Abstract
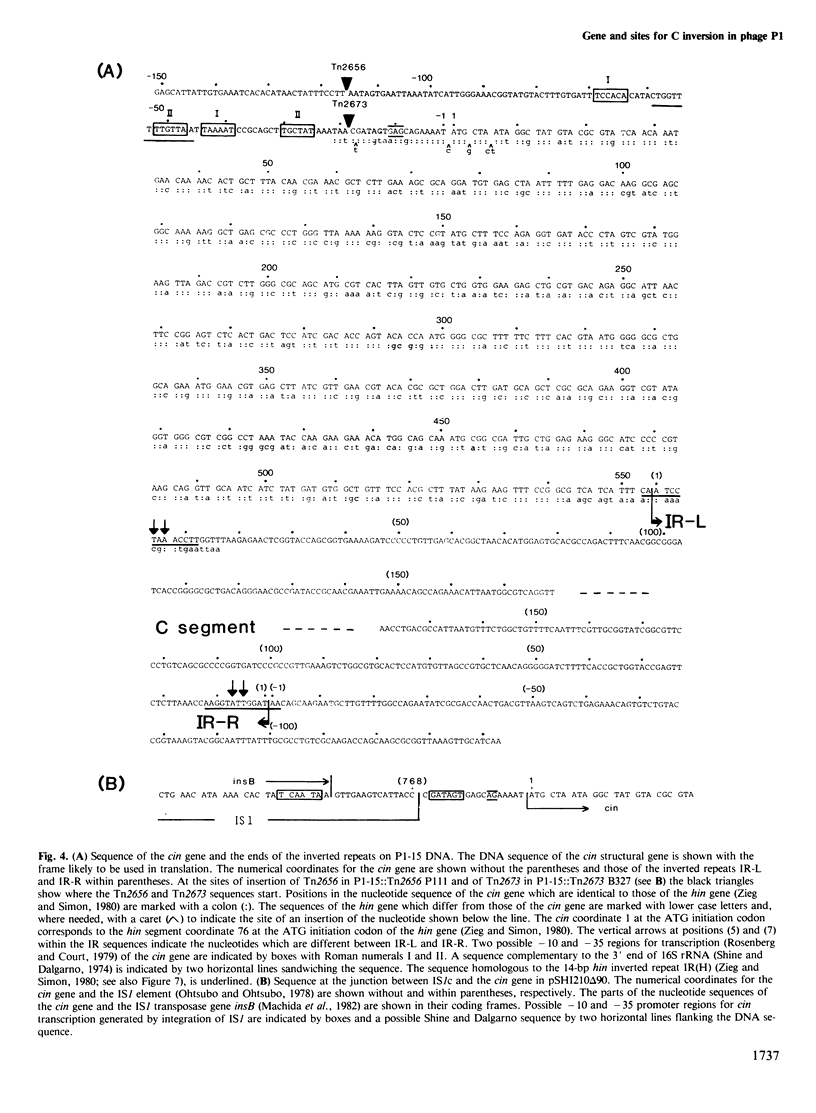
Inversion of the 4.2-kb C segment flanked by 0.6-kb inverted repeats on the bacteriophage P1 genome is mediated by the P1-encoded site-specific cin recombinase. The cin gene lies adjacent to the C segment and the C inversion cross-over sites cixL and cixR are at the external ends of the inverted repeats. We have sequenced the DNA containing the cin gene and these cix sites. The cin structural gene consists of 561 nucleotides and terminates at the inverted repeat end where the cixL site is located. Only two nucleotides in the cixL region differ from those in the cixR and they are within the cin TAA stop codon. The cin promoter was localized by transposon mutagenesis within a 0.1-kb segment, which contains probable promoter sequences overlapping with a 'pseudo-cix' sequence cixPp. In a particular mutant, integration of an IS1-flanked transposon into the cin control region promoted weak expression of the cin gene. The cin and cix sequences show homology with corresponding, functionally related sequences for H inversion in Salmonella and with cross-over sites for G inversion in phage Mu. Based on a comparison of the DNA sequences and of the gene organizations, a possible evolutionary relationship between these three inversion systems and the possible significance of the cixPp sequence in the cin promoter are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bächi B., Arber W. Physical mapping of BglII, BamHI, EcoRI, HindIII and PstI restriction fragments of bacteriophage P1 DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jun 24;153(3):311–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00431596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. T., Lebowitz J. Mapping of RNA polymerase binding sites in R12 derived plasmids carrying the replication-incompatibility region and the insertion element IS1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7295–7311. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Casadaban M. J., Lemaux P. G., Cohen S. N. Identification and characterization of a self-regulated repressor of translocation of the Tn3 element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4020–4024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Bukhari A. I. The invertible DNA segments of coliphages Mu and P1 are identical. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):242–248. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giphart-Gassler M., Plasterk R. H., van de Putte P. G inversion in bacteriophage Mu: a novel way of gene splicing. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):339–342. doi: 10.1038/297339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., Kostriken R., Morita C., Parker R. Tn3 encodes a site-specific recombination system: identification of essential sequences, genes, and the actual site of recombination. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):259–268. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S. A cointegrate of the bacteriophage P1 genome and the conjugative R plasmid R100. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):278–290. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Meyer J., Arber W. Cointegrates between bacteriophage P1 DNA and plasmid pBR322 derivatives suggest molecular mechanisms for P1-mediated transduction of small plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00271186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Meyer J., Arber W. Genesis and natural history of IS-mediated transposons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):27–43. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Meyer J., Kennedy K. E., Arber W. A site-specific, conservative recombination system carried by bacteriophage P1. Mapping the recombinase gene cin and the cross-over sites cix for the inversion of the C segment. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1445–1453. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01336.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T., Kutsukake K. Trans-acting genes of bacteriophages P1 and Mu mediate inversion of a specific DNA segment involved in flagellar phase variation of Salmonella. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):11–16. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp D., Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Kwoh D., Zipser D., Kahmann R. Site-specific recombination in phage mu. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1159–1167. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp D., Kahmann R. The relationship of two invertible segments in bacteriophage Mu and Salmonella typhimurium DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):564–566. doi: 10.1007/BF00352543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwoh D. Y., Zipser D. Identification of the gin protein of bacteriophage mu. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Grice S. F., Matzura H., Marcoli R., Iida S., Bickle T. A. The catabolite-sensitive promoter for the chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene is preceded by two binding sites for the catabolite gene activator protein. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):312–318. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.312-318.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida Y., Machida C., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Factors determining frequency of plasmid cointegration mediated by insertion sequence IS1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):277–281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcoli R., Iida S., Bickle T. A. The DNA sequence of an IS/-flanked transposon coding for resistance to chloramphenicol and fusidic acid. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 28;110(1):11–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney K., Shimatake H., Court D., Schmeissner U., Brady C., Rosenberg M. A system to study promoter and terminator signals recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:383–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Iida S., Arber W. Physical analysis of the genomes of hybrid phages between phage P1 and plasmid p15B. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 25;165(1):191–195. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita M., Oka A. The structure of a transcriptional unit on colicin E1 plasmid. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;97(2):435–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integration and excision of bacteriophage lambda: the mechanism of conservation site specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:143–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Nucleotide sequence of an insertion element, IS1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Rosenberg M. A promoter of pBR322 activated by cAMP receptor protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3365–3377. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rak B., Lusky M., Hable M. Expression of two proteins from overlapping and oppositely oriented genes on transposable DNA insertion element IS5. Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):124–128. doi: 10.1038/297124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Grindley N. D. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination in vitro: DNA cleavage and protein-DNA linkage at the recombination site. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):721–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selzer G., Som T., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. The origin of replication of plasmid p15A and comparative studies on the nucleotide sequences around the origin of related plasmids. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90502-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Zieg J., Mandel G., Simon M. Analysis of the functional components of the phase variation system. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):17–26. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger P. IS elements and transposons. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):241–259. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stüber D., Bujard H. Organization of transcriptional signals in plasmids pBR322 and pACYC184. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toussaint A., Lefebvre N., Scott J. R., Cowan J. A., de Bruijn F., Bukhari A. I. Relationships between temperate phages Mu and P1. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):146–161. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli: bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Simon M. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of an invertible controlling element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4196–4200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Putte P., Cramer S., Giphart-Gassler M. Invertible DNA determines host specificity of bacteriophage mu. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):218–222. doi: 10.1038/286218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]