Abstract
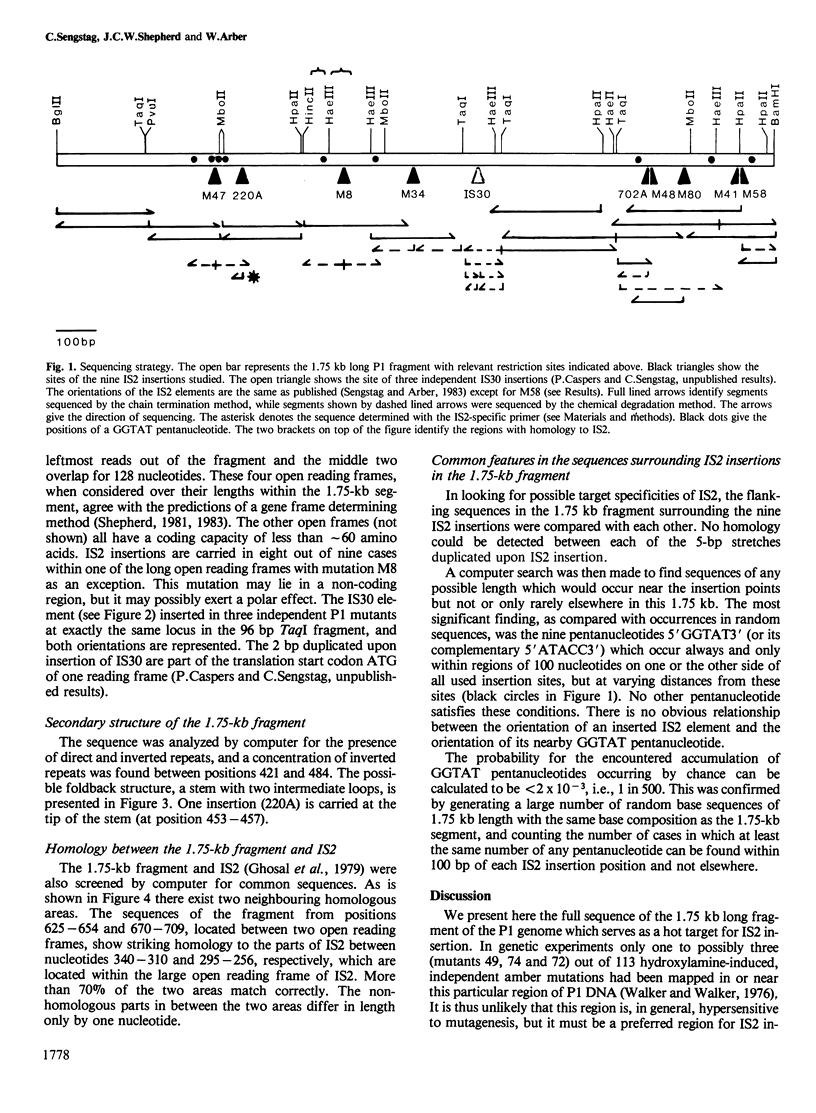
A restriction fragment of the bacteriophage P1 genome known to serve as a hot target for IS2 insertion in its host, Escherichia coli K12, was entirely sequenced. It is 1756 bp long and it contains four long open reading frames, all in the same orientation. The two middle frames overlap partially. Eight of the nine studied IS2 insertions affecting phage reproduction map within three of these reading frames. No common feature was found between the nine target sites which have served for IS2 integration. However, there are two structural elements which might possibly contribute to rendering the studied DNA segment a hot region for IS2 insertion. The first is formed by two neighbouring, 30 and 40 bp regions of homology with an internal segment of IS2. The second is the pentanucleotide 5' GGTAT3', which is carried nine times in the sequenced fragment and which is found always in at least one copy within a variable distance of less than 100 bp of each inserted IS2 element.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arber W., Iida S., Jütte H., Caspers P., Meyer J., Hänni C. Rearrangements of genetic material in Escherichia coli as observed on the bacteriophage P1 plasmid. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1197–1208. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlier D., Piette J., Glansdorff N. IS3 can function as a mobile promoter in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5935–5948. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiandt M., Szybalski W., Malamy M. H. Polar mutations in lac, gal and phage lambda consist of a few IS-DNA sequences inserted with either orientation. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(3):223–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00333860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. C., Howarth A. J., Hahn P., Brown-Luedi M., Shepherd R. J., Messing J. The complete nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of cauliflower mosaic virus by M13mp7 shotgun sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2871–2888. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., Sommer H., Saedler H. Nucleotide sequence of the transposable DNA-element IS2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):1111–1122. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiestand-Nauer R., Iida S. Sequence of the site-specific recombinase gene cin and of its substrates serving in the inversion of the C segment of bacteriophage P1. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1733–1740. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01650.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Tomizawa J. I. Transducing fragments in generalized transduction by phage P1. I. Molecular origin of the fragments. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):85–109. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80232-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Stålhammar-Carlemalm M., Iida S. Denaturation map of bacteriophage P1 DNA. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Karch F., Iida S., Meyer J. The plasmid cloning vector pBR325 contains a 482 base-pair-long inverted duplication. Gene. 1981 Sep;14(4):289–299. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D., Shimatake H., Brady C., Wulff D. L. The relationship between function and DNA sequence in an intercistronic regulatory region in phage lambda. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):414–423. doi: 10.1038/272414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. R., Bennett G. N. Construction and analysis of in vivo activity of E. coli promoter hybrids and promoter mutants that alter the -35 to -10 spacing. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengstag C., Arber W. IS2 insertion is a major cause of spontaneous mutagenesis of the bacteriophage P1: non-random distribution of target sites. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):67–71. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01382.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C. From primeval message to present-day gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1099–1108. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C. Method to determine the reading frame of a protein from the purine/pyrimidine genome sequence and its possible evolutionary justification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1596–1600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Jr, Walker J. T. Genetic studies of coliphage P1. III. Extended genetic map. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):177–187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.177-187.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. T., Walker D. H., Jr Coliphage P1 morphogenesis: analysis of mutants by electron microscopy. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1118–1139. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1118-1139.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



