Abstract
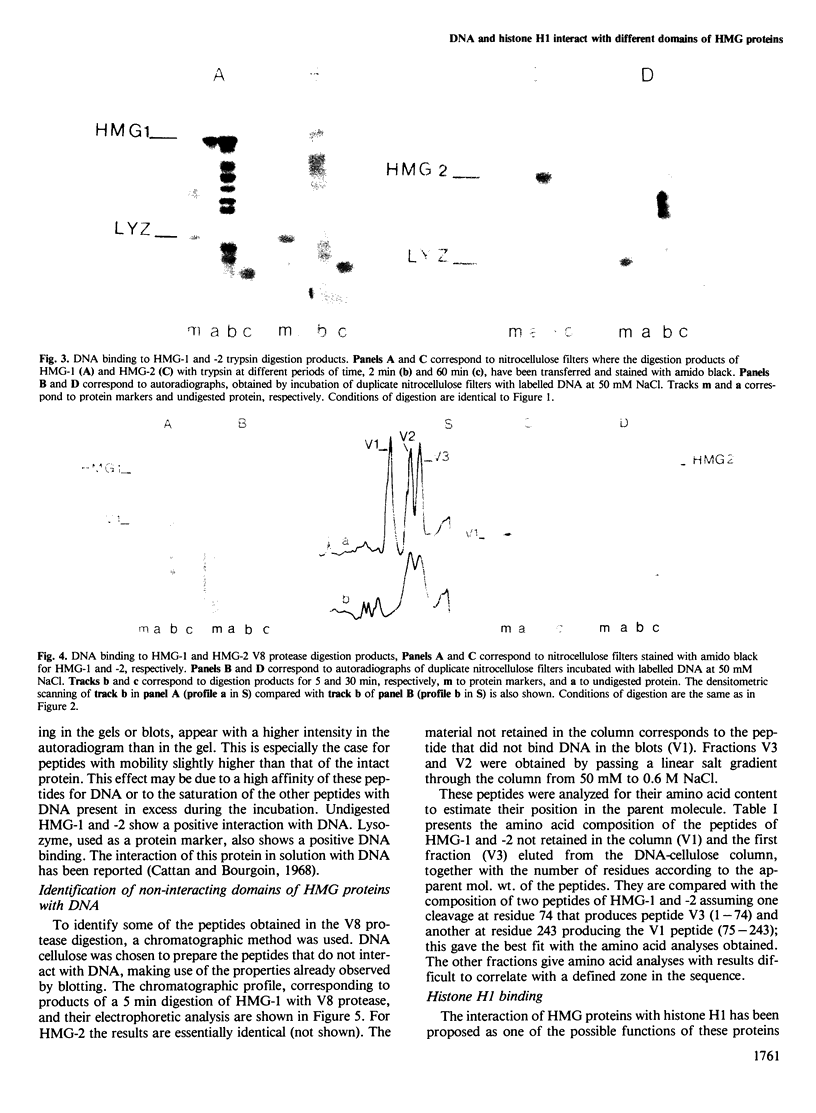
High mobility group (HMG) proteins 1 and 2 from calf thymus have been digested under structuring conditions (0.35 M NaCl, pH 7.1) with two proteases of different specificities, trypsin and V8. The two proteases give a different but restricted pattern of peptides in a time course digestion study. However, when the interactions of the peptides with DNA are studied by blotting, a closely related peptide from HMG-1 and -2 does not show any apparent binding. This peptide, from the V8 protease digestion, has been isolated by DNA-cellulose chromatography and has the amino acid composition predicted for a fragment containing the two C-terminal domains of the protein, i.e., approximately residues 74-243 for HMG-1. The same peptide shows the only interaction detectable with labelled histone H1. A separate function for the different domains of HMG proteins 1 and 2 is proposed.
Full text
PDF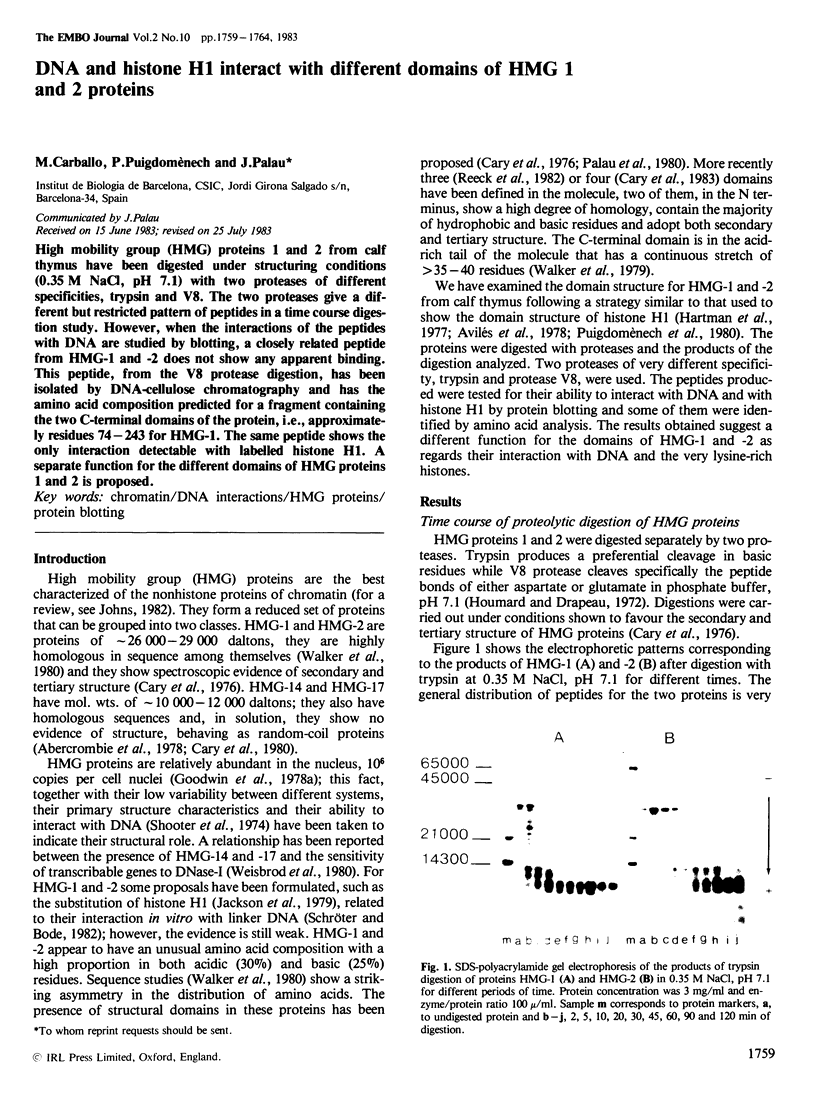




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abercrombie B. D., Kneale G. G., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M., Goodwin G. H., Walker J. M., Johns E. W. Studies on the conformational properties of the high-mobility-group chromosomal protein HMG 17 and its interaction with DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):173–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviles F. J., Chapman G. E., Kneale G. G., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M. The conformation of histone H5. Isolation and characterisation of the globular segment. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):363–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary P. D., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M., Javaherian K., Goodwin G. H., Johns E. W. Conformational studies of two non-histone chromosomal proteins and their interactions with DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 1;62(3):583–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary P. D., King D. S., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M., Rabbani A., Goodwin G. H., Johns E. W. Structural studies on two high-mobility-group proteins from calf thymus, HMG-14 and HMG-20 (ubiquitin), and their interaction with DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;112(3):577–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary P. D., Turner C. H., Mayes E., Crane-Robinson C. Conformation and domain structure of the non-histone chromosomal proteins, HMG 1 and 2. Isolation of two folded fragments from HMG 1 and 2. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 15;131(2):367–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattan D., Bourgoin D. Interactions between DNA and hen's egg white lysozyme. Effects of composition and structural changes of DNA, ionic strength and temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 18;161(1):56–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90294-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Walker J. M., Johns E. W. Studies on the degradation of high mobility group non-histone chromosomal proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 22;519(1):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman P. G., Chapman G. E., Moss T., Bradbury E. M. Studies on the role and mode of operation of the very-lysine-rich histone H1 in eukaryote chromatin. The three structural regions of the histone H1 molecule. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 1;77(1):45–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houmard J., Drapeau G. R. Staphylococcal protease: a proteolytic enzyme specific for glutamoyl bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3506–3509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. B., Pollock J. M., Jr, Rill R. L. Chromatin fractionation procedure that yields nucleosomes containing near-stoichiometric amounts of high mobility group nonhistone chromosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3739–3748. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puigdomenech P., Palau J., Crane-Robinson C. The structure of sea-urchin-sperm histone phi 1 (H1) in chromatin and in free solution. Trypsin digestion and spectroscopic studies. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;104(1):263–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puigdomènech P., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Effect of histone composition on the stability of chromatin structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 29;696(3):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeck G. R., Isackson P. J., Teller D. C. Domain structure in high molecular weight high mobility group nonhistone chromatin proteins. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):76–78. doi: 10.1038/300076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renart J., Reiser J., Stark G. R. Transfer of proteins from gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and detection with antisera: a method for studying antibody specificity and antigen structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3116–3120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Erlichman J., Rosen O. M. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine heart muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:308–315. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. A method for the fractionation of the high-mobility-group non-histome chromosomal proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 10;78(3):1034–1042. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90525-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter H., Bode J. The binding sites for large and small high-mobility-group (HMG) proteins. Studies on HMG-nucleosome interactions in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(2):429–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shooter K. V., Goodwin G. H., Johns E. W. Interactions of a purified non-histone chromosomal protein with DNA and histone. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 1;47(2):263–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. M., Gooderham K., Hastings J. R., Mayes E., Johns E. W. The primary structures of non-histone chromosomal proteins HMG 1 and 2. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 29;122(2):264–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80453-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. M., Hastings J. R., Johns E. W. A novel continuous sequence of 41 aspartic and glutamic residues in a non-histone chromosomal protein. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):281–282. doi: 10.1038/271281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Release of discrete subunits after nuclease and trypsin digestion of chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1212–1216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S. Active chromatin. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):289–295. doi: 10.1038/297289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Interaction of HMG 14 and 17 with actively transcribed genes. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90410-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Simpson R. T. Localization of the sites along nucleosome DNA which interact with NH2-terminal histone regions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6516–6520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









