Abstract
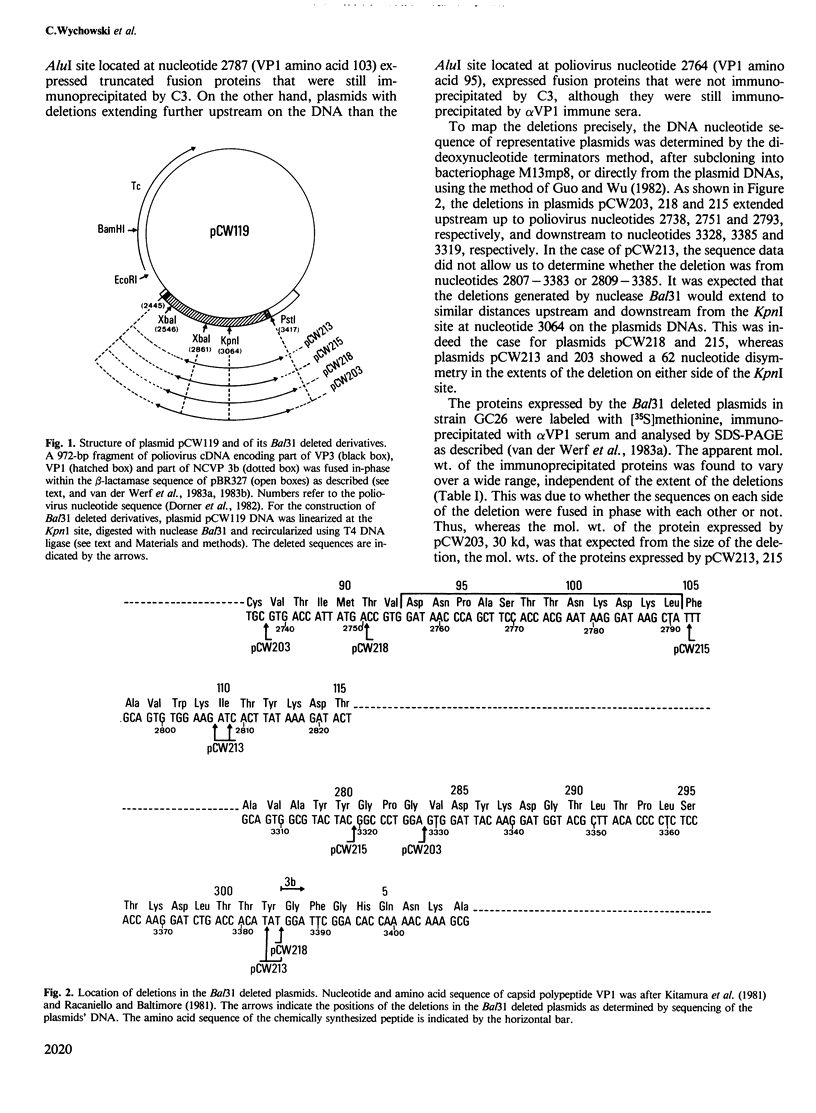
Using nuclease Bal31, deletions were generated within the poliovirus type 1 cDNA sequences, coding for capsid polypeptide VP1, within plasmid pCW119. The fusion proteins expressed in Escherichia coli by the deleted plasmids reacted with rabbit immune sera directed against poliovirus capsid polypeptide VP1 (alpha VP1 antibodies). They also reacted with a poliovirus type 1 neutralizing monoclonal antibody C3, but reactivity was lost when the deletion extended up to VP1 amino acids 90-104. Computer analysis of the protein revealed a high local density of hydrophilic amino acid residues in the region of VP1 amino acids 93-103. A peptide representing the sequence of this region was chemically synthesized. Once coupled to keyhole limpet hemocyanin, this peptide was specifically immunoprecipitated by C3 antibodies. The peptide also inhibited the neutralization of poliovirus type 1 by C3 antibodies. We thus conclude that the neutralization epitope recognized by C3 is located within the region of amino acids 93-104 of capsid polypeptide VP1.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Audibert F., Jolivet M., Chedid L., Alouf J. E., Boquet P., Rivaille P., Siffert O. Active antitoxic immunization by a diphtheria toxin synthetic oligopeptide. Nature. 1981 Feb 12;289(5798):593–594. doi: 10.1038/289593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beneke T. W., Habermehl K. O., Diefenthal W., Buchholz M. Iodination of poliovirus capsid proteins. J Gen Virol. 1977 Feb;34(2):387–390. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-2-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittle J. L., Houghten R. A., Alexander H., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Protection against foot-and-mouth disease by immunization with a chemically synthesized peptide predicted from the viral nucleotide sequence. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):30–33. doi: 10.1038/298030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondel B., Akacem O., Crainic R., Couillin P., Horodniceanu F. Detection by monoclonal antibodies of an antigenic determinant critical for poliovirus neutralization present on VP1 and on heat-inactivated virions. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):707–710. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondel B., Crainic R. A technique to detect the reaction between poliovirus structural polypeptides and neutralizing anti-polio IgG. Dev Biol Stand. 1981;47:335–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondel B., Crainic R., Horodniceanu F. Le polypeptide structural VP1 du poliovirus type 1 induit des anticorps neutralisants. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1982 Jan 11;294(2):91–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet P., Alouf J. E., Duflot E., Siffert O., Rivaille P. Characteristics of guinea-pig immune sera elicited by a synthetic diphtheria toxin oligopeptide. Mol Immunol. 1982 Dec;19(12):1541–1549. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Baltimore D. Isolated poliovirus capsid protein VP1 induces a neutralizing response in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7518–7521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dernick R. Antigenic structure of poliovirus. Dev Biol Stand. 1981;47:319–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Dorner L. F., Larsen G. R., Wimmer E., Anderson C. W. Identification of the initiation site of poliovirus polyprotein synthesis. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1017-1028.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Lewis A. J., Larsen G. R., Wimmer E. Poliovirus neutralization epitopes: analysis and localization with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):997–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.997-1005.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. H., Wu R. New rapid methods for DNA sequencing based in exonuclease III digestion followed by repair synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2065–2084. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icenogle J., Gilbert S. F., Grieves J., Anderegg J., Rueckert R. A neutralizing monoclonal antibody against poliovirus and its reaction with related antigens. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langbeheim H., Arnon R., Sela M. Antiviral effect on MS-2 coliphage obtained with a synthetic antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4636–4640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A. Tapping the immunological repertoire to produce antibodies of predetermined specificity. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):593–596. doi: 10.1038/299592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Butterworth B. E. Investigation of the structure of polio- and human rhinovirions through the use of selective chemical reactivity. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makoff A. J., Paynter C. A., Rowlands D. J., Boothroyd J. C. Comparison of the amino acid sequence of the major immunogen from three serotypes of foot and mouth disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8285–8295. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marglin A., Merrifield R. B. Chemical synthesis of peptides and proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:841–866. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.004205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B., Hans Hopschneider P. Filamentous coliphage M13 as a cloning vehicle: insertion of a HindII fragment of the lac regulatory region in M13 replicative form in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3642–3646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Bootman J., Evans D. M., Ferguson M., Reeve P., Spitz M., Stanway G., Cann A. J., Hauptmann R. Location and primary structure of a major antigenic site for poliovirus neutralization. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):674–679. doi: 10.1038/301674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Omata T., Toyoda H., Kuge S., Horie H., Kataoka Y., Genba Y., Nakano Y., Imura N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the attenuated poliovirus Sabin 1 strain genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff E., Mussgay M., Böhm H. O., Schulz G. E., Schaller H. Antibodies against a preselected peptide recognize and neutralize foot and mouth disease virus. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):869–874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01262.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALK J. E. Principles of immunization as applied to poliomyelitis and influenza. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1953 Nov;43(11):1384–1398. doi: 10.2105/ajph.43.11.1384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetz K., Habermehl K. O. Topographical studies on poliovirus capsid proteins by chemical modification and cross-linking with bifunctional reagents. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):525–534. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Dréano M., Bruneau P., Kopecka H., Girard M. Expression of poliovirus capsid polypeptide VP1 in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Jul;23(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



