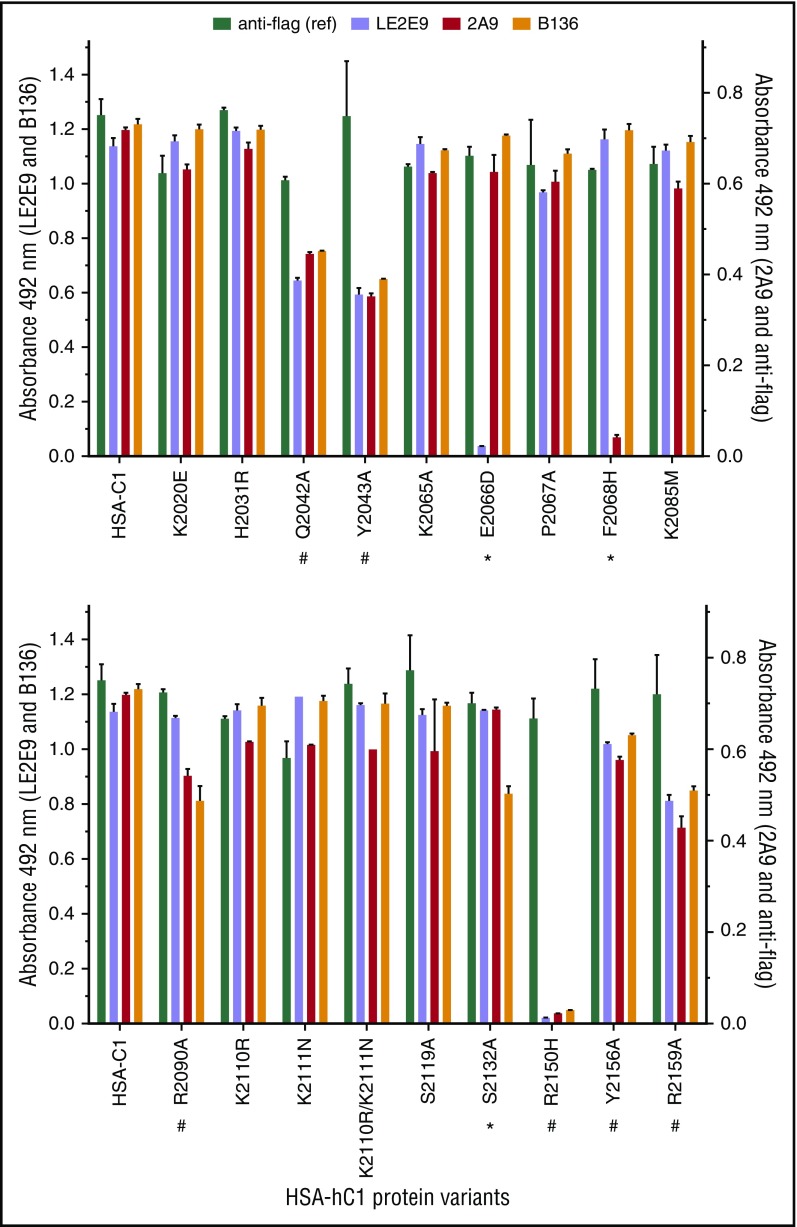
Figure 2.
Identification of C1 domain residues involved in antibody binding using HSA-hC1 variants. Anti-C1 mAbs 2A9 and LE2E9 (group A), anti-C1 mAb B136 (group B), and anti-flag M1 antibody (used to control input) were immobilized onto microtiter plates. Binding of the indicated HSA-hC1 variants (for details, see Table 2) from cell culture media was detected with biotinylated anti-HSA antibody followed by incubation with HRP-conjugated streptavidin. Cell culture media from nontransfected cells were used as negative control for background correction. The experiments were repeated twice with similar results. Comparable changes in binding to HSA-hC1 variants for anti-C1 group A and group B mAbs are denoted by an octothorpe below the substituted residue and point to a global distortion of the C1 domain in these variants. Anti-C1 group A or group B mAb-specific binding defects are denoted by an asterisk below the substituted residue.