Abstract
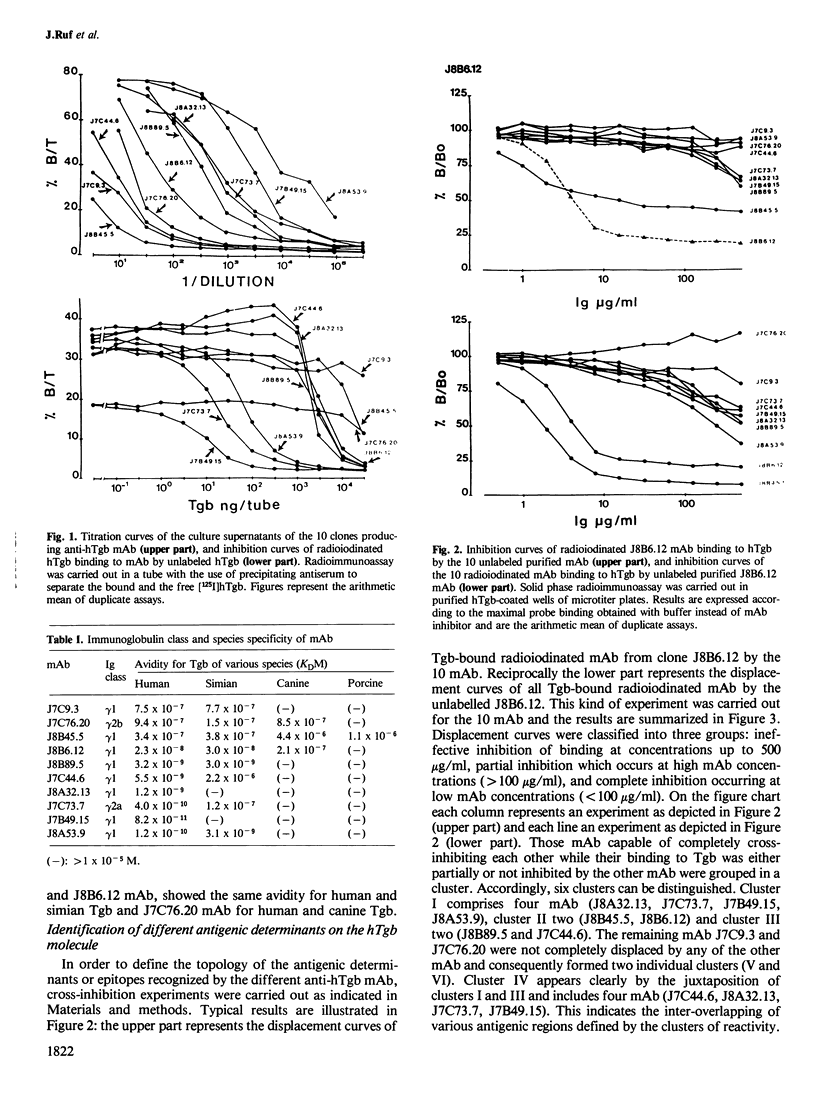
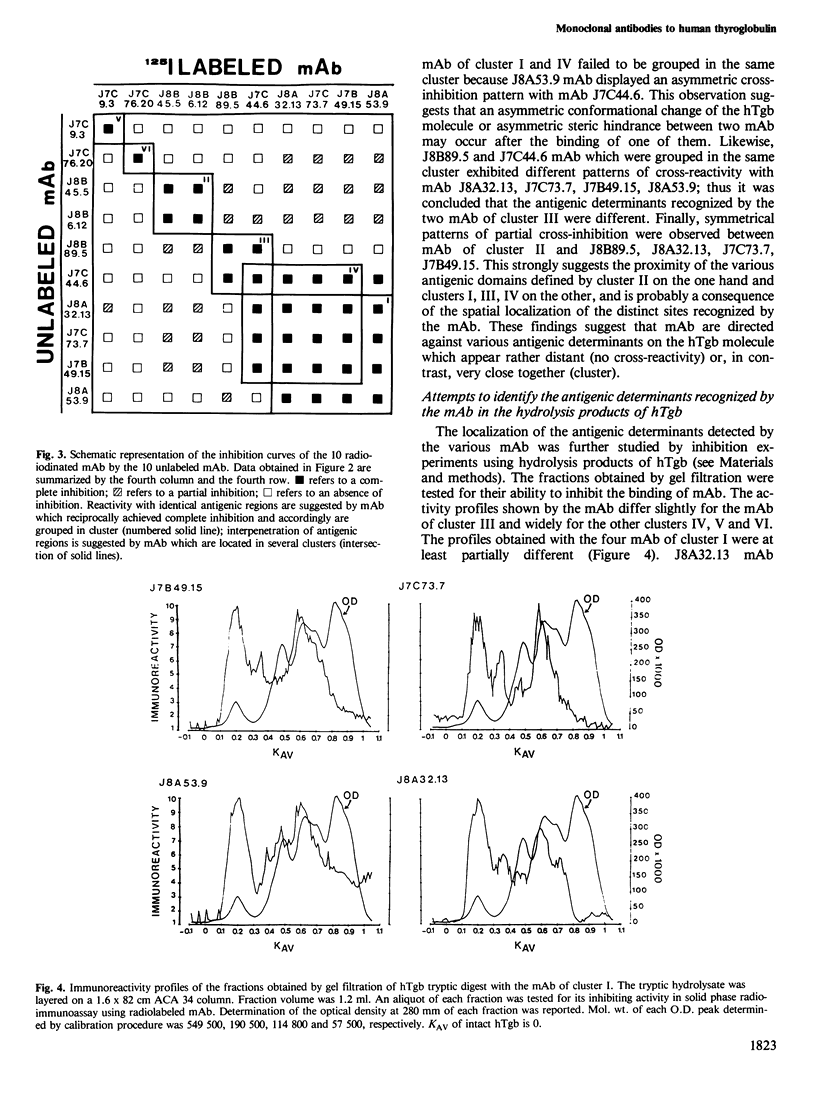
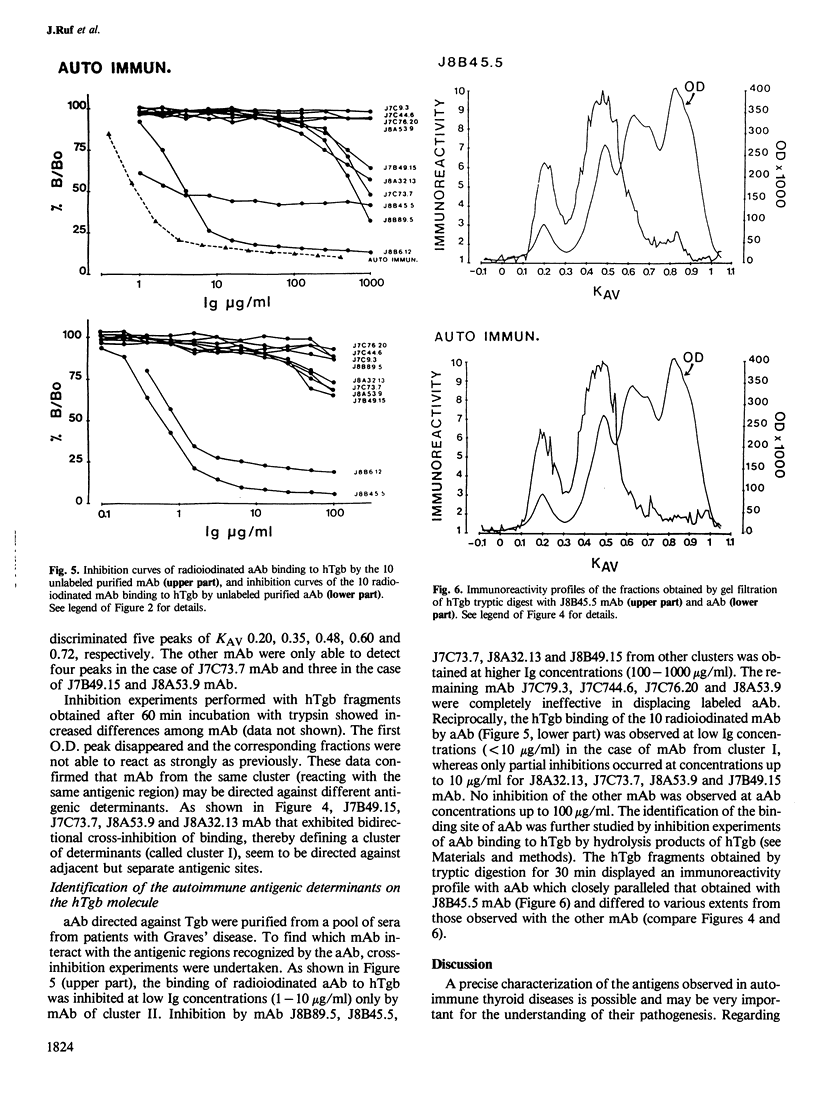
Ten monoclonal antibodies (mAb) directed against human thyroglobulin (hTgb) were produced, purified and characterized. The mAb avidity for hTgb ranged from 10(-10) to 10(-6) M. The species specificity of the mAb was as follows: eight mAb reacted with monkey Tgb, three with dog Tgb and one with pig Tgb; none with bovine and ovine Tgb. The binding of mAb to hTgb was not significantly inhibited in the presence of Tgb carbohydrate moieties, tyrosine, iodotyrosines and iodothyronines. The topology of the antigenic determinants recognized by the 10 mAb on hTgb was explored by inhibition of Tgb binding of radiolabeled mAb by the other antibodies. Six distinct clusters of reactivity were described. Localization of the antigenic determinants recognized by mAb on hTgb was attempted using tryptic fragments of hTgb to inhibit the binding of mAb to hTgb. The inhibitory effect of hydrolysis products was different for each mAb but exhibited partial analogies between mAb of the same cluster of reactivity. Anti-hTgb autoimmune antibodies (aAb) purified from sera of Graves patients cross-reacted essentially with mAb of one out of the six clusters. These results demonstrate that the large number of antigenic determinants presented by the hTgb are not disseminated on the molecule but are clustered in antigenic regions. Furthermore, from the six antigenic regions evidenced in this paper, only one is involved in autoimmune antibody production in Grave's disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHEFTEL C., BOUCHILLOUX S., LISSITZKY S. GLYCOPEPTIDES ISSUS DE LA THYROGLOBULINE. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1964 Aug 17;259:1458–1460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carayon P., Guibout M., Lissitzky S. The interaction of radioiodinated thyrotropin with human plasma membranes from normal and diseased thyroid glands. Relation of thyrotropin binding to adenylate cyclase activity. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 1979;40(3):211–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekholm R., Engström G., Ericson L. E., Melander A. Exocytosis of protein into the thyroid follicle lumen: an early effect of TSH. Endocrinology. 1975 Aug;97(2):337–346. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-2-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissitzky S. Biosynthèse et sécrétion de la thyroglobuline. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 1981 Oct-Nov;42(4-5):363–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriq C., Rolland M., Lissitzky S. Polypeptide chains of 19-S thyroglobulin from several mammalian species and of porcine 27-S iodoprotein. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep 15;79(1):143–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye L., Pontes de Carvalho L. C., Roitt I. M. Restrictions in the response to autologous thyroglobulin in the human. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Aug;41(2):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacini F., Pinchera A., Giani C., Grasso L., Doveri F., Baschieri L. Serum thyroglobulin in thyroid carcinoma and other thyroid disorders. J Endocrinol Invest. 1980 Jul-Sep;3(3):283–292. doi: 10.1007/BF03348277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekonen F., Weintraub B. D. Salt-induced exposure of high affinity thyrotropin receptors on human and porcine thyroid membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8121–8127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres M., Devaux C., Dosseto M., Marchetto S. Clonal analysis of B- and T-cell responses to Ia antigens. I. Topology of epitope regions on I-Ak and I-Ek molecules analyzed with 35 monoclonal alloantibodies. Immunogenetics. 1981 Dec;14(6):481–495. doi: 10.1007/BF00350120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres M., Ju S. T., Waltenbaugh C., Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B., Germain R. N. Fine specificity of antibodies to poly(Glu60Ala30Tyr10) produced by hybrid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2425–2429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROITT I. M., CAMPBELL P. N., DONIACH D. The nature of the thyroid auto-antibodies present in patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis (lymphadenoid goitre). Biochem J. 1958 Jun;69(2):248–256. doi: 10.1042/bj0690248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruf J., Tonnelle C., Rocca-Serra J., Moinier D., Pierres M., Ju S. T., Dorf M. E., Thèze J., Fougereau M. Structural bases for public idiotypic specificities of monoclonal antibodies directed against poly(Glu60Ala30Tyr10) and poly(Glu60Ala40) random copolymers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3040–3044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider A. B., Pervos R. Radioimmunoassay of human thyroglobulin: effect of antithyroglobulin autoantibodies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Jul;47(1):126–137. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-1-126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


