Abstract
Background
The death of a parent is a highly stressful life event for bereaved children. Several studies have shown an increased risk of mental ill-health and psychosocial problems among affected children. The aims of this study were to systematically review studies about effective support interventions for parentally bereaved children and to identify gaps in the research.
Methods
The review’s inclusion criteria were comparative studies with samples of parentally bereaved children. The focus of these studies were assessments of the effects on children of a bereavement support intervention. The intervention was directed towards children 0–18 years; but it could also target the children’s remaining parent/caregiver. The study included an outcome measure that dealt with effects of the intervention on children. The following electronic databases were searched up to and including November 2015: PubMed, PsycINFO, Cinahl, PILOTS, ProQuest Sociology (Sociological Abstracts and Social Services Abstracts). The included studies were analysed and summarized based on the following categories: type of intervention, reference and grade of evidence, study population, evaluation design, measure, outcome variable and findings as effect size within and between groups.
Results
One thousand, seven hundred and-six abstracts were examined. Following the selection process, 17 studies were included. The included studies consisted of 15 randomized controlled studies, while one study employed a quasi-experimental and one study a pre-post-test design. Thirteen studies provided strong evidence with regards to the quality of the studies due to the grade criteria; three studies provided fairly strong evidence and one study provided weaker evidence.
The included studies were published between 1985 and 2015, with the majority published 2000 onwards. The studies were published within several disciplines such as psychology, social work, medicine and psychiatry, which illustrates that support for bereaved children is relevant for different professions. The interventions were based on various forms of support: group interventions for the children, family interventions, guidance for parents and camp activities for children. In fourteen studies, the interventions were directed at both children and their remaining parents. These studies revealed that when parents are supported, they can demonstrate an enhanced capacity to support their children. In three studies, the interventions were primarily directed at the bereaved children. The results showed positive between group effects both for children and caregivers in several areas, namely large effects for children’s traumatic grief and parent’s feelings of being supported; medium effects for parental warmth, positive parenting, parent’s mental health, grief discussions in the family, and children’s health. There were small effects on several outcomes, for example children’s post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms, anxiety, depression, self-esteem and behaviour problems. There were studies that did not show effects on some measures, namely depression, present grief, and for the subgroup boys on anxiety, depression, internalizing and externalizing.
Conclusions
The results indicate that relatively brief interventions can prevent children from developing more severe problems after the loss of a parent, such as traumatic grief and mental health problems. Studies have shown positive effects for both children’s and remaining caregiver’s health. Further research is required including how best to support younger bereaved children. There is also a need for more empirically rigorous effect studies in this area.
Keywords: Bereavement, Grief, Parental death, Death, Dying, Bereavement support, Intervention, Evaluation
Background
In stable developed nations about three to 4 % of children are affected by the loss of a parent through death prior to the age of 18 [1]. The loss of one or both parents can be associated with a higher vulnerability for children, both from a short and long term perspective. Several studies have shown an increased risk of mental health problems and threats to emotional well-being for affected children, such as anxiety, depression and a perceived lack of control over what happens in one’s life [1–5]. The death of a parent has also been linked to increased somatic symptoms and development of stress sensitivity [2, 6, 7]. Scandinavian studies have revealed that the death of a parent in childhood or adolescence is associated with an increased mortality risk during childhood, adolescence and into early adulthood [8, 9]. Parental death in childhood is also associated with an increased long-term risk of suicide [10]. A child’s problems post bereavement may also appear in school as concentration difficulties or behavioural problems [1, 2]. A longitudinal study by Brent et al. [11] reported that suddenly (e.g. unexpected deaths) bereaved youths had lower competence than non-bereaved youths in the areas of work and future education planning.
After the death of a parent some children live with their remaining parent, while other children live with another person, for example a stepmother, stepfather, grandparent, aunt, uncle, sibling, foster parent, adoptive parent. In this article we use the term caregiver to refer to a surviving parent or another significant other who takes on board a parental role.
The death of a parent is a highly stressful life event for children. While children at this time are in significant need of support, the inverse can happen because of changes in the family situation and family roles post bereavement. In some cases, the children’s remaining parent/caregivers are struggling with their own grief and may experience psychological difficulties themselves. As a result, it can be a challenge for them to provide sufficient support for the children. The remaining parent must also deal with additional stressors of being a single parent and the sole provider of support, while simultaneously coping with the loss of their partner [12]. For the children, this can mean reduced time, attention and support from their remaining parent/caregiver.
Some children, who lose a parent under traumatic circumstances (such as deaths due to violence, suicide, accident, war or disaster), may suffer from traumatic grief. In some instances, death from natural anticipated causes may also result in traumatic grief, if the child’s experience of the death was shocking. The children can re-experience the traumatic event through intrusive memories, thoughts and feelings. The distress leads to avoidance of trauma and loss reminders. The child may avoid thinking or talking about the deceased parent, places and activities associated with the parent. The traumatic experience often complicates the children’s grieving process [13]. After the loss of a parent children can also develop prolonged grief disorder, a disorder that includes a persistent and disruptive yearning [14]. The child may also have difficulties in accepting the parent’s death and difficulties in moving on in their own lives. The child may also experience feelings of bitterness, and a sense that life is meaningless as part of the syndrome detachment [14].
When a parent dies, the children and the remaining parent/caregiver may need advice and support in their grieving process from a health care professional, in order that their mental health needs are met and so that they can continue their development in a positive direction. However, a key question in the field is what kinds of support are most effective for the children and their caregivers?
While previous reviews in the field have had a broader focus, namely treatment effects for children who have lost a “loved one”, such as a family member, grandparent, relative or friend [15–17], the review presented in this paper focuses on the effects of support interventions for children who are parentally bereaved. The rationale for this in-depth focus is that it is recognised that there are distinct difficulties for children losing a parent and caregiver, as this is often the person that previously was central in the provision of love, security and daily care. This closer relationship means higher impact for the child and heightened feelings of loss and bereavement [2].
In this paper, we present findings from a systematic review of empirical studies evaluating the effectiveness of supportive interventions for children when a parent or caregiver dies. In so doing we may identify gaps in the research. Our research questions are: Which support interventions have been evaluated that focus on effects for children? What is known about the effects of support interventions for the children? What are the needs for further research in the field?
Method
Our review inclusion criteria were studies:
Published in English or Scandinavian languages.
Sample populations of parentally bereaved children to 18 years of age.
Evaluating the effects of bereavement interventions for the children. Family programs were included if children were included in the intervention and the evaluation.
Those were randomized controlled design, quasi experimental design or pre-post-test design.
Working with an information specialist at the National Board of Health and Welfare Sweden, a systematic literature search was undertaken in April 2013 to identify relevant references. Six electronic databases were searched, PubMed, PsycINFO, Cinahl, PILOTS, ProQuest Sociology (Sociological Abstracts and Social Services Abstracts). An updated database search was undertaken in November 2015 to identify studies of bereavement support interventions. We used search terms including: bereavement; grief; parental death; parental bereavement; parentally bereaved child; parentally bereaved youth; parental loss; dying parents; loss of a parent; childhood bereavement; children’s grief; grieving child; combined with search terms related to interventions and evaluation (For full details please contact the first author). Reference lists in the identified literature and previous reviews in the field were also scanned to locate additional relevant studies.
During the selection of studies The Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Review of Interventions (http://handbook.cochrane.org/) was used as a guide. All retrieved studies were reviewed independently by two of the authors. In the initial screening stage, only studies that were obviously irrelevant were excluded. In cases where the researchers made different selections, the studies were included for further review by two authors reading the full paper. In the case of disagreement, two researchers discussed the studies until consensus was reached. Studies were excluded for the following reason: the study population in the evaluation was small, i.e. studies with a population of less than 30 participants.
The evidence was graded according to the rigour of the study design and analysis. We used the same grading criteria as Harding & Higginson [18] and Hudson et al. [19] in their reviews of intervention studies [20]. The assessment and grading criteria are shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Grade Criteria
| Grade I (Strong evidence) RCTs or review of RCTS IA Calculation of sample size and accurate standard definition of appropriate outcome variables IB Accurate and standard definition of appropriate outcome variables IC Neither of the above |
| Grade II (Fairly strong evidence) Prospective study with a comparison group (non-randomized controlled trial, good observational study or retrospective study that controls effectively for confounding variables) IIA Calculation of sample size and accurate, standard definition of appropriate outcome variables and adjustment for the effects of important confounding variables IIB One or more of the above |
| Grade III (Weaker evidence) Retrospective or observational studies IIIA Comparison group, calculation of sample size, accurate and standard definition of appropriate outcome variables IIIB Two or more of the above IIIC None of these |
| Grade IV (Weak evidence) Cross-sectional study, Delphi exercise, consensus of experts |
Cancer Guidance Subgroup of the Clinical Guidance Outcomes Group. Improving outcomes in breast cancer – the research evidence. Leeds: NHS Executive, 1996 [20]
Data analysis
Our analysis of the included studies were grouped in a table based on the following categories: type of intervention, reference (comparison), grade of evidence, study population, evaluation design, measure, outcome variable and findings as effect size within (at baseline and follow-up) and between study comparison groups.
For any ordinal or continuous variables, to be able to calculate effect size even when a means and standard deviation were not reported in studies, the standardized mean difference effect size for within-subjects design was used, which is referred to as Cohen’s dz. The effect size estimate Cohen’s dz. can be calculated directly from the t-value using the formula . A commonly used interpretation of Cohen’s d is that value of 0.2 can be considered a small effect, 0.5 a medium effect and 0.8 a large effect [21].
The Common Language effect size (CL) [22] is also reported. The CL is also known as the probability of superiority [21], represents the probability in percent that a randomly selected person will score a different observed measurement post- than pre intervention, after controlling for individual differences. In addition when possible, the effect size of difference between groups was calculated (dm) using a method proposed by Morris in which effect size is calculated on the mean pre-post change in the treatment group minus the mean pre-post change in the control group, divided by the pooled pre-test standard deviation [23]. For categorical data, Chi-squared tests were made. Phi is reported as the effect size proposed by Fritz and colleagues using the formula [24]. A value of 0.1 is considered a small effect, 0.3 a medium effect and 0.5 a large effect.
Results
The total number of citations identified in the database searches in April 2013 was 1706. Following the screening process, 371 references were selected for further review of full texts. After examination of full texts, a total of 15 studies were identified that evaluated the effectiveness of bereavement interventions with parentally bereaved children [25–39]. We identified an additional study from checking of the reference lists [40]. The number of citations generated in the updated search in November 2015 was 921. Of these five citations were reviewed in full texts. An additional relevant study was identified [41], resulting in a total of 17 selected studies for the review, see Fig. 1 below.
Fig. 1.
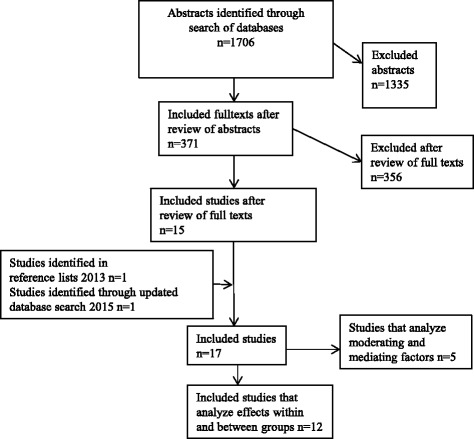
Search flow diagram
Included studies
The included 17 studies were published between 1985 and 2015, the majority, 13 were published after 1999. Most studies were conducted in the United States [26, 27, 29–39, 41]; two in England [25, 40], and another was an international collaborative study involving Iran, UK and Norway [28].
Quality of included studies
The studies differed; they were based on different study designs, contained a variety of outcome measures and varied in quality. According to our quality grading criteria (Table 1) [18–20] 13 studies provided strong evidence. These studies were randomized controlled trials involving validated measures. Three studies provided fairly strong evidence and one study provided weaker evidence [18–20]. Two of the included bereavement interventions were evaluated with a population of more than 100 children. Namely, “The Parent Guidance Program” [26] and “The Family Bereavement Program” [27, 29, 30, 33–35, 37, 39, 41]. One of the interventions, Family Therapy sessions, was tested in two papers [25, 40] and one, The Family Bereavement Program, in as many as ten papers [27, 29, 30, 33–35, 37–39, 41].
Study design
One study employed a quasi-experimental design [31] and one study had a pre-test/post-test design [36], the others were randomized controlled trials. What the intervention was compared with varied: no intervention [25, 28, 40]; delayed treatment [31, 32]; a telephone support intervention [26]; and a self-study program [27, 29, 30, 33–35, 37–39, 41].
The core concepts addressed in the outcome measures were:
Children’s health, in particular their mental health (internalization, externalization, coping, stress, cortisol-levels)
Children’s grief symptoms (traumatic grief, problematic grief)
Children’s behaviour and school problems
Children’s self-esteem
Children’s concepts of death and communication about the deceased parent
Parenting (communication, caregiver-child relationship, parental warmth, acceptance, consistent discipline)
Caregiver’s mental health
Fifty different outcome measures were employed. We present the most commonly reported outcomes in the included studies which focus on children’s health, behaviour, grief, self-esteem, parenting factors and caregivers’ mental health [42–54] (see Table 2 below).
Table 2.
The most common outcome measures employed in the included studies
| Children’s health and behaviour | Child Behaviour Checklist (CBCL) [42] Children’s Depression Inventory (CDI) [43] Youth Self-Report (YSR) [42] Children’s Manifest Anxiety Scale-Revised (R-CMAS) [44] |
| Children’s grief | The Extended Grief Inventory (EGI) [51] Intrusive Grief Thoughts Scale (IGTS) [52] Adapted Inventory of Traumatic Grief: Symptoms of prolonged grief disorder (ITG) [45] Traumatic Grief Inventory for Children (TGIC) [46] The Texas Revised Inventory of Grief (TRIG) [47] |
| Children’s self-esteem | The Self Perception Profile for Children (SPPC) [53] |
| Parenting factors | Children’s Reports of Parental Behaviour Inventory (CRPBI) [48] Parent Perception Inventory (PPI) [54] |
| Caregiver’s mental health | Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) [49] Psychiatric Epidemiology Research Interview (PERI) [50] |
Interventions
A key research question for this review is: What types of support interventions were evaluated in the studies? We found studies varied in their theoretical under-pinning and aim. They also took various forms: group interventions for the children [28, 36], family interventions [25, 27, 29, 30, 32–35, 37–41], parental guidance [26], and camp activities for children [31].
Some interventions were designed based on resilience, risk and protective factors for parentally bereaved children [27, 29, 30, 32–35, 37–39, 41]. Others were based on theory of trauma and/or the grieving process [28, 31]; psycho-education [26]; psychodynamic theory [36]; and attachment theory [25, 40]. To a large extent, the interventions were directed towards children at an early stage in their grief process. “The Family Bereavement Program” and “The Parent Guidance Program” were explicitly intended to be preventive interventions [26, 33]. However, the intervention “Writing for recovery” was directed at refugee children with high symptoms of traumatic grief [28]. For some of the refugee children, many years had passed since their parents died.
In three of the studies, the interventions were primarily directed at the bereaved child in the form of support groups and/or camp activities [28, 31, 36]. The intentions in these studies were: to provide emotional support; to normalize the children’s experiences after the loss; to provide a safe environment where the child can express emotions and thoughts; to facilitate the child’s grieving process and to aim to improve the child’s physical and mental health. For further description of the interventions, see Table 3.
Table 3.
Intervention description
| Study | Intervention description |
|---|---|
| Schilling et al. 1992 [36] (USA) |
Group intervention, “Bereavement groups for inner-city children” Groups consisting of 6–8 children, age 6–12 years 12 sessions divided into 3 phases, each of 4 sessions Opening phase: rules of confidentiality, conduct, purpose of the group; focus on the children’s relationship to the deceased and the impact of the loss on their family; sharing experiences related to death; supportive environment; normalizing bereavement issues Working phase: focus on children’s feelings of sadness, anger, ambivalence related to the loss; demystifying irrational thoughts and fears about the death; identifying and expressing painful feelings Ending phase: the termination of the group as another loss; encourage children to utilize their family as support system; children were reassessed to determine the need for further treatment |
| McClatchey et al. 2009 [31, 55] (USA) |
Group intervention, camp activities, “Camp MAGIC” Groups consisting of 5–8 children, separate groups for children age 7–11 and 12–17 years Camp activities: such as ropes course, canoeing, archery, interacting with new friends Counseling sessions: 6 counseling sessions during a weekend (Friday-Sunday) Focus on: trauma experience; trauma and loss reminders; post-traumatic adversities; interplay of trauma and grief; resumption of developmental progression Grief-oriented tasks and cognitive behavioural aspects such as exposure, cognitive restructuring, stress inoculation techniques Activities: related to grief processing such as creation, play, puppetry show, memorial service Psychoeducational workshop for parents about children’s grieving process |
| Kalantari et al. 2012 [28] (Iran/UK/Norway) |
Group intervention “Writing for recovery” Intervention for children age 12–18 years 6 sessions in school during three consecutive days, each day consists of two 15-min sessions Writing about traumatic experiences to decrease negative thoughts and feelings Writing sessions: Progress from unstructured expressive writing about innermost feelings and thoughts about the traumatic event/loss, to more structured writing where children reflect on what they would have given as advice to another in the same situation as themselves. In the last writing session children are asked to imagine that 10 years has passed and they look back and think about what they have learned from their experience |
| Black & Urbanowicz 1985 [40]; Black & Urbanowicz 1987 [25] (UK) |
Family intervention, family therapy sessions, with children age 0–16 years and their families 6 family therapy sessions spaced at 2–3 weeks intervals, in the families’ homes Focus on: help with emotional and practical problems arising from bereavement; promote mourning in both children and surviving parent; improve communication between children and parent; improve communication about death; encourage children to talk about the dead parent and their feelings of loss and grief; encourage expression of grief in the family Separate sessions for parents alone to enable him/her to talk about his/her own grief, anger, needs |
| Christ et al. 2005 [26] (USA) |
Intervention directed to the well parent and the family when a parent has cancer and is terminally ill, “The Parent Guidance Program” Families with children age 7–17 years 6 or more 60–90 min therapeutic sessions during the terminal stage of the parents illness and 6 or more sessions after the parents death, including meetings with parent(s), children and family Focus on: to affect the children’s adjustment to the loss by enhancing the surviving parents ability to sustain competence in providing support and care or the children; provide an environment in which the children feel able to express painful or conflicting feelings, thoughts, fantasies about the loss; maintain consistency and stability in the children’s environment; support to parents in their own grief work in order to enhance their capacity to function effectively during the family crisis; problem solving around the immediate crisis; communication about illness, loss, grief, reactions; future planning for the family |
| Sandler et al. 1992 [32] (USA) |
Family intervention “The Family Bereavement Program” Intervention for families with children age 7–17 years Program including a total of 13 sessions, consisting of a family grief workshop and a family adviser program Family grief workshop, with 8 bereaved families per session Focus on: to fulfil the perceived needs of bereaved families to meet with other families who have similar experiences; to improve warmth in the parent-child relationship; improve communication about grief experiences Family adviser program, 12 sessions, including 6 individual sessions for parents and 6 family sessions Focus on: parental support; provide emotional support; decrease parental demoralization; increase warmth of the parent-child relationship; increase positive exchanges between family members; increasing quality time between parent and child; communication in the family; planning of stable events; helping improve coping with stressful family events |
| Sandler et al. 2003 [33]; Schmiege et al. 2006 [37]; Tein et al. 2006 [39]; Sandler et al. 2010 [34]; Sandler et al. 2010 [35]; Luecken et al. 2010 [29]; Hagan et al. 2012 [27]; Schoenfelder et al. 2013 [38]; Luecken et al. 2014 [30]; Schoenfelder et al. 2015 [41] (USA) |
Family intervention “The Family Bereavement Program” Intervention for families with children age 8–16 years Program including a total of 14 sessions, consisting of 12 sessions in separate groups for caregivers, children and adolescents Four of these include conjoint activities for children and caregivers. The program also include 2 individual family meetings Groups consisting of 5–9 children, separate groups for children age 8–12 and 12–16. Sessions for caregivers Focus on: improving positive caregiver-child relationship; positive parenting; effective discipline strategies; coping with grief; talking to children about grief; increase positive activities; reduce children’s exposure to negative events; family routines; family time; one on one time; communication; listening skills; decrease caregiver mental health problems Sessions for children Focus on: improving caregiver-child relationship; positive coping; coping efficacy; control-related beliefs; self-esteem; reduce negative appraisals for stressful events; provide opportunities for expression and validation of grief-related feelings; encouraging sharing of feelings with caregivers; individual goals selected by the children |
In the majority of the included studies, the interventions were directed at both the child and their remaining caregiver [25–27, 29, 30, 32–35, 37–41]. The intentions in the included studies were: to provide support for the children and their caregivers; to improve family communication and the caregiver–child relationship; to facilitate participants’ grieving process; to improve their health; strengthen parenting; increase stability and predictability for the children; and to reduce the occurrence of negative events among the children (see Table 3).
In general, the interventions were brief. The shortest program was “Writing for recovery”, involving two 15-min sessions in school during three consecutive days, each day consisted of two sessions (i.e. six 15-min sessions and a total of 90 min) [28]. The camp-based program “CampMAGIC” was delivered over a weekend [31, 55]. The longest, “The Parent Guidance Program” lasted a year, it began when the parent was ill, and continued during the terminal illness and at least 6 months after the parent’s death [26]. It involved at least six sessions during the terminal illness and six after the parent had died. The other interventions were based on a total of 6–14 sessions (see Table 3 for more details).
All interventions were professionally led, in most cases by social workers or counsellors with extensive experience of working with child guidance, grief or psychiatry. The highest educational attainment of professionals were those who led “The Family Bereavement Program”, who had at least a master’s degree [34]. In several studies the intervention leaders received supervision in the implementation of the support program [26, 32, 33, 36].
Study population
The included interventions in this review were directed at children from school age up to 18 years of age. This is with the exception of two studies where younger children (0–16) were involved in family therapy sessions [25, 40]. Most of the studies concerned children who had experienced a parental death from a range of causes, namely illness, accident, suicide or homicide [25, 27, 29, 30, 32–41]. Commonly parents died because of an illness (65–82%), thereafter due to an accident (15–20%) or suicide/homicide (10–14%). In most studies there was a lack of information about what kind of illness the parent suffered from, where there was information, diseases included those of the heart and cancer [25, 32, 40]. One study compared intervention effects for children who had lost a parent to expected versus unexpected deaths [31]. One study focused on children during their parent’s terminal cancer illness as well as after the parent’s death [26]. Finally one study focused on support directed at refugee adolescents who had lost their parents in war [28]. Except for this evaluation directed at refugee children from Afghanistan, the majority of included studies had samples that were diverse in ethnicity, including for example Caucasian, Hispanic, African American, Native American, Asian/Pacific and other ethnicities [33].
In the studies, the most common deceased parent was the child’s father with the remaining caregiver being the mother. In two of the studies, women as remaining caregivers were over-represented as participants in the study populations [32, 36]. In one study 86% of the deceased parents were fathers and 14% mothers [32]. In another study, fathers as remaining caregivers only represented 5 % of the sample [36].
Effectiveness of the interventions
Another key research question for this review was: What is known about the effects of support interventions that are targeted at/or include support for parentally bereaved children? The included studies were analysed and summarized in a matrix. The results are presented in table form (see Table 4 below). There were 12 studies that analysed effects within and between trial arms, while five studies analysed moderating and mediating factors. The latter are excluded from the analysis of effects in Table 4, but are nevertheless informative and are therefore included in the article. Our focus is on comparing differences between groups, but we have also chosen to present results within groups in Table 4, as this may be relevant from a benchmarking perspective, both for researchers and clinicians [56]. The results from the analyses of included studies revealed positive effects of the support interventions both for the children and their remaining caregivers in several areas.
Table 4.
Study effects within and between treatment groups
| Interventions directed to the bereaved children | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention | Reference and grade of evidence | Study population | Evaluation design | Measure | Outcome variable | Effect size TG | Effect size CG | Effect size between groups | |||||
| sig | dz | CL % | sig | dz | CL % | sig | dm (ϕ) | ||||||
| “Bereavement groups for inner-city children” | Schilling et al. 1992 [36] | 38 children (age 6–12) | Pre-test/post-test-design | BID | Depr. (Parent) Depr. (Child) |
.26 .29 |
−.22 .21 |
−59 58 |
na na |
na na |
na na |
na na |
na na |
| IIIC | Evaluation: post treatment | ATCD | Attitudes and Concepts of Death | .01 | .52 | 70 | na | na | na | na | na | ||
| Grief camp “Camp MAGIC” (CG) delayed treatment | McClatchey et al. 2009 [31] | 100 children (age 6–16) | Quasi experimental design | UCLA PTSD | PTSD-symptoms | .08 | .33 | 63 | .73 | −.05 | 52 | .08 | .27 |
| IIB | TG = 46 CG = 54 | Evaluation: post treatment | EGI | Childhood Traumatic Grief | .00 | .73 | 77 | .90 | −.02 | 51 | .01 | .50 | |
| “Writing for recovery” (CG) no treatment | Kalantari et al. 2012 [28] IB |
61 children (age 12–18) TG = 29 CG = 32 |
RCT Evaluation: 1 week post treatment |
TGIC | Traumatic grief | .00 | 1.26 | 90 | .03 | −.39 | 65 | .00 | 1.21 |
| Family-intervention (CG) no treatment | Black & Urbanowicz 1985 [40]; 1987 [25] IIB |
83 children (age 0–16) TG = 38 CG = 45 45 families TG = 21 CG = 24 |
RCT Evaluation: 1 year post treatment |
Clinical Interview | Behavior Sleep Depressed parent |
na na na |
na na na |
na na na |
na na na |
na na na |
na na na |
.05 .09 .01 |
(.21) (.21) (.33) |
| Talk about dead parent | na | na | na | na | na | na | .04 | (.26) | |||||
| Rutter A Rutter A |
Restless Nail-biting |
na na |
na na |
na na |
na na |
na na |
na na |
.01 .03 |
(.34) (.28) |
||||
| School problems | na | na | na | na | na | na | .10 | (.19) | |||||
| Family-intervention (CG) no treatment | Black & Urbanowicz 1987 [25] IIB |
73 children (age 0–16) TG = 38 CG = 35 39 families TG = 21 CG = 18 |
RCT Evaluation: 2 years post treatment |
Clinical Interview | Behavior Talk dead parent |
na na |
na na |
na na |
na na |
na na |
na na |
.09 .04 |
(.28) (.24) |
| School Health |
na na |
na na |
na na |
na na |
na na |
na na |
.03 .04 |
(.28) (.39) |
|||||
| “Parent Guidance Program” (CG) telephone monitoring intervention | Christ et al. 2005 [26] IA |
104 families with children (age 7–17) TG = 79 CG = 25 |
RCT Evaluation: 8 and 14 months after parent’s death |
CDI SEI STAI-S STAI-T CBCL-soc |
Depression Self-Esteem State anxiety Trait anxiety Social competence |
.00 .00 .00 .00 .29 |
.56 .64 .89 .61 .17 |
71 74 81 73 57 |
.03 .21 .12 .87 .27 |
.48 .29 .35 .04 −.31 |
69 61 64 51 62 |
.53 .36 .12 .31 .32 |
.14 .28 .44 .43 .36 |
| CBCL-bprob | Behavior problem | .17 | .16 | 59 | .80 | −.07 | 53 | .69 | .26 | ||||
| POPM-tot | Perceived Parenting |
.06 | .25 | 60 | .31 | −.22 | 59 | .11 | .37 | ||||
| “The Family Bereavement Program” (first version) (CG) delayed treatment | Sandler et al. 1992 [32] IB |
72 families with 72 children (age 7–17) TG = 35 CG = 37 |
RCT Evaluation: post treatment |
CRPBI PRS PRS |
Par. warmth Grief discussion Par. Support |
.00 .78 .00 |
.97 .07 .88 |
83 53 81 |
.25 .00 .11 |
.22 −.70 −.31 |
59 76 62 |
.03 .03 .01 |
.50 .62 .83 |
| “The Family Bereavement Program” (revised version) (CG) self-study program | Sandler et al. 2003 [33] IA |
156 families TG = 90 CG = 66 244 children (age 8–16) TG = 135 CG = 109 |
RCT Evaluation: Posttest and 11 months post treatment |
Posttest | |||||||||
| Comp. GLESC Comp. Comp. AIS TAS SPPC MCPCS CBCL CBCL |
Pos. parenting Negative events Ment. health Positive coping Inhibition Neg. thoughts Self-esteem Control belieifs Internalizing Externalizing |
na na na na na na na na na na |
na na na na na na na na na na |
na na na na na na na na na na |
na na na na na na na na na na |
na na na na na na na na na na |
na na na na na na na na na na |
.00 .03 .01 .02 .01 .78 .37 .72 .03 .11 |
.58a
.43a .50a .30a .48a .05a .19a .06a .41a .28a |
||||
| 11-mth | |||||||||||||
| Comp. GLESC Comp. Comp. AIS TAS SPPC MCPCS CBCL CBCL |
Pos. parenting Negative events Ment.health Positive coping Inhibition Neg. thoughts Self-esteem Control belieifs Internalizing Externalizing |
na na na na na na na na na na |
na na na na na na na na na na |
na na na na na na na na na na |
na na na na na na na na na na |
na na na na na na na na na na |
na na na na na na na na na na |
.03 .11 .10 .20 .06 .18 .16 .00 .61 .19 |
.39a
.32a .32a .18a .39a .29a .27a .40a .10a .24a |
||||
| “The Family Bereavement Program” (CG) self-study program | Schmiege et al. 2006 [37] IA |
156 families TG = 90 CG = 66 244 children (age 8–16) TG = 135 CG = 109 |
RCT Evaluation: 3 and 11 months post treatment |
3-months | |||||||||
| CMAS-R | Anxiety Girls Anxiety Boys |
.08a
.17a |
.32a
.23a |
59 57 |
.32a
.04a |
.20a
.38a |
56 61 |
.41c
.25c |
.11 −.13 |
||||
| CDI | Depression Girls Depression Boys |
.10a
.19a |
.30a
.22a |
58 56 |
.28a
.37a |
.21a
.17a |
56 55 |
.58c
.98c |
.11 .06 |
||||
| YSR | Externaliz. Girls Externaliz. Boys |
.03a
.08a |
.39a
.30a |
61 58 |
.09a
.05a |
.34a
.38a |
59 61 |
.36c
.50c |
.08 −.03 |
||||
| CBCL | Intrenaliz. Girls Internaliz. Boys |
.00a
.00a |
.74a
.48a |
70 63 |
.01a
.00a |
.53a
.69a |
65 69 |
.88c
.39c |
.19 −.16 |
||||
| CBCL | Externaliz. Girls Externaliz. Boys |
.00a
.01a |
.56a
.43a |
65 62 |
.07a
.00a |
.37a
.57a |
60 66 |
.43c
.44c |
.23 −.12 |
||||
| 11-months | |||||||||||||
| CMAS-R | Anxiety Girls Anxiety Boys |
.02a
.01a |
.43a
.44a |
62 62 |
.80a
.01a |
.05a
.48a |
51 63 |
.06c
.73c |
.36 .02 |
||||
| CDI | Depression Girls Depression Boys |
.02a
.07a |
.41a
.32a |
62 59 |
.55a
.05a |
.12a
.37 |
53 60 |
.16c
.65c |
.28 −.01 |
||||
| YSR | Externaliz. Girls Externaliz. Boys |
.08a
.27a |
.33a
.19a |
59 55 |
.89a
.13a |
-.03a
.30a |
51 58 |
.03c
.45c |
.36 −.08 |
||||
| CBCL | Intrenaliz. Girls Internaliz. Boys |
.00a
.01a |
.80a
.47a |
72 63 |
.01a
.00a |
.57a
.63a |
66 67 |
.93c
.58c |
.20 −.10 |
||||
| CBCL | Externaliz. Girls Externaliz. Boys |
.00a
.02a |
.55a
.42a |
65 62 |
.32a
.00a |
.20a
.69a |
56 69 |
.11c
.86c |
.40 −.22 |
||||
| “The Family Bereavement Program” (CG) self-study program | Luecken et al. 2010 [29] IA |
139 children TG = 78 CG = 61 (age 8–16) |
RCT Evaluation: 6 years post treatment |
Cortisol | Cortisol level before and after a conflict discussion task | na | na | na | na | na | na | .03b | .39b |
| “The Family Bereavement Program” (CG) self-study program | Sandler et al. 2010 [34] IA |
156 families TG = 90 CG = 66 |
RCT Evaluation: Post-test, 11 months and 6 years post treatment |
Post (3-months) | |||||||||
| TRIG IGTS |
Present grief Intrusive grief |
.19a
.16a |
-.16a
.17a |
54 55 |
.09a
.50a |
-.23a
.09a |
57 53 |
.72c
.43c |
.05 .09 |
||||
| 244 children (age 8–16) TG = 135 CG = 109 |
11-months | ||||||||||||
| TRIG IGTS |
Present grief Intrusive grief |
.69a
.00a |
.05a
.47a |
51 63 |
.87a
.12a |
-.02a
.21a |
51 56 |
.88c
.06c |
.08 .27 |
||||
| 6-years | |||||||||||||
| TRIG IGTS |
Present grief Intrusive grief |
.00a
.00a |
.73a
1.30a |
70 82 |
.00a
.00a |
.63a
1.08a |
67 78 |
.75c
.03c |
.14 .21 |
||||
| “The Family Bereavement Program” (CG) self-study program | Sandler et al. 2010 [35] IA |
140 families TG = 78 CG = 62 |
RCT Evaluation: 6 years post treatment |
DISC Compsite | Mental Disorder Externalizing Internalizing |
na na na |
na na na |
na na na |
na na na |
na na na |
na na na |
.28b
.02b .57b |
nab
.31b nab |
| 218 children TG = 116 CG = 102 |
RSE PERI BDI |
Self-esteem Demoralization Depression |
na na na |
na na na |
na na na |
na na na |
na na na |
na na na |
.01b
.03b .04b |
.40b
.42b .40b |
|||
Note: TG = Treatment Group; CG = Control Group. Effect size is presented in Cohen’s d and Common Language effect size (CL). The CL effect size indicates that after controlling for individual differences, the likelihood in percent that a person scores a different observed measurement for Mean 1 than for Mean 2. For categorical data ϕ is presented. Numerical data in the publications have been used or recalculated when possible, na = not available, e.g. numbers are missing or calculating not possible based on information in the publication
Abbreviations: AIS active inhibition scale, BID bellevue index of depression, CAS child assessment schedule, CBCL child behavior checklist, CDI children’s depression inventory, CMAS-R children’s manifest anxiety scale-revised, Comp composite scale, CRPBI children’s reports of parental behavior inventory, DISC the diagnostic interview schedule for children, EGI the extended grief inventory, GLESC general life events schedule for children, IGTS intrusive grief thoughts scale, MCPCS multidimensional measure of children’s perceptions of control scale, PERI psychiatric epidemiology research interview, POPM perception of parenting measure, PRS parent report scale, RSE Rosenberg self-esteem scale, SEI self-esteem inventory – short form, SPPC self perception profile for children, STAIC state-trait anxiety inventory for children, STAIY state-trait anxiety inventory for youth, TAS threat appraisal scale, TGIC traumatic grief inventory for children, TRIG Texas Revised Inventory of Grief (Present), UCLA PTSD University of California–Los Angeles Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Reaction Index for the DSM-IV for Children
aDue to data presented in article calculated as independent t-test, effect size ds
bCohen’s d and p-value as reported by the authors of the study in reference. Only findings with p ≤ .05 were reported
cDue to data presented in article calculated as independent t-test at each time-point (post, follow-up respectively), when controlled for no statistical significant difference in pre-rating
Large effects
There were two studies with strong evidence (from robust studies, see definition in Table 1, Grade criteria) that showed large effects between groups: for children’s traumatic grief [28]; and parent’s feelings of being supported [32].
Medium effects
Four studies showed medium effects between groups. Two studies with strong evidence showed medium effects for the parents: for parental warmth [32]; positive parenting [33]; parent’s mental health [33]; and for grief discussions in the family [32]. The following studies with fairly strong evidence showed medium effects: for children’s traumatic grief symptoms [31]; restlessness [40]; and children’s health [25]. One study with fairly strong evidence showed medium effects for parental depression [40].
Small effects
Some studies showed small effects between groups. The following studies with strong evidence showed small effects: for children’s symptoms of intrusive grief [34]; children’s PTSD symptoms [31]; self-esteem [26, 33, 35]; anxiety [26]; anxiety (girls) [37]; depression (girls) [37]; behaviour problems [26]; social competence [26]; externalizing [33, 35]; externalizing (girls) [37]; internalizing [33]; internalizing (girls) [37]; cortisol level before and after a conflict discussion task [29]; negative events [33]; negative thoughts [33]; control beliefs [33]; positive coping [33]; inhibition [33]; perceived parenting [26]. One study with strong evidence showed small effects for parent’s depression [35]; mental health [33]; demoralization [35]; and positive parenting [33]. The following studies with fairly strong evidence showed small effects: for children’s behaviour problems [25, 40]; sleep problems [40]; nail-biting [40]; talking about the dead parent [25, 40]; and school problems [25, 40].
No effects and negative effects
There were a few studies that failed to reveal any effect on measures at any of the post-test or subsequent follow-up test periods. With “No effect” we mean studies where the between group effect size were on Cohen’s d between 0.00 and 0.19 and the effect size calculated as Phi between 0.00 and 0.09. The following studies with strong evidence showed no effects on depression [26] and present grief [34]. One study did not show effects for the subgroup boys on the measures anxiety, depression, internalizing and externalizing [37].
Finally one study showed a small but negative effect for boys’ externalizing behaviour (−0.22), which means that the reduction of externalizing behaviour in boys 11 months post intervention was less in the intervention group than in the control group [37].
Discussion
The aims of this article were to systematically review empirical studies about effective methods of support for children when a parent or caregiver dies and secondly, to identify gaps in the research. Seventeen studies were included in the review. The included studies were mainly randomized controlled studies, with the exception of two studies, one of which was a quasi-experimental study and the other study employed a pre-post-test design. Thirteen studies provided strong evidence with regards to the quality grading criteria, three provided fairly strong evidence and one provided weaker evidence.
In this review we found large as well as moderate and small between group effects for children and their caregivers. There were effects on children’s grief symptoms, health, behaviour and self-esteem, as well as effects on parenting factors and caregiver’s mental health. There were effects from group interventions directed at children [28], family interventions [25, 29, 32–35, 37, 40], parental guidance [26] and camp activities for children [31].
There were studies that did not show effects on some measures, on depression, present grief, and boy’s anxiety, depression, internalization and externalization. The latter results indicate a need to pay attention to possible gender differences. However, it should also be noted that several of the studies in the review consisted of small numbers of participants, indicating that there is a risk that in some cases there might actually have been a difference between the intervention and control group, which may not have been detected due to the fact that samples were too small to find statistically significant differences when the effect sizes were small. It is also important to keep in mind that most of the included interventions were primary or secondary preventive in nature. That is, they sought to prevent the development of an illness or disease before it even occurred or lower the impact if indeed it already had occurred [57], and thus effect sizes could be expected to be small, but nevertheless remain important for a large group of children [58].
The overall results suggest that even relatively brief supportive interventions can prevent children from developing more severe problems after the loss of a parent [34, 35]. The randomized controlled studies of “The Family Bereavement Program” stand out among the included studies, as the intervention has been evaluated several times, with different outcomes and longitudinally (6 year follow-up period) [27, 29, 30, 34, 35, 41]. After the first included effect study that was published in 1992, the support program has been subsequently revised and refined. The program consists of a total of 14 sessions, including separate groups for caregivers, children and adolescents; joint activities for children and their caregivers; and individual family meetings [59]. The studies concerning “The Family Bereavement Program” from the year 2003 and onwards concern the same version of the support program whose effects have been evaluated from different perspectives. The evaluations of the program also include fidelity of program implementation, assessed as attendance and implementation of the items described in the manuals [33]. The results showed positive effects for both children and caregivers. Studies of the program indicated that some children and families may require more intensive interventions [35, 41] or additional support [38] as the intervention itself is brief.
The results of our review differ from previous reviews that have reported relatively small effect of supportive interventions for bereaved children [15–17]. One reason for the differing results may be that previous reviews often adopted a broader focus by including children who have lost other types of “loved ones”, for example a family member, grandparent, relative or friend [15–17], while this review is focused exclusively on parentally bereaved children. Another reason for the differing results may be that several studies included in previous reviews were excluded in this review for quality reasons, as in some studies the sample was too small for the results to be generalizable. A third reason for the differing results is that some studies of high scientific rigour were published after the previously published systematic reviews. The latest systematic review we found was published in 2010 [17], while eight out of 17 studies in this review were published during the period 2010–2015.
Implications for practice
The included studies in this review were published within several disciplines, namely psychology, social work, medicine, psychiatry, lending weight to the argument that the subject of support for parentally bereaved children is relevant for a range of different professional groups.
One conclusion from this review of interventions is that there were studies that have shown effects for children and their caregivers. The results indicate that supportive interventions can be directed exclusively to the children or to both the bereaved child and the child’s remaining parent or caregiver. Support for the children’s caregivers can strengthen their own health and their capacity to support their children. A supportive parenting is a protective resource for parentally bereaved children [60]. Previous research indicates that when the bereaved children’s caregivers are supported, they demonstrate an enhanced capacity to support their children [60–62].
At the same time, support also needs to be directed at the children. In the evaluation of a parental guidance program, the remaining parents expressed that they perceived a need for more support directed to their children [26]. In one of the included studies, both children and parents indicated that they wished to discuss grief-related experiences with other people who had similar experiences [32]. Being and connecting with other bereaved children can be helpful for children who attend a support group, as it can help them to feel less isolated and alone [55, 63, 64]. Simultaneous family sessions involving both children and the remaining parent may be an important component in a support program as such sessions are sometimes the first occasion that the parent and children have had the opportunity to sit down together and talk about the loss and their feelings about it [25]. Some children avoid talking about their problems or showing their feelings as they try to protect their remaining parent or other people around them. This can sometimes be misinterpreted as a sign that the child is not affected by the loss [65]. The included effect-evaluated interventions were not sufficient for all children. The majority of intervention programs were brief. Studies indicated that some children may need more intensive support or additional support [31, 35, 36, 38, 41]. Therefore, it is important to reassess children’s further needs for support at the end of an intervention [36].
Implications for research
Given that there are currently relatively few scientifically rigorous studies in this area, there is a clear need for further research about the effects of support interventions directed at parentally bereaved children. Indeed, there were only 17 studies that met the criteria for this review. All studies, with the exception of one [28], were comprised of studies about English language interventions that were evaluated in the USA or UK (see Table 4). It is evident that there is a need for more effect studies with longer follow-up, with the Family Bereavement Program being a notable exception, as children’s problems can appear later and it may also take time before changes in the participant families stabilize post intervention and have an effect for the children [33]. Furthermore, there is a need for studies with populations sufficiently large enough to make comparisons of the effects for various categories, so that the interventions can be modified to various children’s needs. Some studies for example, showed differences in the efficacy of interventions for children at different ages [35, 41], for girls and boys [26, 33, 35, 37], for mothers and fathers [26] and for children with different levels of problems at baseline [35, 41]. In the majority of included studies the sample were diverse in ethnicity, but did not analyse effects for different ethnic minority groups. The sample sizes of minority groups were too small to allow the testing of program effects for various groups [34]. In the studies, the most common deceased parent was the child’s father with the remaining caregiver the mother. This is consistent with mortality statistic rates as children under the age of 18 are more likely to experience the death of a father than the death of a mother [1].
This systematic review highlights that interventions evaluated with a focus on effects for children have almost exclusively been directed at school age children, while the bereavement research shows increased risks for the youngest children when one or both parents dies [4]. The younger children are especially vulnerable as they are totally dependent on their caregivers. In addition, they often find it more difficult to comprehend what has happened to their deceased parent and what this means [66]. Consequently, development of supportive interventions and evaluation of bereavement interventions for younger children is an important issue for further research. Involving younger children in evaluations of interventions may require innovative methods, where the children are given the opportunity to express themselves in a way that is adapted to their capacity and cognitive development. Such evaluations may also include qualitative interviews where the children can express themselves in their own words or through creative methods such as art or play [63, 67]. Further, children need to be enabled to participate in the research to develop knowledge about their experiences, to explore with children what they themselves perceive as helpful in the grieving process and what kinds of outcome measures are most important from their perspective. For example, few of the outcome measures in the included studies concerned children’s physical health and somatic symptoms, their situation in school and their peer relationships. It is also important that children have the opportunity to be involved in evaluations of support programs as parental reports have a tendency to underestimate children’s problems and report less symptomatology in their children than do the children themselves [68]. Qualitative data from evaluations could also be helpful to identify opportunities to improve current bereavement interventions.
Finally, studies of bereavement interventions for children are more generally focused on children that are living in a nuclear family, where one parent dies and the other parent is the child’s remaining caregiver. However, there are also children who have lived with a single parent who dies, and there are children who lose both their parents through death. These children have to change caregivers and residence. The death of a parent engenders secondary losses that occur as a result of the primary loss. When the child’s only parent or both parents die, the secondary losses are increased, in number and complexity [69]. Therefore, special attention is merited towards these groups of children. One explanation why these children are underrepresented in evaluation studies is that the largest proportion of children in the western world live together with both their parents. It is difficult to conduct evaluation studies with this vulnerable group of children.
Conclusion
The results of this systematic review of support interventions for parentally bereaved children indicate that relatively brief interventions may help prevent children from developing more severe problems, such as mental health problems and traumatic grief after the loss of a parent. Further research is required including how to best support younger bereaved children. There is also a need for more empirically rigorous studies in this area.
Acknowledgements
The review presented in this paper was undertaken by the Swedish Family Care Competence Centre, Linnaeus University, and commissioned and funded by the National Board of Health and Welfare Sweden as part of a major initiative to support health care regions in Sweden to implement the change in the Health Care Act. According to the Swedish Health Care Act (2010) health care professionals shall give special attention to children’s needs for information, advice and support when their parent or another adult with whom the child lives unexpectedly dies [70]. The act aims to highlight the needs of affected children and improve their situation in the health care system, which is in line with the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child [71].
We would like to thank Maja Fredriksson Kärrman, information specialist at the National Board of Health and Welfare Sweden (NBHWS), who conducted the initial literature search and Ann-Louise Larsson, librarian at Linnaeus University, for help with the updated literature search.
Funding
This review was commissioned and funded by the National Board of Health and Welfare Sweden.
Availability of data and materials
The data analysed in the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AIS
Active inhibition scale
- BID
Bellevue index of depression
- CAS
Child assessment schedule
- CBCL
Child behavior checklist
- CDI
Children’s depression inventory
- CMAS-R
Children’s manifest anxiety scale-revised
- Comp
Composite scale
- CRPBI
Children’s reports of parental behavior inventory
- DISC
The diagnostic interview schedule for children
- EGI
The extended grief inventory
- GLESC
General life events schedule for children
- IGTS
Intrusive grief thoughts scale
- MCPCS
Multidimensional measure of children’s perceptions of control scale
- PERI
Psychiatric epidemiology research interview
- POPM
Perception of parenting measure
- PRS
Parent report scale
- RSE
Rosenberg self-esteem scale
- SEI
Self-esteem inventory – short form
- SPPC
Self perception profile for children
- STAIC
State-trait anxiety inventory for children
- STAIY
State-trait anxiety inventory for youth
- TAS
Threat appraisal scale
- TGIC
Traumatic grief inventory for children
- TRIG
Texas revised inventory of grief (Present)
- UCLA PTSD
University of California–Los Angeles post-traumatic stress disorder reaction index for the DSM-IV for Children
Authors’ contributions
AB and EH were responsible for the design of the study and the review process. UA contributed with the quantitative analyses of the included studies. AB was responsible for drafting the initial manuscript. UA and EH reviewed and provided regular feedback on the manuscript. All authors contributed to, read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Ann-Sofie Bergman, Email: ann-sofie.bergman@lnu.se.
Ulf Axberg, Email: ulf.axberg@psy.gu.se.
Elizabeth Hanson, Email: elizabeth.hanson@anhoriga.se.
References
- 1.Lutzke J, Ayers T, Sandler I, Barr A. Risks and interventions for the parentally bereaved child. In: Wolchik S, Sandler I, editors. Handbook of Children’s coping. Issues in clinical child psychology. US: Springer; 1997. pp. 215–243. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Worden JW, Silverman PR. Parental death and the adjustment of school-age children. Omega J Death Dying. 1996;33(2):91–102. doi: 10.2190/P77L-F6F6-5W06-NHBX. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Christ GH. Children bereaved by the death of a parent. In: Corr CA, Balk DE, editors. Children's encounters with death, bereavement and coping. New York: Springer Publishing Company; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nickerson A, Bryant RA, Aderka IM, Hinton DE, Hofmann SG. The impacts of parental loss and adverse parenting on mental health: findings from the National Comorbidity Survey-Replication. Psychol Trauma Us. 2013;5(2):119–127. doi: 10.1037/a0025695. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gray LB, Weller RA, Fristad M, Weller EB. Depression in children and adolescents two months after the death of a parent. J Affect Disord. 2011;135(1–3):277–283. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Luecken LJ, Kraft A, Appelhans BM, Enders C. Emotional and cardiovascular sensitization to daily stress following childhood parental loss. Dev Psychol. 2009;45(1):296–302. doi: 10.1037/a0013888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Luecken LJ, Roubinov DS. Pathways to lifespan health following childhood parental death. Soc Personal Psychol Compass. 2012;6(3):243–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-9004.2011.00422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rostila M, Saarela JM. Time does not heal all wounds: mortality following the death of a parent. J Marriage Fam. 2011;73(1):236–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-3737.2010.00801.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li J, Vestergaard M, Cnattingius S, Gissler M, Bech BH, Obel C, et al. Mortality after parental death in childhood: a Nationwide cohort study from three Nordic countries. PLoS Med. 2014;11(7) doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Guldin MB, Li J, Pedersen HS, Obel C, Agerbo E, Gissler M, et al. Incidence of suicide among persons who had a parent who died during their childhood: a population-based cohort study. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72(12):1227–1234. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.2094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Brent DA, Melhem NM, Masten AS, Porta G, Payne MW. Longitudinal effects of parental bereavement on adolescent developmental competence. J Clin Child Adolesc. 2012;41(6):778–791. doi: 10.1080/15374416.2012.717871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kwok OM, Haine RA, Sandler IN, Ayers TS, Wolchik SA, Tein JY. Positive parenting as a mediator of the relations between parental psychological distress and mental health problems of parentally bereaved children. J Clin Child Adolesc. 2005;34(2):260–271. doi: 10.1207/s15374424jccp3402_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cohen JA, Mannarino AP, Knudsen K. Treating childhood traumatic grief: a pilot study. J Am Acad Child Psy. 2004;43(10):1225–1233. doi: 10.1097/01.chi.0000135620.15522.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Spuij M, Reitz E, Prinzie P, Stikkelbroek Y, de Roos C, Boelen PA. Distinctiveness of symptoms of prolonged grief, depression, and post-traumatic stress in bereaved children and adolescents. Eur Child Adoles Psy. 2012;21(12):673–679. doi: 10.1007/s00787-012-0307-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Curtis K, Newman T. Do community-based support services benefit bereaved children? A review of empirical evidence. Child Care Hlth Dev. 2001;27(6):487–495. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2214.2001.00232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Currier JM, Holland JM, Neimeyer RA. The effectiveness of bereavement interventions with children: a meta-analytic review of controlled outcome research. J Clin Child Adolesc. 2007;36(2):253–259. doi: 10.1080/15374410701279669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rosner R, Kruse J, Hagl M. A meta-analysis of interventions for bereaved children and adolescents. Death Stud. 2010;34(2):99–136. doi: 10.1080/07481180903492422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Harding R, Higginson IJ. What is the best way to help caregivers in cancer and palliative care? A systematic literature review of interventions and their effectiveness. Palliative Med. 2003;17(1):63–74. doi: 10.1191/0269216303pm667oa. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hudson PL, Remedios C, Thomas K. A systematic review of psychosocial interventions for family carers of palliative care patients. BMC Palliat Care. 2010;9:17. doi: 10.1186/1472-684X-9-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Group CGO . Improving outcomes in breast cancer - the research evidence. Leeds: NHS Executive; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lakens D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: a practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs. Front Psychol. 2013;4 doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 22.McGraw KO, Wong SP. A common language effect size statistic. Psychol Bull. 1992;111(2):361–365. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.111.2.361. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Morris SB. Estimating effect sizes from pretest-posttest-control group designs. Organ Res Methods. 2008;11(2):364–386. doi: 10.1177/1094428106291059. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fritz CO, Morris PE, Richler JJ. Effect size estimates: current use, calculations, and interpretation. J Exp Psychol Gen. 2012;141(1):2–18. doi: 10.1037/a0024338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Black D, Urbanowicz MA. Family intervention with bereaved children. J Child Psychol Psyc. 1987;28(3):467–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1987.tb01767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Christ GH, Raveis VH, Seigel K, Karus D, Christ AE. Evaluation of a preventive intervention for bereaved children. J Soc Work End Life Palliat Care. 2005;1(3):57–81. doi: 10.1300/J457v01n03_05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hagan MJ, Tein JY, Sandler IN, Wolchik SA, Ayers TS, Luecken LJ. Strengthening effective parenting practices over the long term: effects of a preventive intervention for parentally bereaved families. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2012;41(2):177–188. doi: 10.1080/15374416.2012.651996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kalantari M, Yule W, Dyregrov A, Neshatdoost H, Ahmadi SJ. Efficacy of writing for recovery on traumatic grief symptoms of Afghani refugee bereaved adolescents: a randomized control trial. Omega J Death Dying. 2012;65(2):139–150. doi: 10.2190/OM.65.2.d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Luecken LJ, Hagan MJ, Sandler IN, Tein JY, Ayers TS, Wolchik SA. Cortisol levels six-years after participation in the family bereavement program. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2010;35(5):785–789. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Luecken LJ, Hagan MJ, Sandler IN, Tein JY, Ayers TS, Wolchik SA. Longitudinal mediators of a randomized prevention program effect on Cortisol for youth from parentally bereaved families. Prev Sci. 2014;15(2):224–232. doi: 10.1007/s11121-013-0385-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.McClatchey IS, Vonk ME, Palardy G. Efficacy of a camp-based intervention for childhood traumatic grief. Res Social Work Prac. 2009;19(1):19–30. doi: 10.1177/1049731508314276. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sandler IN, West SG, Baca L, Pillow DR, Gersten JC, Rogosch F, et al. Linking empirically based theory and evaluation: the family bereavement program. Am J Community Psychol. 1992;20(4):491–521. doi: 10.1007/BF00937756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sandler IN, Ayers TS, Wolchik SA, Tein JY, Kwok OM, Haine RA, et al. The family bereavement program: efficacy evaluation of a theory-based prevention program for parentally bereaved children and adolescents. J Consult Clin Psych. 2003;71(3):587–600. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.71.3.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sandler IN, Ma Y, Tein JY, Ayers TS, Wolchik S, Kennedy C, et al. Long-term effects of the family bereavement program on multiple indicators of grief in parentally bereaved children and adolescents. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2010;78(2):131–143. doi: 10.1037/a0018393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sandler I, Ayers TS, Tein JY, Wolchik S, Millsap R, Khoo ST, et al. Six-year follow-up of a preventive intervention for parentally bereaved youths a randomized controlled trial. Arch Pediat Adol Med. 2010;164(10):907–914. doi: 10.1001/archpediatrics.2010.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Schilling RF, Koh N, Abramovitz R, Gilbert L. Bereavement groups for Inner-City children. Res Social Work Prac. 1992;2(3):405–419. doi: 10.1177/104973159200200315. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schmiege SJ, Khoo ST, Sandler IN, Ayers TS, Wolchik SA. Symptoms of internalizing and externalizing problems - modeling recovery curves after the death of a parent. Am J Prev Med. 2006;31(6):S152–SS60. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2006.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Schoenfelder EN, Sandler IN, Millsap RE, Wolchik SA, Berkel C, Ayers TS. Caregiver responsiveness to the family bereavement program: what predicts responsiveness? What does responsiveness predict? Prev Sci. 2013;14(6):545–556. doi: 10.1007/s11121-012-0337-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tein JY, Sandler IN, Ayers TS, Wolchik SA. Mediation of the effects of the family bereavement program on mental health problems of bereaved children and adolescents. Prev Sci. 2006;7(2):179–195. doi: 10.1007/s11121-006-0037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Black B, Urbanowicz M. Bereaved children - family intervention. In: Stevenson J, editor. Recent research in developmental psychopathology: a book supplement to the journal of child psychology and psychiatry. 1985. pp. 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schoenfelder EN, Tein JY, Wolchik S, Sandler IN. Effects of the family bereavement program on academic outcomes, educational expectations and job aspirations 6 years later: the mediating role of parenting and youth mental health problems. J Abnorm Child Psych. 2015;43(2):229–241. doi: 10.1007/s10802-014-9905-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA. Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms and profiles. Burlington: University of Vermont, Research Center Children, Youth & Families; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kovacs M. Children's depression inventory: CDI manual. North Tonawanda: Multi-Health Systems; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Reynolds CR, Richmond BO. What I think and feel - revised measure of Childrens manifest anxiety. J Abnorm Child Psych. 1978;6(2):271–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00919131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Prigerson HG, Vanderwerker LC, Maciejewski PK. A case for inclusion of prolonged grief disorder in DSM-V. In: Stroebe M, Hansson RO, Scut H, Stroebe W, Van den Blink E, editors. Handbook of bereavement research and practice: advances in theory and intervention. Washington: American Psychological Association; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Dyregrov A, Yule W, Smith P, Perrin S, Gjestad R, Prigerson H. Traumatic grief inventory for children (TGIC) Norway: Children and War Foundation; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Faschingbauer TR. Texas inventory of grief-revised manual. Houston: Honeycomb; 1981. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Schaefer ES. Childrens reports of parental behavior - an inventory. Child Dev. 1965;36(2):413–424. doi: 10.2307/1126465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK. Manual for the Beck depression inventory. San Antonio: The Psychological Corporation; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Dohrenwend BP, Shrout PE, Egri G, Mendelsohn FS. Nonspecific psychological distress and other dimensions of psychopathology - measures for use in the general-population. Arch Gen Psychiat. 1980;37(11):1229–1236. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1980.01780240027003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Layne CM, Savjak N, Salzman WR, Pynoos RS. Extended grief inventory. Los Angeles: University of California at Los Angeles and Brigham Young University; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Family bereavement program documentation . Program for prevention research. Tempte: Arizona State University; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Harter S. The perceived competence scale for children. Child Dev. 1982;53(1):87–97. doi: 10.2307/1129640. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hazzard A, Christensen A, Margolin G. Children's perception of parental behaviors. J Abnorm Clin Psychol. 1983;11(1):49–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00912177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.McClatchey IS, Wimmer JS. Healing components of a bereavement camp: children and adolescents give voice to their experiences. Omega J Death Dying. 2012;65(1):11–32. doi: 10.2190/OM.65.1.b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Weersing VR. Benchmarking the effectiveness of psychotherapy: program evaluation as a component of evidence-based practice. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2005;44(10):1058–1062. doi: 10.1097/01.chi.0000172682.71384.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Mrazek PB, Haggerty RJ, Institute of Medicine (U.S.). Committee on Prevention of Mental Disorders., United States. Congress . Reducing risks for mental disorders : frontiers for preventive intervention research. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press; 1994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.McCartney K, Rosenthal R. Effect size, practical importance, and social policy for children. Child Dev. 2000;71(1):173–180. doi: 10.1111/1467-8624.00131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ayers TS, Wolchik SA, Sandler IN, Twohey JL, Weyer JL, Padgett-Jones S, et al. The family bereavement program: description of a theory-based prevention program for parentally-bereaved children and adolescents. Omega (Westport) 2013;68(4):293–314. doi: 10.2190/OM.68.4.a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Haine RA, Wolchik SA, Sandler IN, Millsap RE, Ayers TS. Positive parenting as a protective resource for parentally bereaved children. Death Stud. 2006;30(1):1–28. doi: 10.1080/07481180500348639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Biank NM, Werner-Lin A. Growing up with grief: revisiting the death of a parent over the life course. Omega J Death Dying. 2011;63(3):271–290. doi: 10.2190/OM.63.3.e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Lin KK, Sandler IN, Ayers TS, Wolchik SA, Luecken LJ. Resilience in parentally bereaved children and adolescents seeking preventive services. J Clin Child Adolesc. 2004;33(4):673–683. doi: 10.1207/s15374424jccp3304_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rolls L, Payne SA. Children and young people's experience of UK childhood bereavement services. Mortality. 2007;12(3):281–303. doi: 10.1080/13576270701430585. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Braiden HJ, McCann M, Barry H, Lindsay C. Piloting a therapeutic residential for children, young people and families bereaved through suicide in Northern Ireland. Child Care Pract. 2009;15(2):81–93. doi: 10.1080/13575270802685344. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Chalmers A. Clinical practice: helping bereaved children and parents. J Fam Health Care. 2006;16(4):115–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Christ GH. Impact of development on children's mourning. Cancer Pract. 2000;8(2):72–81. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-5394.2000.82005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Walker A. Ethics, research, and dying or bereaved children. In: Corr CA, Balk DE, editors. Children's encounters with death, bereavement and coping. New York: Springer Pub. Co.; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Dowdney L. Annotation: childhood bereavement following parental death. J Child Psychol Psyc. 2000;41(7):819–830. doi: 10.1111/1469-7610.00670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Mahon MM. Secondary losses in bereaved children when both parents have died: a case study. Omega J Death Dying. 1999;39(4):297–314. doi: 10.2190/PQQV-VJJE-PU56-LV26. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.The Swedish Health Care Act . SFS. 1982. p. 763. [Google Scholar]
- 71.The UN Convention on the Rights of the Child. https://www.unicef.org/crc/.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data analysed in the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.


