Abstract
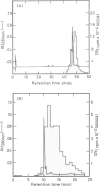
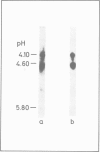
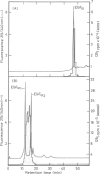
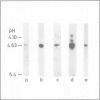
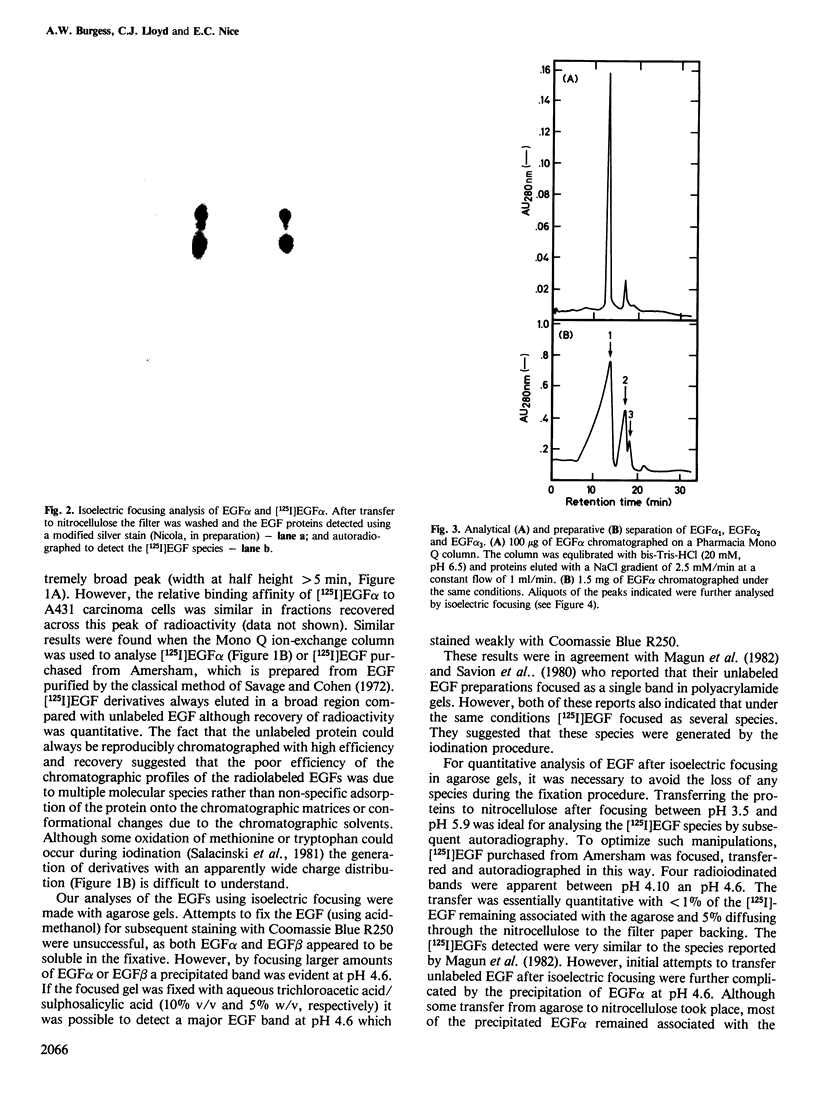
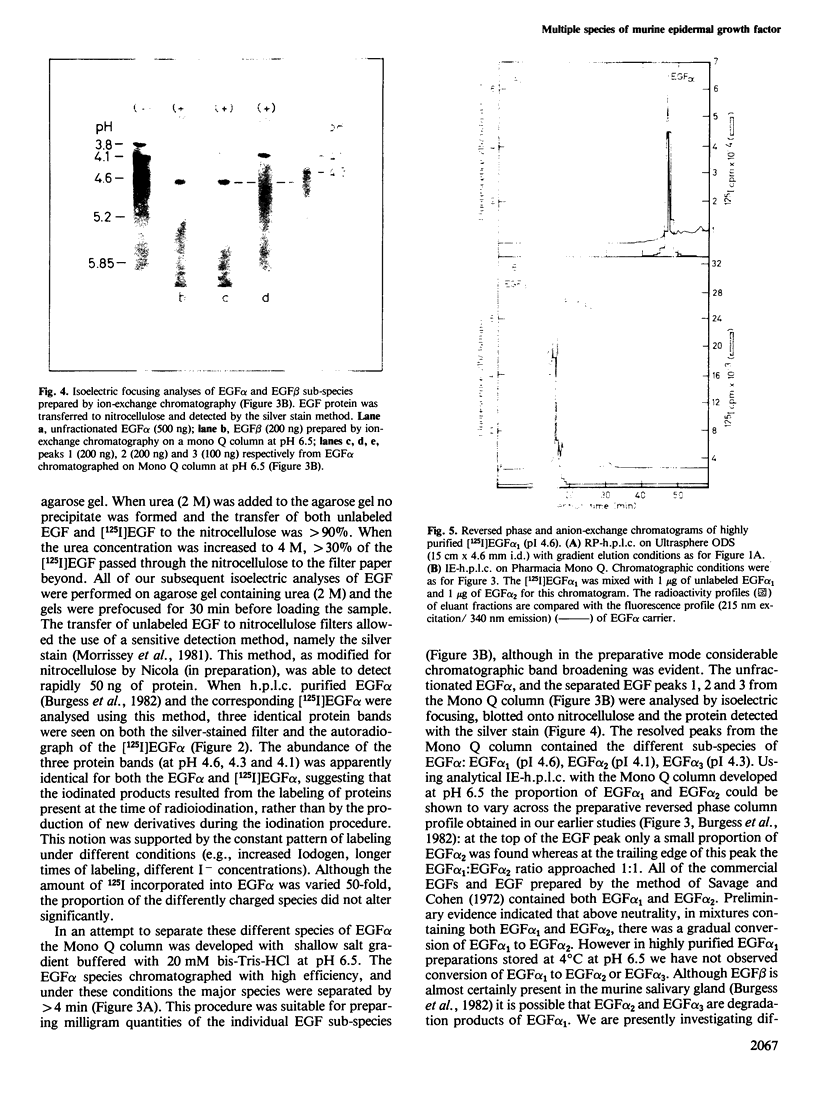
We have shown that epidermal growth factor (EGF) purified either by the classical method of Savage and Cohen, or solely by h.p.l.c. techniques can be resolved into two species, EGF alpha and EGF beta. However, despite the apparent purity of such materials, as determined both chromatographically and by amino acid analysis, they failed to give homogeneous products on radioiodination. Analysis by isoelectric focusing on agarose gels followed by transfer to nitrocellulose and silver staining showed that EGF alpha could be further resolved into three sub-species which focused at pH 4.6, 4.3 and 4.1. EGF beta (which also focused at pH 4.6) contained very small amounts of the species with isoelectric points of 4.1 and 4.3, probably due to slight contamination of this preparation by EGF alpha. Preparative separation of the sub-species of EGF alpha was achieved by high performance anion-exchange chromatography at pH 6.5 on a Pharmacia Mono Q column. Radioiodination of these purified sub-species did not produce significant charge heterogeneity. However, two slightly different forms of [125I]EGF alpha 1 (pH 4.6 species) were separable by anion-exchange chromatography on the Mono Q column. All of the EGF species competed for binding to EGF receptors on A431 cells and were active mitogens for BALB/c 3T3 fibroblasts.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess A. W., Knesel J., Sparrow L. G., Nicola N. A., Nice E. C. Two forms of murine epidermal growth factor: rapid separation by using reverse-phase HPLC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5753–5757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb A. Preparation of electroendosmosis-free agarose gel and exemplification of its use in crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1973 Oct;55(2):582–592. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H., Ash J. F., Singer S. J., Cohen S. Visualization by fluorescence of the binding and internalization of epidermal growth factor in human carcinoma cells A-431. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magun B. E., Planck S. R., Matrisian L. M., Finch J. S. Binding, internalization and intracellular processing of 125I-epidermal growth factor purified by isoelectric focusing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 16;108(1):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91866-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Larsen B. R., Finch J. S., Magun B. E. Further purification of epidermal growth factor by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):339–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart M. P., Malamud D. Protein transfer from isoelectric focusing Gels: the native blot. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 1;123(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salacinski P. R., McLean C., Sykes J. E., Clement-Jones V. V., Lowry P. J. Iodination of proteins, glycoproteins, and peptides using a solid-phase oxidizing agent, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3 alpha,6 alpha-diphenyl glycoluril (Iodogen). Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savion N., Vlodavsky I., Gospodarowicz D. Role of the degradation process in the mitogenic effect of epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1466–1470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Mitchell W. M., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Physical and chemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5928–5934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]