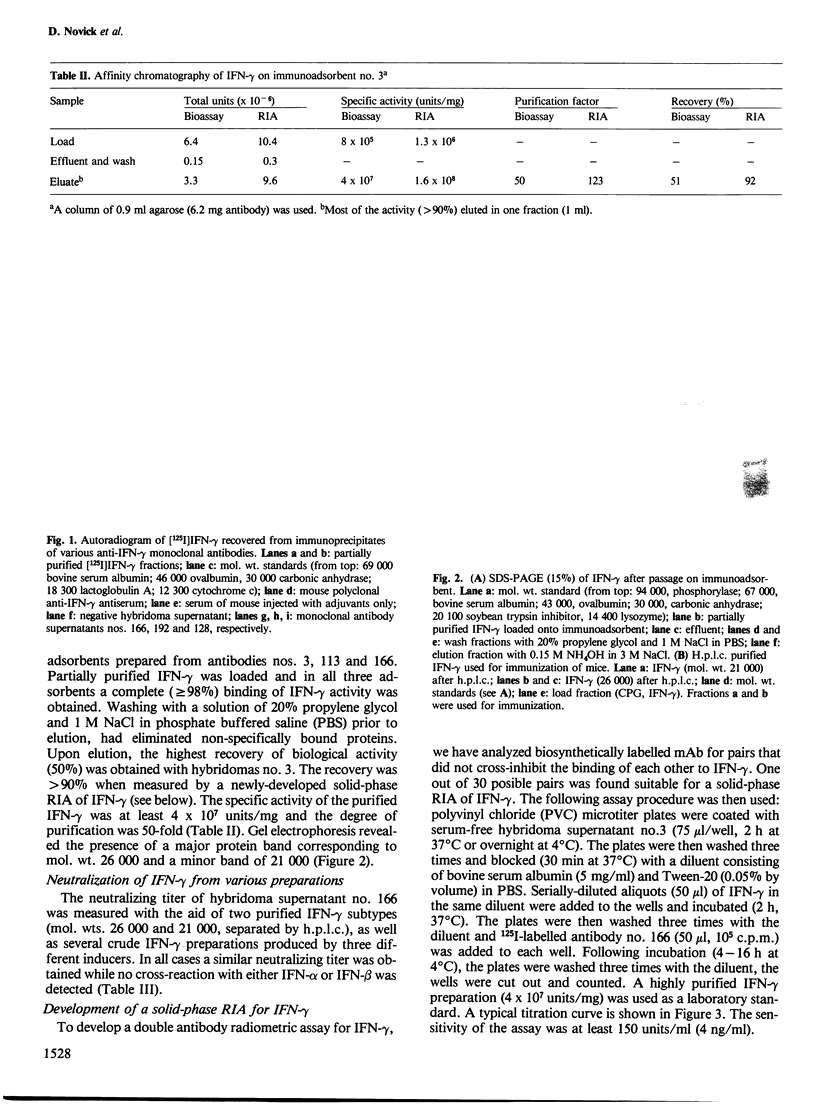
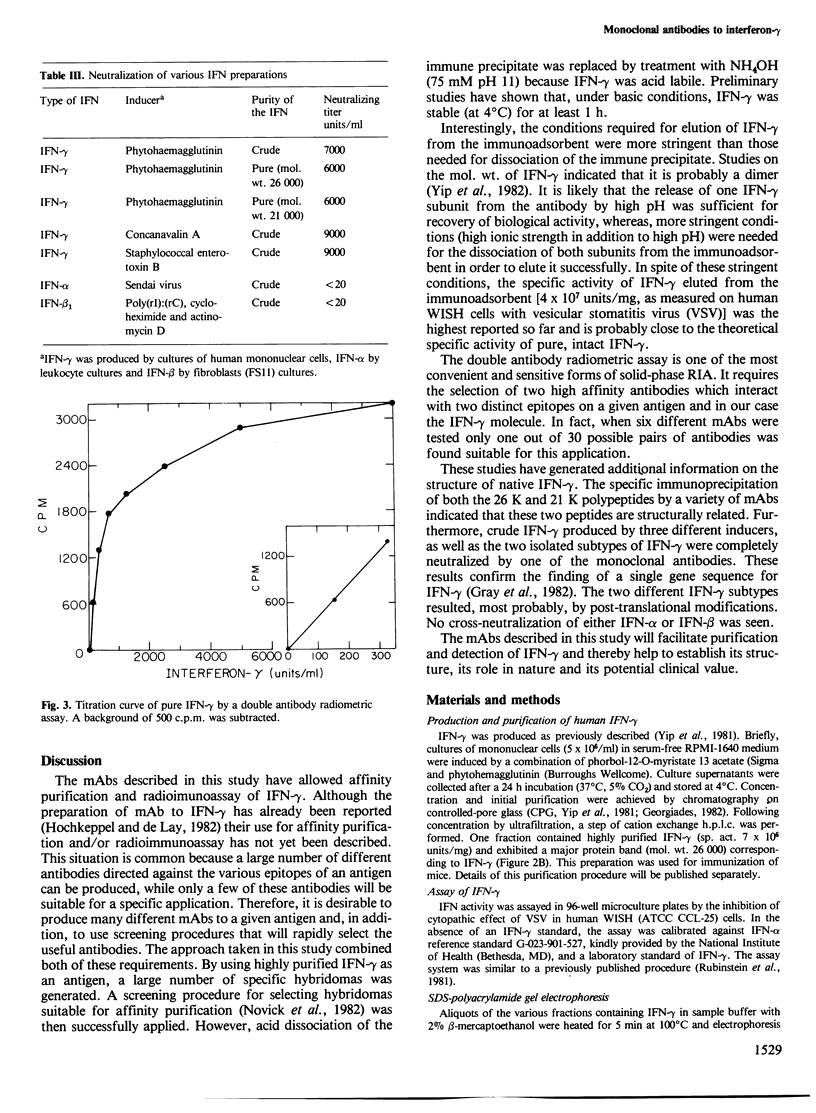

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshhar Z., Ofarim M., Waks T. Generation of hybridomas secreting murine reaginic antibodies of anti-DNP specificity. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):775–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiades J. A. Production and purification of the human interferon gamma (HuIFN-gamma). Tex Rep Biol Med. 1981;41:179–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Pennica D., Yelverton E., Najarian R., Simonsen C. C., Derynck R., Sherwood P. J., Wallace D. M., Berger S. L. Expression of human immune interferon cDNA in E. coli and monkey cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):503–508. doi: 10.1038/295503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochkeppel H. K., Menge U., Collins J. Monoclonal antibodies against human fibroblast interferon. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):500–501. doi: 10.1038/291500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochkeppel H. K., de Ley M. Monoclonal antibody against human IFN-gamma. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):258–259. doi: 10.1038/296258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Interferon nomenclature. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2353–2353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Eshhar Z., Gigi O., Marks Z., Revel M., Rubinstein M. Affinity chromatography of human fibroblast interferon (IFN-beta 1) by monoclonal antibody columns. J Gen Virol. 1983 Apr;64(Pt 4):905–910. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-4-905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Eshhar Z., Rubinstein M. Monoclonal antibodies to human alpha-interferon and their use for affinity chromatography. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2244–2247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. The cloning of normal "mast" cells in tissue culture. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Dec;66(3):319–324. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein S., Familletti P. C., Pestka S. Convenient assay for interferons. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):755–758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.755-758.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secher D. S., Burke D. C. A monoclonal antibody for large-scale purification of human leukocyte interferon. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):446–450. doi: 10.1038/285446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S., Moschera J. High-performance liquid chromatography and picomole-level detection of peptides and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):7–16. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek M., Miron T. Polymers coupled to agarose as stable and high capacity spacers. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:72–76. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip Y. K., Barrowclough B. S., Urban C., Vilcek J. Purification of two subspecies of human gamma (immune) interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1820–1824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip Y. K., Pang R. H., Urban C., Vilcek J. Partial purification and characterization of human gamma (immune) interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1601–1605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]