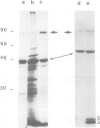
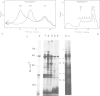
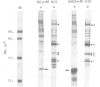
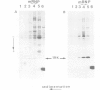
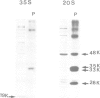
Abstract
Two types of in vivo untranslated 'free' mRNA-protein particles (mRNP) were isolated from duck erythroblast cytoplasm and characterised. Both types, namely the highly purified globin mRNA-specific '20S' mRNP and the '35S' mRNP containing a heterogenous non-globin mRNA population, are not translatable in rabbit reticulocyte lysates, but yield active mRNA upon deproteinisation. In vivo, 90% of globin mRNA is translated, but the majority of mRNA types are found in the inactive mRNP fraction, including fully repressed mRNA species. Searching for the factors controlling differential mRNA repression, we characterised and compared the protein composition of globin and '35S' mRNP using two dimensional gel electrophoresis, in vivo labelling with [35S]methionine and in vivo phosphorylation. The major proteins ubiquitously bound to globin or any other mRNA in the polyribosomes (e.g., the 73 K mol. wt. poly(A) binding protein) were not detected in purified inactive mRNP. In the latter some polypeptides appear to be associated with only one of the two inactive mRNA types while some others are common to both mRNPs. Furthermore, different rates of synthesis and phosphorylation characterize the protein populations of the two types of repressed mRNP. The specificity in composition and metabolism of the populations of polypeptides associated with different subpopulations of inactive cytoplasmic mRNA, as shown here, argues in favour of a role of mRNP proteins in mRNA recognition and selective translational repression, possibly in association with the ScRNA previously found as components of the free mRNP and able to inhibit protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bienz M., Gurdon J. B. The heat-shock response in Xenopus oocytes is controlled at the translational level. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):811–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
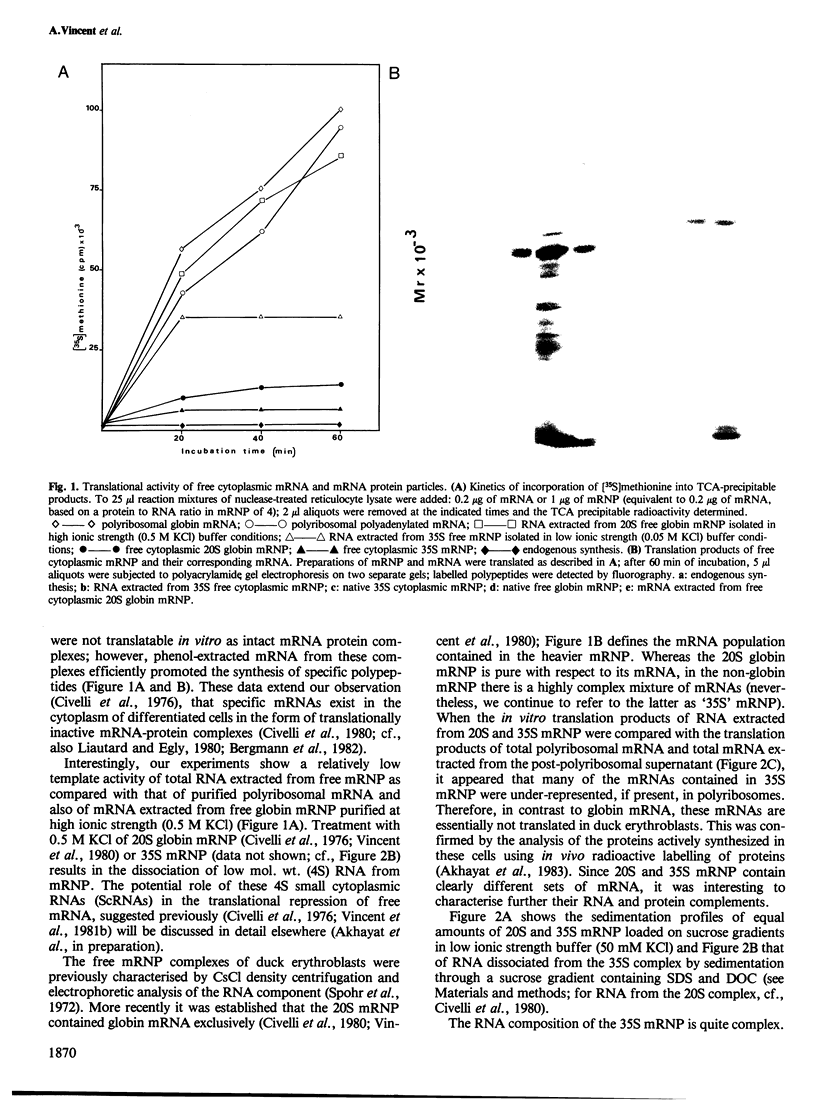
- Civelli O., Vincent A., Buri J. F., Scherrer K. Evidence for a translational inhibitor linked to globin mRNA in untranslated free cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 15;72(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80815-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civelli O., Vincent A., Maundrell K., Buri J. F., Scherrer K. The translational repression of globin mRNA in free cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):577–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon A. M., Jinks C. S., Yamamoto M., Nomura M. Expression of ribosomal protein genes cloned in a hybrid plasmid in Escherichia coli: gene dosage effects on synthesis of ribosomal proteins and ribosomal protein messenger ribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):383–396. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.383-396.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. R., Ben-Ze'av A., Benecke B. J., Penman S. Altered translatability of messenger RNA from suspended anchorage-dependent fibroblasts: reversal upon cell attachment to a surface. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favre A., Morel C., Scherrer K. The secondary structure and poly(A) content of globin messenger RNA as a pure RNA and in polyribosome-derived ribonucleoprotein complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):147–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gander E. S., Stewart A. G., Morel C. M., Scherrer K. Isolation and characterization of ribosome-free cytoplasmic messenger-ribonucleoprotein complexes from avian erythroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Oct 18;38(3):443–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoghegan T., Cereghini S., Brawerman G. Inactive mRNA-protein complexes from mouse sarcoma-180 ascites cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5587–5591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Meyuhas O., Perry R. P., Johnson L. F. Regulation of ribosomal protein mRNA content and translation in growth-stimulated mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):685–693. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., O'Farrell P. Z., Russel M. Regulation of gene 32 expression during bacteriophage T4 infection of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7251–7262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg S., Scherrer K. The specificity of interaction between mRNP proteins and globin mRNA in polyribosomal and cytoplasmic free mRNP. FEBS Lett. 1981 Oct 26;133(2):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80508-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heindell H. C., Liu A., Paddock G. V., Studnicka G. M., Salser W. A. The primary sequence of rabbit alpha-globin mRNA. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
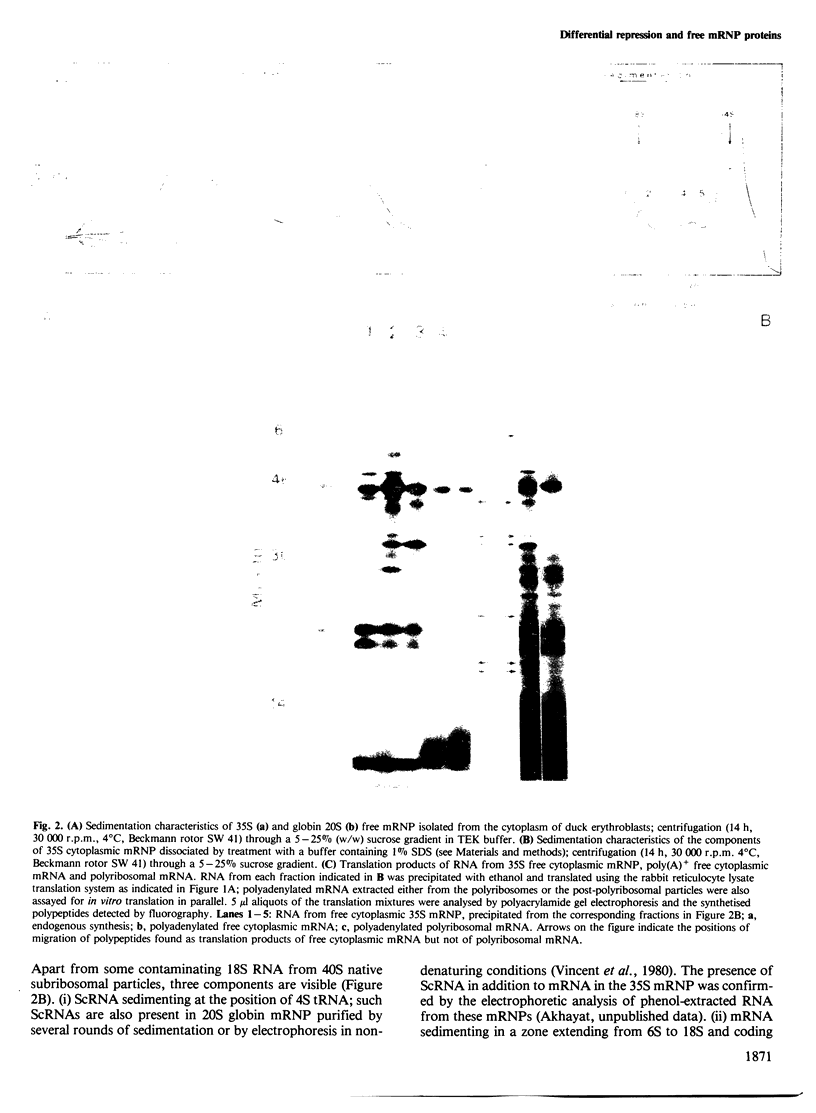
- Imaizumi-Scherrer M. T., Maundrell K., Civelli O., Scherrer K. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation in duck erythroblasts. Dev Biol. 1982 Sep;93(1):126–138. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liautard J. P., Egly J. M. In vitro translation studies of the cytoplasmic nonpolysomal particles containing messenger RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1793–1804. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liautard J. P., Setyono B., Spindler E., Köhler K. Comparison of proteins bound to the different functional classes of messenger RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 2;425(4):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Secondary structure of bacteriophage f2 ribonucleic acid and the initiation of in vitro protein biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):689–702. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Valbuena O., Perry R. P. Isolation, purification, and properties of mouse heavy-chain immunoglobulin mRNAs. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1723–1733. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K., Imaizumi-Scherrer M. T., Maxwell E. S., Civelli O., Scherrer K. Messenger RNA for the 73,000-dalton poly(A)-binding protein occurs as translationally repressed mRNP in duck reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1387–1390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K., Scherrer K. Characterization of pre-messenger-RNA-containing nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles from avian erythroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(2):225–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel C., Gander E. S., Herzberg M., Dubochet J., Scherrer K. The duck-globin messenger-ribonucleoprotein complex. Resistance to high ionic strength, particle gel electrophoresis, composition and visualisation by dark-field electron microscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 16;36(2):455–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preobrazhensky A. A., Spirin A. S. Informosomes and their protein components: the present state of knowledge. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1978;21:1–38. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff R. A., Brandis J. W., Huffman C. J., Koch A. L., Leister D. E. Protein synthesis as an early response to fertilization of the sea urchin egg: a model. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal E. T., Hunt T., Ruderman J. V. Selective translation of mRNA controls the pattern of protein synthesis during early development of the surf clam, Spisula solidissima. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90635-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Mukherjee A. K., Guha C. A ribonuclease-resistant cytoplasmic 10 S ribonucleoprotein of chick embryonic muscle. A potent inhibitor of cell-free protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5077–5086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer K. Control of gene expression in animal cells: the cascade regulation hypothesis revisited. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974 Jun;44(1):169–219. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3246-6_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair G. D., Dixon G. H. Purification and characterization of cytoplasmic protamine messenger ribonucleoprotein particles from rainbow trout testis cells. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 13;21(8):1869–1877. doi: 10.1021/bi00537a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spohr G., Kayibanda B., Scherrer K. Polyribosome-bound and free-cytoplasmic-hemoglobin-messenger RNA in differentiating avian erythroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Nov 21;31(1):194–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standart N., Vincent A., Scherrer K. The polyribosomal poly(A)-binding protein is highly conserved in vertebrate species. Comparison in duck, mouse and rabbit. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 30;135(1):56–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80942-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Thomas G., Luther H. Transcriptional and translational control of cytoplasmic proteins after serum stimulation of quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5712–5716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Civelli O., Buri J. F., Scherrer K. Correlation of specific coding sequences with specific proteins associated in untranslated cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes of duck erythroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1977 May 15;77(2):281–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Civelli O., Maundrell K., Scherrer K. Identification and characterization of the translationally repressed cytoplasmic globin messenger-ribonucleoprotein particles from duck erythroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;112(3):617–633. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Goldenberg S., Scherrer K. Comparisons of proteins associated with duck-globin mRNA and its polyadenylated segment in polyribosomal and repressed free messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Feb;114(2):179–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Goldenberg S., Standart N., Civelli O., Imaizumi-Scherrer T., Maundrell K., Scherrer K. Potential role of mRNP proteins in cytoplasmic control of gene expression in duck erythroblasts. Mol Biol Rep. 1981 May 22;7(1-3):71–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00778736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Scherrer K. A rapid and sensitive method for detection of proteins in polyacrylamide SDS gels: staining with ethidium bromide. Mol Biol Rep. 1979 Dec 31;5(4):209–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00782890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumbé A., Stähli C., Trachsel H. Association of a Mr 50,000 cap-binding protein with the cytoskeleton in baby hamster kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2927–2931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]